Changing Cultural Traditions Revision Notes | NCERT Textbooks (Class 6 to Class 12) - CTET & State TET PDF Download
Meaning of Renaissance
- The term ‘Renaissance’ literally means ‘rebirth’, this French word was first used by a Swiss scholar, Jacob Burckhardt, in 1860. During the fourteenth to seventeenth centuries, a new humanist culture popularised the idea that man is an individual. Italian universities were centres of legal studies.
- Renaissance meant revival of the ancient Greek and Latin culture. It first began in Italy, followed by Rome, Venice and Florence.
- The term ‘Renaissance Man’ is often used to describe a person with many interests and skills, because many of the individuals who became well known at this time were people of many parts.
- Renaissance aroused the spirit of equality among the people and attacked the superstitions and rituals prevailing in society.
- Social, political and economic life of the people were deeply affected by Renaissance.
The Revival of Italian cities
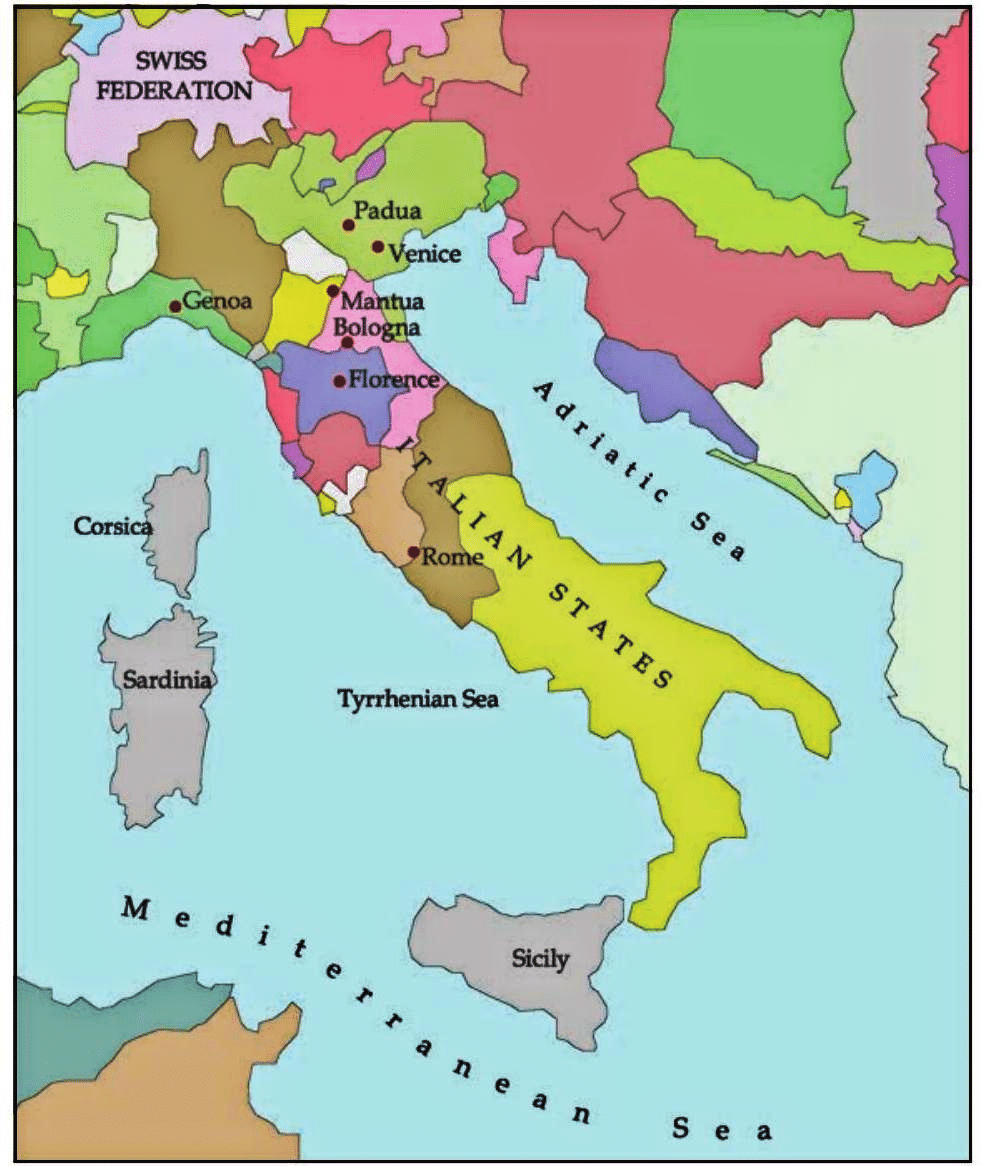
- Western Europe was being reshaped by feudal bonds and unified under the Latin Church and Eastern Europe under the Byzantine Empire, and Islam was creating a common civilisation further west, Italy was weak and fragmented.
