RS Aggarwal Solutions: Volume and Surface Area of Solids- 2 | RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 10 Mathematics PDF Download
Exercise: 19b
Q.1. The dimensions of a metallic cuboid are 100 cm × 80 cm × 64 cm. It is melted and recast into a cube. Find the surface area of the cube.
Given,
The dimensions of a metallic cuboid = 100 cm × 80 cm × 64 cm
Let’s find out the volume of the cuboid first;
Volume of the cuboid = l × b × h
⇒ 100 × 80 × 64 = 512000cm3
As cuboid is recast into a cube;
So,
Volume of cube = volume of cuboid
⇒ l3 = 512000 ⇒ l =⇒ l = 80 cm
Now,
As the length of the side of the cube = 80 cm
The surface area of the cube = 6(l)2
= 6 x 80 x 80
= 38400 cm2
So, the surface area of the cube is 38400 cm2
Q.2. A cone of height 20 cm and radius of base 5 cm is made up of modelling clay. A child reshapes it in the form of a sphere. Find the diameter of the sphere.
We have,
The radius of the cone (r) = 5cm and
The height of the cone (h) = 20cm
Let the radius of the sphere be R;
As,
Volume of sphere = Volume of cone
⇒ R = 5 cm
Diameter of the sphere = 2R = 2 x 5 = 10 cm
So, the diameter of the sphere is 10 cm.
Q.3. Metallic spheres of radii 6 cm, 8 cm and 10 cm respectively are melted to form a single solid sphere. Find the radius of the resulting sphere.
Given,
The radius (r1) of 1st sphere = 6 cm
Radius of 2nd sphere (r2) = 8 cm and
Radius f third sphere (r3) = 10 cm
Let the radius of the resulting sphere be R;
So now we have,
Volume of resulting sphere = Volume of three metallic spheres
⇒ R3 = 216 + 512 + 1000
⇒ R3 = 1728
R = 12 cm
So, the radius of the resulting sphere is 12cm.
Q.4. A solid metal cone with radius of base 12 cm and height 24 cm is melted to form solid spherical balls of diameter 6 cm each. Find the number of balls thus formed.
Let the number of balls formed = n
Since the metal cone is melted to form spherical balls;
So we have;
Volume of metal cone = Total volume of n spherical balls
Volume of cone = n(Volume of 1 spherical ball)
n = 32
So, 32 spherical balls can be formed.
Q.5. The radii of internal and external surface of a hollow spherical shell are 3 cm and 5 cm respectively. It is melted and recast into a solid cylinder of diameter 14 cm. Find the height of the cylinder.
We have,
The internal base radius of spherical shell, r1 = 3 cm,
The external base radius of spherical shell, r2 = 5 cm and
The base radius of solid cylinder, r = 7 cm
Let the height of the cylinder be h
As,
The hollow spherical shell is melted into a solid cylinder;
So,
Volume of solid cylinder = Volume of spherical shell
⇒ h = (4/3) x 9849
Therefore,
h = 8/3
So, the height of the cylinder is 8/3.
Q.6. The internal and external diameters of a hollow hemispherical shell are 6 cm and 10 cm respectively. It is melted and recast into a solid cone of base diameter 14 cm. Find the height of the cone so formed.
Given,
Internal diameter of the hemisphere = 6 cm
External diameter of the hemisphere = 10 cm
Diameter of cone = 14 cm
So we have,
Internal radius(r) of the hemisphere = 3 cm
External radius(R) of the hemisphere = 5 cm
Radius of cone = 7 cm
Now,
Volume of the hollow hemisphere = Volume of the cone
Volume of the hollow hemisphere =
Volume of the cone =
So,
= 2 × 98 = 49 × h
⇒2 x (98/49) = h
So,
h = 196/49 = 4 cm
Thus, the height of the cone formed is 4 cm.
Q.7. A copper rode of diameter 2 cm and length 10 cm is drown into a wire of uniform thickness and length 10 m. Find the thickness of the wire.
Given,
Diameter of the copper Rod = 2cm
Length of the Rod = 10 cm
Length of the wire = 10 m = 1000cm
So here we have,
Radius of the copper rod = 1 cm
Let suppose the radius of the wire = r
Volume of the rod = volume of the wire
πr2h = πr2h
1 × 1 × 10 = 1000 × r
10 = 1000r
r == 0.1 cm
The diameter of the wire = 2r = 2 × 0.1 = 0.2 cm
So, the thickness of the wire is 0.2 cm or 2mm.
