Reported Speech - Class 10 PDF Download
Reported Speech
When we say things that have been said, we use two ways of expressing it. The first is direct speech when we express what the speaker said as it is and the second is indirect speech where we express what was said in our words.
Examples:
If you ask your friend Pradeep, ‘Did you take my book?’, the reply could be ‘Your book is with Jai.’
Now, we can report this statement in two ways:
- Pradeep told me, ‘Your book is with Jai’.
- Pradeep told me that my book is with Jai.
Rules For Reported Speech
While changing direct speech into reported speech or vice versa, the following change:
- the reporting verb
- the pronouns
- the tenses
- the situations
- report using present and future tenses
- modal verbs
- word order with who, which, and what
1. Changes in reporting verb
- Affirmative sentences: said, told (object), asserted, replied, assured, informed, responded, whispered, alleged, believed, assumed, though.
- Interrogative sentences: asked, inquired, wanted to know, enquired When we report.
- Imperative sentences: ordered, begged, pleaded, implored, advised, demanded.
2. Change of pronouns
- Direct speech: Surabhi said, “I am reading.”
- Indirect speech: Surabhi said that she was reading.
- A first-person and second-person generally change to a third person (depending upon the object to reporting verb).
3. Change of tenses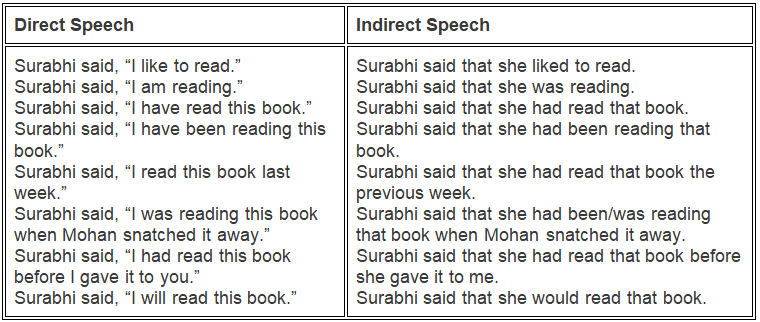
In general, the present tense becomes past tense; past and perfect tenses become the past perfect tense.
4. Change Of Situations
Examples:
- Surabhi said, “I read this book last week.” (direct speech)
- Surabhi said that she had read that book the previous week, (indirect speech)
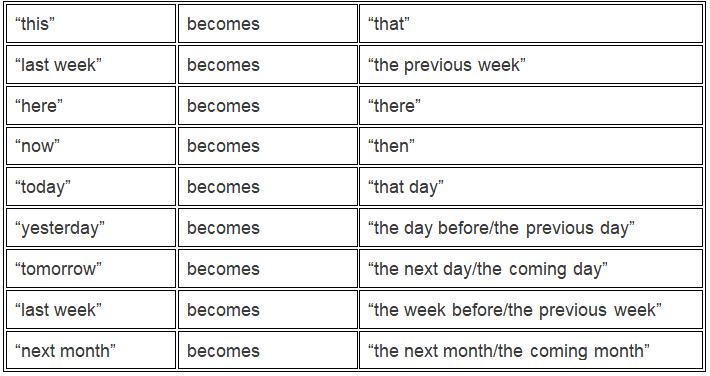

If the speaker talks about a universal truth, the tense is unchanged.
In case of questions and answers:
Examples:
- Surabhi asked, “Have you read this book?” (Direct Speech)
- Surabhi asked if/whether I had read that book. (Indirect Speech)
- Surabhi asked, “Where is the book?” (Direct Speech)
- Surabhi asked where the book was. (Indirect Speech)
(a) yes/no questions – use if/whether
(b) wh-questions – use the wh-word
Word Order
- Surabhi asked, “What’s the matter?”
- Surabhi asked what the matter was. (what + the matter + was)
- Surabhi asked what was the matter, (what + was + the matter)
Can Be Either
- who/which/what + complement + be or
- who/which/what + be + complement
Reported speech using present and future tenses:
Examples:
- Surabhi said, “The sun rises in the east.” (Direct Speech)
- Surabhi said that the sun rises in the east. (Indirect Speech)
- Surabhi said, “I will read this book.” (Direct Speech)
- Surabhi said that she will read that book. (Indirect Speech)
If the original speaker’s present and future are still present and future, the tense remains unchanged.
In case of modal verbs: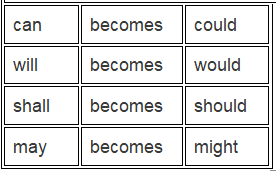
would, should, could, might, ought to, and must remain unchanged.
Example:
- Surabhi said, “I can solve this sum.” (Direct Speech)
- Surabhi said that she could solve that sum. (Indirect Speech)
In our daily lives, we use reported speech in many forms. We use reported speech to report statements, questions, requests, or even commands. There are certain things we need to keep in mind when we report each of them.
- When we report statements, we have to make sure what changes need to be made in the pronoun, tense or temporal-spatial expression.
- When we transform questions into reported speech, we have to check whether or not to change the tense, pronoun as well as place and time expression.
- Upon changing, we have to ensure that the question is an indirect question.
- We also have to make use of words such as where, when, how, if, whether, etc.
- In transforming requests and commands into reported speech, tenses are not relevant.
- We only have to ensure that there are changes in the pronoun and the place and time expression.



