- The ports on the Italian coast were revived. From the fourteenth to the end of the seventeenth-century towns were growing in many countries of Europe.
- A distinct ‘ Urban Culture’ also developed in Florence, Venice and Rome became centers of art and learning.
- A sense of history also developed in Europe. Religion came to be seen as something which each individual should choose for himself.
Printing Press
- Johannes Gutenberg invented the first printing press in 1455.
- The first printing press was set up by Caxton in 1477 in Europe.
- The invention of printing press increased the volume of books. It also helped in the spread of education
City State
The concept of a city-state, as reflected in the text, refers to an independent political entity consisting of a city and its surrounding territory, governed by its own laws and institutions. In the case of Venice, it functioned as a self-contained political unit with a distinct system of governance that combined elements of aristocracy and limited democracy.From Contarini’s description, Venice’s city-state was ruled by a Council of Nobles, excluding common people to maintain stability and prevent unrest. The governance structure was designed to balance power among noble families rather than allowing rule by wealth or a select few aristocrats. This highlights the city-state’s autonomous governance, social hierarchy, and emphasis on noble lineage as a criterion for political participation.
Universities and Humanism
Universities
- The first universities in Europe were established in Italian cities.
- Padua and Bologna were known for their legal studies from the eleventh century, focusing on the creation and interpretation of rules and agreements essential for large-scale trade.
- As commerce thrived, the need for lawyers and notaries (who combined the roles of solicitor and record-keeper) grew.
- Law became a popular subject, but there was a new focus emerging.
- It began to be studied through the lens of ancient Roman culture.
- Francesco Petrarch (1304-78) viewed antiquity as a unique culture that could be best understood through the actual texts of ancient Greeks and Romans, emphasising careful reading of these authors.
Humanism
- The educational approach indicated that there was much to learn beyond what religious teachings offered.
- This cultural shift was later termed ‘humanism’ by historians in the nineteenth century.
- By the early fifteenth century, the term ‘humanist’ referred to teachers who instructed in grammar, rhetoric, poetry, history, and moral philosophy.
- These groundbreaking ideas captured interest across various universities. Until the late thirteenth century, this city had not been recognised as a centre for trade or learning, but this changed significantly in the fifteenth century.
- During the fifteenth and early sixteenth centuries, many scholars in northern European universities were drawn to humanist concepts. They, like their Italian counterparts, focused on classical Greek and Roman texts alongside Christian holy scriptures. However, unlike Italy, where professional scholars led the humanist movement, in northern Europe, it attracted many church members.
- Christian humanists, such as Thomas More (1478-1535) in England, urged Christians to follow their faith according to the ancient texts, rejecting unnecessary rituals that they saw as later additions to a simpler form of religion.
- Dante Alighieri (1265-1321) was known for his works on religious themes andGiotto (1267-1337) gained fame for his realistic portraits.
- Many prominent individuals were skilled in multiple areas, combining roles as scholars, diplomats, theologians, and artists. The Renaissance was not only a time of artistic progress but also a moment that encouraged new ideas about personal identity and political rights, driven by the broader effects of humanism.
The term “Renaissance Man” describes a person with a wide range of interests and skills, especially during the Renaissance, a time that saw a revival of classical learning and the arts. This period was a major cultural shift in Europe, focusing on humanism and personal potential.
The Humanist view of History
- The humanists thought that an age of darkness existed for centuries after the decline of the Roman Empire, which they termed as ‘dark age’.
- Later scholars assumed that ‘new age’ began after the 14th century.
- The period of thousand years(a millennium) after the fall of Roman Empire was considered as ‘Middle Ages’or ‘Medieval Period’.
- About ‘middle ages, they said that religion or church-controlled the minds of all men in a way that all the learning of the Greeks and Romans had been washed out.
- The humanists termed the period from the 15th century as ‘modern’.
- Modern historians were debating over labelling of an age as dark which they thought as an unfair thing.
Periodisation used by humanists
- 5th-14th Century: The Middle Ages
- 5th-9th Century: TheDarkAges
- 9th-11th Century: The Early Middle Ages
- 11th-14th Century: The Late Middle Ages
- 15th Century onwards: The Modern Age
Science and Philosophy: The Arabs' Contribution
- During the 'Middle Ages', monks and clergymen were familiar with many Greek and Roman writings, but these were not widely shared.
- By the 14th century, a number of scholars began to read translated texts of Greek authors such as Plato and Aristotle (known as Aflatun and Aristu in Arabic).
- Arab translators preserved and translated these works from ancient manuscripts with great care.
- While some European scholars studied Greek texts in Arabic translation, the Greeks also translated works from Arab and Persian scholars for wider distribution.
- These contributions included fields like natural science, mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and chemistry.
- Ptolemy's Almagest, an astronomy text written in Greek before 140 CE and later translated into Arabic, highlights this connection through the Arabic definite article 'al'.