Q.8. A hemispherical bowl of internal diameter 30 cm contains some liquid. This liquid is to be filled into cylindrical- shaped bottles each of diameter 5 cm and height 6 cm. Find the number of bottles necessary to empty the bowl.
Let the required bottles = n
Internal diameter of the hemispherical sphere = 30 cm
Internal Radius of the hemispherical sphere = 15 cm
Diameter of the cylindrical bottle = 5 cm
Radius of the cylindrical bottle = 2.5 cm
Now,
Volume of the hemispherical sphere = 2/3πr3
= 2/3π × 15 × 15 × 15
= π10 × 15 × 15
= 2,250π cm3
And,
Volume of 1 cylindrical bottle = πr2h = π × 2.5 × 2.5 × 6 = 37.5π cm3
Amount of water in n bottles = Amount of water in bowl
n × 37.5π = 2,250π
n == 60 bottles
So, 60 numbers of bottles are required to empty the bowl.
Q.9. A solid metallic sphere of diameter 21 cm is melted and recast into a number of smaller cones, each of diameter 3.5 cm and height 3 cm. Find the number of cones so formed.
Given,
Diameter of the sphere = 21 cm
Diameter of the cone = 3.5 cm = 7/4 cm
Height of the cone = 3 cm
So here we have,
Radius of the sphere = 10.5 cm
Radius of the cone = 1.75 cm
Volume of the sphere = 4/3πr3
Volume of the cone =
No of cones =
= 504
So, 504 numbers of cones are formed.
Q.10. A spherical cannon ball 28 cm in diameter is melted and recast into a right circular conical mould, base of which is 35 cm in diameter. Find the height of the cone.
Given,
Diameter of cannon ball = 28cm
So the Radius of cannon ball = 14 cm
Volume of cannon ball = 4/3πr3 = 4/3π × 143
Radius of the cone = 35/2 cm
Let the height of cone be h cm.
Volume of cone = 1/3π (35/2)2× h cm3
Here we have,
= h = 35.84 cm
Hence, the height of the cone = 35.84 cm.
Q.11. A spherical ball of radius 3 cm is melted and recast into three spherical balls. The radii of two of these balls are 1.5 cm and 2 cm. Find the radius of the third ball.
Given,
Radius of the spherical ball = 3 cm
After recasting the ball into three spherical balls;
Radius of the first ball = r1 = 1.5 cm
Radius of the first ball = r2 = 2 cm
Let the radius of the third ball be r3 cm.
Then,
Volume of third ball = Volume of spherical ball – volume of 2 small balls
Volume of the third ball =
36π – 9π/2 – 32π/3cm3 = 125π/6cm3
4/3πr3 = 125π/6
r3 = 125π × 3/6 × 4 × π = 125/8
r = 5/2 = 2.5 cm
Hence, the radius of the third ball is 2.5cm.
Q.12. A spherical shell of lead whose external and internal diameter are respectively 24 cm and 18 cm, is melted and recast into a right circular cylinder 37 cm high. Find the diameter of the base of the cylinder.
External diameter of shell = 24cm and
Internal diameter of shell = 18cm
So,
External radius of shell = 12 cm and
Internal radius = 9 cm
Volume of lead in the shell = 4/3 π[123–93]cm3
Let the radius of the cylinder be r cm
Height of the cylinder = 37 cm
Volume of the cylinder = πr2h = πr2(37)
Hence, diameter of the base of the cylinder = 12 cm
Q.13. A hemisphere of lead of radius 9 cm is into a right circular cone of height 72cm. Find the radius of the base of the cone.
Volume of hemisphere of radius 9 cm
= 2/3 × π × 9 × 9 × 9cm3
Volume of circular cone (height = 72 cm)
1/3 × π × r2 × 72cm
Volume of cone = volume of hemisphere
Hence, radius of the base of the cone = 4.5 cm
Q.14. A spherical ball of diameter 21 cm is melted and recast into cubes, each of side 1 cm. Find the number of cubes so formed
Diameter of sphere = 21 cm
Hence, radius of the sphere = 21/2
Volume of sphere =
Volume of cube = a3 = 13
Let the number of cubes formed be n
Volume of sphere = n(volume of cube)
11 × 21 × 21 = n × 1
4851 = n
So,
Hence, the number of cubes is 4851
Q.15. How many lead balls, each of radius 1 cm, can be made from a sphere of radius 8 cm?
