Regional Divisions of Himalayas - UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
Sir Sidney Burrard divided the entire length of the Himalayas into the following divisions based on the river valleys:
(a) The Punjab Himalayas
(b) The Kumaon Himalayas
(c) The Nepal Himalayas
(d) The Assam Himalayas

(a) The Punjab Himalayas
- It is 560 km long
- It lies between the Indus and the Satluj rivers
- A large portion of this sector lies in Jammu and Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh and hence is called Kashmir and Himachal Himalaya.
- Main Ranges: Karakoram, Ladakh, Pir Panjal, Zanskar and Dhauladhar.
- Zojila pass provides an easy passage here.
(b)The Kumaon Himalayas
- It lies between the Sutlej and the Kali river and is 320 km long.
- Its western part is called the Garhwal Himalaya and the eastern part is called Kumaon Himalaya.
- Important Peaks: Nanda Devi, Kamet, Trishul, Badrinath, Kedarnath and Gangotri.
- The sources of Ganga and Yamuna rivers originate here.
- Important Lakes: Nainital and Bhimtal.
- Many duns are present here.
- Important glaciers in Kumaon Himalayas are:
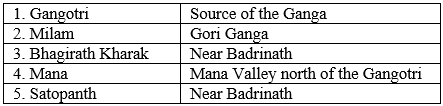
(c) The Nepal Himalayas
- It lies between the Kali and the Tista rivers and stretches for a distance of about 800 km (most of it lies in Nepal).
- It is the tallest section of the Himalayas and the peaks are covered by snow.
- Mount Everest is the tallest peak in the world (8850m)
- Other major peaks: Kanchenjunga, Lhotse I, Makalu, Dhaulagiri, Cho Oyu and Annapurna.
- Famous valley: Kathmandu.
- Important Glaciers:
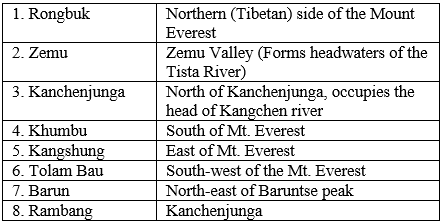
(d) The Assam Himalayas
- The Himalayan ranges from the Tista to Brahmaputra rivers covering a distance of 750 km are called the Assam Himalayas.
- Elevation: lesser the Nepal Himalayas.
- It spreads over large parts of Sikkim, Assam and Arunachal Pradesh
- Important peaks: Namcha Barwa, Kula Kangri and ChomoLhari.
Syntaxial Bends of The Himalayas
The Himalayas extend in the east-west direction from the Indus Gorge in the west to the Brahmaputra gorge in the east. This east-west trend of the Himalayas is terminated suddenly at its eastern and western extremities after which the ranges take a sharp southward bend. These bends are called the Syntaxial bends.
The bend on western extremity is called the western syntaxial bend (near Nanga Parbat) and that on the eastern extremity is the eastern syntaxial bend (near Namcha Barwa).
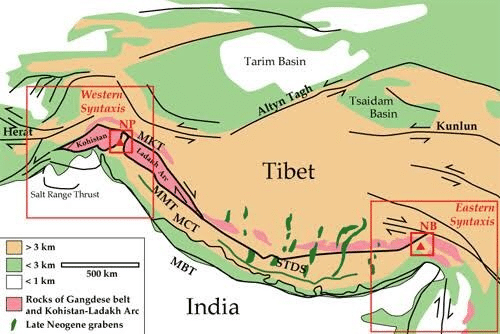
Syntaxial bend of the Himalayas
Significance of The Himalayas
The Himalayas comprise the most dominating geographical feature of India and its significance include:
1. Climatic Influence
- By their high altitude, length and direction, they effectively intercept the summer monsoons coming from the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian sea and cause precipitation in the form of rain or snow.
- They prevent the cold continental air masses of Central Asia from entering into India.
- Had there been no Himalayas, the whole of Indian subcontinent would have been a desert in the absence of precipitation and winters would have been very severe under the influence of cold air masses from Central Asia.
- The Himalayas are also responsible for splitting the jet stream into two branches and these, in turn, play an extremely important role in bringing monsoons in India.
2. Defence: The Himalayas have been protecting India from invaders since the early times and thus despite the advancement in modern warfare technology, the defence significance of the Himalayas cannot be ignored.