Given,
Radius of the sphere = 8 cm
Radius of the ball we made = 1 cm
So,
Volume of sphere (when r = 1 cm) = 4/3πr3
= 4/3 × 1 × 1 × 1 × π cm3
Volume of sphere (when r = 8 cm) = 4/3πr3
= 4/3 × 8 × 8 × 8 × π cm3
Let the number of balls be n;
Then we have;
Hence, the number of lead balls can be made is 512.
Q.16. A solid sphere of radius 3 cm is melted and them cast into small spherical balls, each of diameter 0.6 cm. Find the number of small balls so obtained.
Given,
Radius of sphere = 3 cm
Volume of sphere =
Radius of small sphere = 0.6/2 cm = 0.3 cm
Volume of small sphere = 4/3 × π × 0.3 × 0.3 × 0.3cm3
Let the number of small balls be n;
n = 1000
Hence, the number of small balls = 1000
Q.17. The diameter of a sphere is 42 cm. It is melted and drawn into a cylindrical wire of diameter 2.8 cm. Find the length of wire.
Given,
Diameter of sphere = 42 cm
Radius of sphere = 21 cm
Volume of sphere =
Diameter of cylindrical wire = 2.8 cm
Radius of cylindrical wire = 1.4 cm
Volume of cylindrical wire = πr2h = π × 1.4 × 1.4 × h cm3 = 1.96πh cm3
Volume of cylindrical wire = volume of sphere
1.96πh = 4/3 × π × 21 × 21 × 21
h = 6300
h(6300/100) m = 63 m
Hence, length of the wire = 63 m
Q.18. The diameter of a copper sphere is 18 cm. It is melted and drown into a long wire of uniform cross section. If the length of the wire is 108 m, find its diameter.
Given,
Diameter of sphere = 18 cm
Length of wire = 108 m = 10800 cm
Radius of copper sphere = 3600/100 m = 36 m
Volume of sphere = 4/3πr3 = 4/3 × π × 9 × 9 × 9cm3 = 972π cm3
Let the radius of wire be r cm
= πr2l = πr2 × 10800
But the volume of wire = volume of sphere
⇒ πr2 × 10800 = 972π
Hence, the diameter = 2r = 0.6 cm
Q.19. A hemispherical bowl of internal radius 9 cm is full of water. Its contents are emptied into a cylindrical vessel of internal radius 6 cm. Find the height of water in the cylindrical vessel.
Given,
Internal radius of hemispherical bowl (r1) = 9 cm
Internal radius of cyclical vessel (r2) = 6 cm
Let the height of water in the cylindrical vessel be h.
So,
Volume of hemispherical bowl = volume of cylindrical vessel
h = 13.5 cm
Hence, height of water in the cylindrical vessel is 13.5 cm.
Q.20. A hemispherical tank, full of water, is emptied by a pipe at the rate of 25/7 litres per second. How much time will it take to empty half the tank if the diameter of the base of the tank is 3 m?
Given,
Diameter of the hemispherical tank = 3 m
Radius of hemispherical tank = 3/2m
Volume of tank =
Half the tank =
Now,
In 1 sec = 25/7 L of water is emptied
Required time
=
= 693000/700
= 990 sec
So,
= 990/60
= 16.5 min
To empty half the tank 16.5 min are required.
Q.21. The rain water from a roof of 44 m × 20 m drains into a cylindrical tank having diameter of base 4 m and height 3.5 m. If the tank is just full, find the rainfall in cm.
Length of the roof = 44 m
Breadth of the roof = 20 m
Diameter of the cylindrical tank = 4 m
Radius of the cylindrical tank = 2 m
Height of the cylindrical tank = 3.5 m
Volume of roof = l x b x h
= 44X20 X h
volume of cylinder =22/7 x 2 x 2 x 35/10
Height of roof = height of rainfall
And
Volume of water on roof = Volume of Water in cylindrical tank
44X 20 X h = 22/7 × 2 x 2 x 35/10
44 X 20 X h = 22 × 2 × 2 × 5/10
880 × h = 44
h = 44/800 = 1/20
h = .05 m
h = 5 cm
Q.22. The rain water from a 22 m × 20 m roof drain into a cylindrical vessel of diameter 2 m and height 3.5 m. If the rain water collected from the roof fills 4/5th of the cylindrical vessel then find the rainfall in centimetre.
Given,
Length of the roof = 22 m
Breadth of the roof = 20 m
Diameter of the cylindrical vessel = 2 m
Radius of the cylindrical vessel = 1 m
Height of the cylindrical vessel = 3.5 m
4/5 Volume of the rainfall = area of the roof × depth of the rainfall
4/5πr2h = area of the roof × d
4/5 × 3.14 × 1 × 3.5 = 22 × 20 × d
4/5 × 11 = 440d
8.8 = 440d
0.02 = d
d = 0.02 m
So,
The rainfall is 2 cm.
Q.23. A solid right circular cone of height 60 cm and radius 30 cm is dropped in a right circular cylinder full of water, of height 180 cm and radius 60 cm. Find the volume of water left in the cylinder, in cubic metres.
Height of a cone = 60 cm,
Radius of a cone = 30 cm
volume of cone = 1/3πr2h
Height of cylinder = 180 cm,
Radius of cylinder = 60 cm
Volume of cylinder = πr2h
Volume of the remaining water = volume of cylinder - volume of cone
= π × 60 × 60 × 180 – 1/3 × π × 30 × 30 × 60
= 648000π – 1800π (Taking 1800 as common)
= 18000(36π-π)
= 18000 x 35 x 22/7 = 1.98 m3
Q.24. Water is flowing through a cylindrical pipe of internal diameters 2 cm, into a cylindrical tank of base radius 40 cm, at the rate of 0.4 m per second. Determine the rise in level of water in tank in half an hour.
Given,
Diameter of the cylindrical pipe = 2 cm
Radius of the cylindrical pipe = 1 m
Height of the cylindrical pipe = 0.4m/s = 40 cm/s
Water flown in 1 sec = 40 cm
Water flown in 30 minutes (30 × 60 seconds)
= 40 × 60 × 30 m = 72000 cm
Radius of cylindrical tank = 40 cm
Let Height be h,
As we can see the volume of water which passes through the cylindrical pipe is equal to the volume of water present in the cylindrical tank after half an hour.
So,
Volume of water which passes through the cylindrical = volume of water present in the cylindrical tank after half an hour
πr2h = πr2h
(1)2 × 72000 = (40)2 × h
72000 = 1600 × h
h = 45 cm
Hence,
The rise in level of water in tank in half an hour will be 45 cm.
Q.25. Water is flowing at the rate of 6 km/hr through a pipe of diameter 14 cm into a rectangular tank which is 60 m long and 22 m wide. Determine the time in which the level of water in the tank will rise by 7 cm.
Given,
Speed of the water flowing through the pipe, H = 6 km/hr
=cm/s
Diameter of the pipe = 14 cm
Radius (R) of pipe = 14/2 = 7 cm
Length (l) of the rectangular tank = 60 m = 6000 cm,
Breadth (b) of the rectangular tank = 22 m = 2200 cm and
Height (h) or Rise in the level of water in the tank = 7 cm
Now,
Volume of the water in rectangular tank = l × b × h = 6000 x 2200 x 7 = 92400000cm3
Also,
Volume of the water flowing through the pipe in 1 s = πR2H
=cm3
So,
The time taken to rise the water =cm3
= 92400 x (3/77) = 3600s = 1 hr
So,
In 1 hour time the level of water in the tank will rise by 7cm.
Q.26. Water in a canal, 6 m wide and 1.5 m deep, is flowing at a speed of 4 km/hr. How much area will it irrigate in 10 minutes if 8 cm of standing water is needed for irrigation?