3. Source of Rivers: Almost all the great rivers of India have their sources in the Himalayan ranges. Abundant rainfall and vast snow-fields, as well as large glaciers, are the feeding grounds of many important rivers in India. Snowmelt in summer provides water to these rivers even during the dry season and these are perennial rivers.
4. Fertile soil: The rivers and their tributaries carry with them enormous alluvium while descending from the Himalayas which is deposited in the Great Plain of North India in the form of fertile soil (estimated amount of silt carried by the Ganga and the Indus is 10-19 lakh tonnes per day).
5. Hydroelectricity: The Himalayan region offers several sites which can be used for producing hydroelectricity. There are natural waterfalls at certain places while dams can be constructed across rivers at other places. The vast power potential of the Himalayan rivers still awaits proper utilisation.
6. Forest wealth: The Himalayan ranges are very rich in forest resources. They show a succession of Vegetation cover from the Tropical to the Alpine. They provide fuelwood and a large variety of raw materials for forest based industries. Several medicinal plants also grow in the Himalayan region. Some areas also serve as good pastoral grounds for grazing animals.
7. Agriculture: The Himalayas do not offer extensive flat lands for agriculture but some of the slopes are terraced for cultivation. Rice is the main crop on the terraced slopes. The other crops include wheat, maize, potatoes, tobacco and ginger. Tea is also grown and a variety of temperate fruits such as apples, grapes, cherries, mulberry, chestnuts, peaches etc are also grown.
8. Tourism:
- By their scenic beauty and healthy environment, the Himalayan Ranges have developed a large number of tourist spots. The hilly areas in the Himalayas offer cool and comfortable climate when the neighbouring plains are reeling under the scorching heat of the summer season.
- Snowfall attracts a lot of tourists and the important areas of snowfall include Srinagar, Dalhousie, Dharamshala, Shimla, Kulu, Manali, Mussoorie, Nainital, Gangtok, etc.
9. Pilgrimage:
- The Himalayas are studded with sanctified shrines which are considered to be the abodes of the Gods. A large number of Hindu, Muslim and Buddhist pilgrims trek through difficult terrain to pay their reverence to these sacred shrines.
- Kailash, Amarnath, Badrinath, Kedarnath, Vaishno Devi, Jwalaji, Uttarkashi, Gangotri, Yamunotri etc. are important places of pilgrimage.
10. Minerals:
- The Himalayan region contains the most valuable minerals. There are vast potentialities of mineral oil in the Tertiary rocks.
- High quality Anthracite Coal is found in Kashmir. Copper, lead, zinc, nickel, gold, silver, tungsten, zinc, nickel, cobalt, antimony are also found here.
- But due to the adverse Geographical conditions and the present level of technological advancement, many of the mineral resources cannot be exploited.
MAINS QUESTIONS
Q.1. Give an account of the longitudinal division of the Himalayas. (250 words)
Approach to the answer:-
Introduction - A Couple of lines on Himalayas and types of divisions
Body - Explain Longitudinal division - Kashmir, Kumaon, Garhwal, Arunachal, etc with map.Conclusion - End the answer with 2 lines on the significance of such a division.
Q.2. Analyse the significance of the Himalayas to India. Has India fully utilised the potential of the Himalayan range? (250 words)
Approach to the answer:-
Introduction - Brief account of the Himalayas
Body - (1) List and explain the importance of Himalayas and its various functions. (2) describe how India has not fully exploited Himalayas potential
Conclusion - Way forward as to how India can maximise the potential of the Himalayas.
Q.3. Why is it believed that the Himalayas are still rising? Describe the origin of the Himalayas? (250 words)
Approach to the answer:-
Introduction - Brief description about Himalayas
Body - (1) State the reasons for continued rise of the Himalayas. (2) Explain in detail the theory of origin of the Himalayas.Conclusion - Briefly state the future of Himalayas and the Indian plate.
FAQs on Regional Divisions of Himalayas - UPSC
| 1. What are the regional divisions of the Himalayas? |  |
| 2. What are some prominent peaks in the Greater Himalayas? |  |
| 3. Which region of the Himalayas is famous for its hill stations? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the Trans-Himalayas region? |  |
| 5. What is the Shivalik Range and its role in the Himalayas? |  |




