Given,
Width of the canal = 6 m
Depth of the canal, = 1.5 m
Length of the cuboid = 666.67 m
Water is flowing at a speed of 4 km/hr = 4000m/hr
Thus,
Area irrigated in 10 minutes = 1/6 hour = (1/6) x 4000 = 666.67 m
Hence,
Volume of the water flowing in 1/6 hour = Volume of the canal
⇒ Volume of the water flowing in 1/6 hour = 666.67 x 6 x 1.5 = 6000.03 = 60000 m3
Let a m2 is the area irrigated in 1/6 hour,
Then,
⇒ a × (8/100) = 6000
⇒ a = 600000/8 m2 = 75000 m2
Q.27. A farmer connects a pipe of internal diameter 25 cm from a canal into a cylindrical tank in his field, which is 12 m in diameter and 2.5 m deep. If water flows through the pipe at the rate of 3.6km/hr, in how much time will the tank be filled? Also, find the cost of water if the canal department charges at the rate of Rs 0.07 per m3.
Given,
Internal diameter of the pipe = 25 cm
Radius (r) of the pipe = 25/2 cm = 1/8m
Diameter of the cylindrical tank = 12 m
Radius (R) of the tank = 6 m
Height (h) of the tank = 2.5 m
In 1 hour water comes out of the pipe = 3.6 km = 3600 m
Let the total hrs = n
Volume of the water coming out of the pipe in n hrs = volume of the cylindrical tank
3600 n = 36 × 2.5 × 8 × 8
100 n = 8 × 8 × 2.5
1000 n = 8 × 8 × 25
n = 16/10 = 1.6 hrs
n = 1 hrs 36 minutes
Now calculate the cost;
Cost of the water = Volume of the cylindrical tank × 0.07=
= 19.80 rs
So,
Total time required to fill the tank is 1 hr 36 minutes and the cost is 19.80 rs.
Q.28. Water running in a cylindrical pipe of inner diameter 7 cm, is collected in a container at the rate of 192.5 litres per minute. Find the rate of flow of water in the pipe in km/hr.
Given,
Diameter of the cylindrical pipe = 7 cm
Radius of the pipe = 3.5 cm
Volumetric flow rate = 192.5 l/min
Flow rate =
Area = pi × r2 = 3.14 × 3.5 × 3.5 = 38.5 cm2
Since 1 l = 1dm3 = 1000 cm3
Volumetric flow rate = 192.5 × 1000 cm3/min
So,
Flow rate == 5000 cm/min
Flow rate in km/h = 5000 cm/min = 5000 × 0.00001 km/(1/60 h) = 3 km/h
Q.29. 150 spherical marbles, each of diameter 14 cm, are dropped in a cylindrical vessel of diameter 7 cm containing some water, which are completely immersed in water. Find the rise in the level of water in the vessel.
Given,
Diameter of marble = 1.4 cm
Radius of marble = 0.7 cm
Number of marbles = 150
Diameter of cylinder = 7cm
Radius of cylinder = 3.5cm
150 × Volume of spherical marbles = volume of cylindrical vessel
⇒ 150 x 4/3 × π × 0.7 × 0.7 × 0.7 = π × 3.5 × 3.5 × h
⇒ 50 x 4 x (0. 7)3 = (3.5)2 x h
⇒ 200 x 0.343 = 12.25 x h
⇒ 68.6/12.25 = 5.6 = h
So,
h = 5.6 cm
The rise in the level of water in the vessel (h) = 5.6 cm
Q.30. Marbles of diameters 1.4 cm are dropped into a cylindrical beaker of diameter 7 cm, containing some water. Find the number of marbles that should be dropped into beaker so that the water level rises by 5.6 cm.
Given,
Diameter of marble = 1.4 cm
Diameter of cylinder = 7 cm
Radius of cylinder = 3.5 cm
Cylinder height = 5.6 cm
Radius of marble = 0.7 cm
Volume of 1 marble = 4/3πr3
== 1.4373
So,
Let the number of marbles be n,
Increase in the Volume of cylinder due to n marbles = πr2h
= 3.14 × 3.5 × 3.5 × 5.6 = 215.6 cm3
Hence the total numbers of marble required == 150 marbles
Q.31. In a village, a well with 10 m inside diameter, is dug 14 m deep. Earth taken out of it is spread all around to a width of 5 m to form an embankment. Find the height of the embankment. What value of the villagers is reflected here?
Given,
Diameter of the well = 10 m
Radius of the well = 5 m
Height of the well = 14 m
Width of the embankment = 5 m
Therefore radius of the embankment = 5 + 5 = 10 m
Let h be the height of the embankment,
Hence,
The volume of the embankment = volume of the well
π(R – r)2h = πr2h
(102 – 52) x h = 52 x 14
(100 – 25) x h = 25 x 14
h =
Therefore,
The height of the embankment, h = 4.67 m
Q.32. In a corner of a rectangular field with dimensions 35 m × 22 m, a well with 14m inside diameters is dug 8 m deep. The earth dug out is spread evenly over the remaining part of the field. Find the rise in the level of the field.
Given,
Diameter of the well = 14 m
Radius of the well = 7 m
Height of the well = 8 m
Now,
Volume of the earth dug out of the well = πr2h
= 22/7 × 7 × 7 × 8 = 1,232 m3
Area on which earth dug out is spread = l × b - r2h
= 35 × 22 - 22/7 × 7 × 7
= 770 - 154 = 616 m
Level of the earth raised = 1232/616 = 2 m
So, the rise in the level of the field is 2 m.
Q.33. A copper wire of diameter 6 mm is evenly wrapped on a cylinder of length 18 cm and diameter 49 cm to cover its whole surface. Find the length and the volume of the wire. If the density of copper be 8.8 g per cu-cm, find the weight of the wire.
Given,
Diameter of the copper wire = 6 mm = 0.6 cm
Radius of the copper wire = 0.3 cm
Length of the cylinder = 18 cm
Diameter of the cylinder = 49 cm
Radius of the cylinder =49/2 cm
Density of the copper = 8.8g
Number of the rotations on the cylinder = 18/0.6 = 30 cm
Base circumference of the cylinder = 2πr == 154 cm
So,
Length of the wire = 154 × 30 = 4620 cm
Volume of the wire = πr2h
= 22/7 × 0.3 × 0.3 × 4620 = 1306.8
Weight of the wire = volume × density
= 1306.8 × 8.8 = 11,499.84 gm
Q.34. A right triangle whose sides are 15 cm and 20 cm (Other than hypotenuse) , is made to revolve about its hypotenuse. Find the volume and surface area of the double cone so formed. (Choose value of π as found appropriate)
Let name the triangle, ABC
Given,
Sides of the triangle are 15 and 20 cm,
BD ⟘ AC.
In the given case BD is the radius of the double cone generated by triangle by revolving.
Now by Pythagoras theorem,
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
AC2 = (15)2 + (20)2
AC2 = 225 + 400
AC2 = 625 = (25)2
AC = 25 cm
Let AD be m cm;
∴ CD = (25 – m) cm
By using the Pythagoras theorem in ∆ABD and ∆CBD;
∆ABD,
AD2 + BD2 = AB2
m2 + BD2 = 225
BD2 = 225 – m2 ……….(i)
∆CBD,
BD2 + CD2 = BC2
BD2 + (25 – m)2 = (20)2
BD2 = (20)2 – (25 – m)2 …..(ii)
By putting both the equations (i) and (ii) together,
225 – m2 = (20)2 – (625 – m)2
225 – m2 = 400 – (625 + m2 – 50m) ……….by (a2 – b2)
225 – m2 = - 225 – m2 + 50m
225 – m2 + 225 + m2 = 50m
450 = 50m
So,
m = 450/50 = 9 cm
BD2 = (15)2 – (9)2
BD2 = 225 – 81 = 144 cm
BD = 12 cm
Radius of the generated double cone = 12 cm
Now,
Volume of the cone generated = Volume of the upper cone + Volume of the lower cone(AD + CD)
(12)2× (25)
= 1200π cm3 = 3,771.42 cm3
Surface area of the double cone formed;
= L.S.A of upper cone + L.S.A of the lower cone
= π (BD) × (AB) + π (BD) × (BC)
= π × 12cm × 15 cm + π × 12 cm × 20 cm
= 420π cm2 = 1320 cm2
So, the volume is 1200π cm3 and surface area is 420π cm2, of the double cone so formed.
|
53 docs|15 tests
|
|
53 docs|15 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
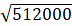
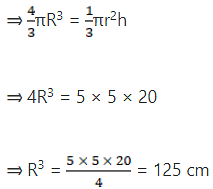
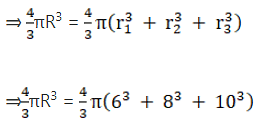
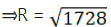
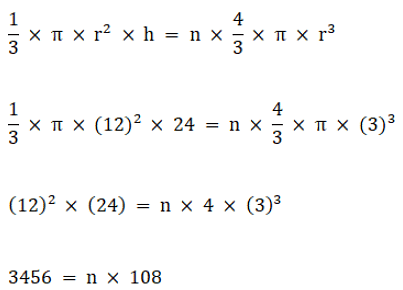

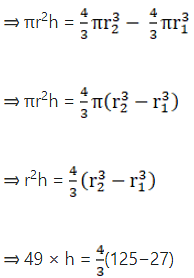
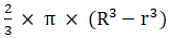
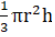
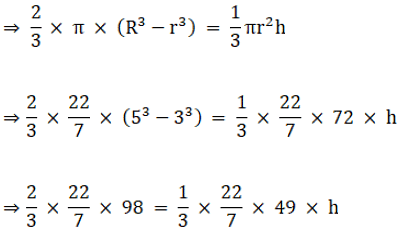
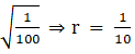 = 0.1 cm
= 0.1 cm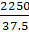
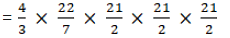
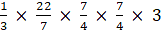
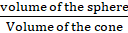
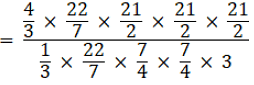
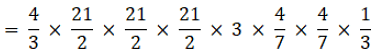
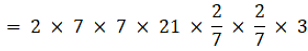
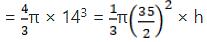
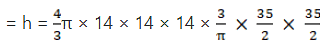
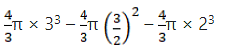
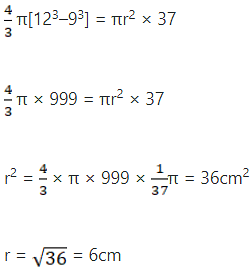
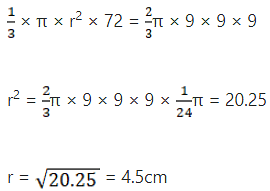
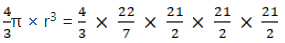
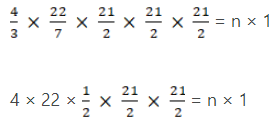
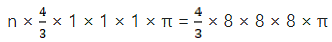
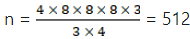
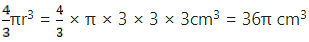
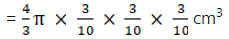
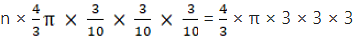
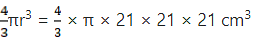
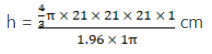
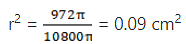

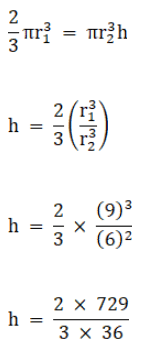
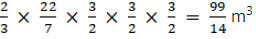
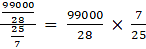
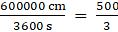
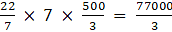

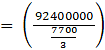
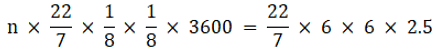
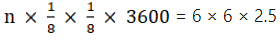
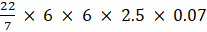

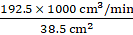
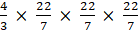 = 1.4373
= 1.4373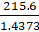
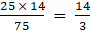
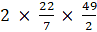 = 154 cm
= 154 cm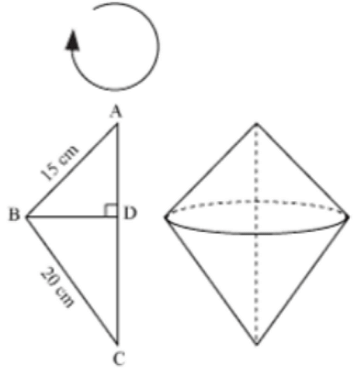
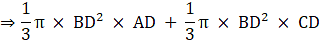
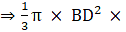
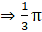 (12)2× (25)
(12)2× (25)