- Notable Muslim scholars in Italy included Ibn Sina (known as Avicenna in Latin, 980-1037), an Arab physician and philosopher from Bukhara, and al-Razi (or Rhazes), who wrote a medical encyclopaedia.
- Ibn Rushd (known as Averroes in Latin, 1126-98), an Arab philosopher from Spain, sought to reconcile philosophical knowledge (faylasuf) with religious beliefs, influencing Christian thinkers.
Artists and Realism
- Formal education was not the only way through which humanists shaped the minds of their age.
- Art, architecture and books were wonderfully effective in transmitting humanist ideas.
- The material remains of Roman culture were sought after.
- The figures of ‘perfectly’ proportioned men and women were sculpted so many centuries ago.
- In 1416, Donatello (1386- 1466) broke new ground with his lifelike statues.
- To study bone structures, artists went to the laboratories of medical schools. Andreas Vesalius a Belgian and a professor of medicine at the University of Padua, was the first to dissect the human body.
- Painters did not have older works to use as a model. But they, like sculptors, painted as realistically as possible.
- They found that a knowledge of geometry helped them understand perspective, and that by noting the changing quality of light, their pictures acquired a three-dimensional quality. The use of oil as a medium for painting also gave a greater richness of colour to paintings than before.
- There is Chinese and Persian art, available to them by the Mongols.
- Thus, anatomy, geometry, physics, as well as a strong sense of what was beautiful, gave a new quality to Italian art, which was to be called ‘realism’ and which continued till the nineteenth century.
 |
Test: Changing Cultural Traditions
|
Start Test |
Architecture
 Michelangelo Buonarroti
Michelangelo Buonarroti
- In the 15th century, Rome experienced a significant revival due to the stronger political influence of the popes, which began in 1417 after the end of the conflict caused by two rival popes since 1378.
- The popes promoted the study of Rome's history, and archaeologists carefully excavated the ruins, leading to a 'new' architectural style that was actually a revival of the imperial Roman style, now known as 'classical'.
- This revival was embraced by popes, wealthy merchants, and aristocrats who hired architects skilled in classical architecture.
- Florence also played a key role during the Renaissance, becoming an intellectual and artistic hub, largely influenced by figures like Dante Alighieri (1265-1321).
- Artists and sculptors were commissioned to enhance buildings with paintings, sculptures, and reliefs, with some individuals excelling in painting, sculpting, and architecture.
- The most notable example is Michelangelo Buonarroti (1475-1564), celebrated for the Sistine Chapel ceiling, the sculpture 'The Pieta', and the dome of St Peter's Church in Rome.
- Filippo Brunelleschi (1337-1446), who designed the magnificent Duomo of Florence, began his career as a sculptor.
- Another significant change was that artists started to be identified individually by name rather than as members of a group or guild.
- Leon Batista Alberti (1404-72) contributed to art theory and architecture, stating, “Him I call an Architect who is able to devise and to complete all those Works which, by the movement of great Weights, and by the conjunction and amassment of Bodies can, with the greatest Beauty, be adapted to the uses of Mankind.”
The First Printed Books
- If people in other countries wanted to see paintings, sculptures, or buildings by great artists, they had to travel to Italy. However, when it came to the written word, what was created in Italy spread to other countries. This was due to the major revolution of the sixteenth century—the development of printing technology.
- Europeans owed this advancement to other cultures, particularly the Chinese for their printing techniques, and to Mongol rulers, as European traders and diplomats learned about it during their visits to these courts. This also applied to other significant innovations, such as firearms, the compass, and the abacus.
- Previously, texts were only available in a few hand-written copies. In 1455, 150 copies of the Bible were printed in the workshop of Johannes Gutenberg (1400-1458), the German inventor of the first printing press. A monk would have needed the same amount of time to write out just one copy of the Bible!
- By 1500, many classical texts, mostly in Latin, had been printed in Italy. As printed books became available for purchase, students no longer had to rely only on lecture notes. Ideas, opinions, and information could spread more widely and quickly than ever before. A printed book introducing new ideas could reach hundreds of readers in no time.
- This also allowed individuals to own books, which encouraged the habit of reading among people.
- The circulation of printed books was key to the rapid spread of humanist culture across Europe, explaining why earlier intellectual movements had been confined to specific regions.
A New Concept of Human Beings
- One feature of humanist culture was a reduction in the control of religion over everyday life.
- Italians were interested in material wealth, power, and glory, but this did not necessarily mean they were irreligious.
- Francesco Barbaro (1390-1454), a humanist from Venice, defended the acquisition of wealth as a virtue in his writings.
- Lorenzo Valla (1406-1457), in his work On Pleasure, criticized the Christian injunction against pleasure, advocating for a life of perfection through the study of history.
- The period also emphasized good manners, including polite speech, proper dress, and the skills a cultured person should acquire.
- Humanism promoted the idea that individuals could shape their own lives through means beyond the mere pursuit of power and money, challenging the feudal society’s rigid social orders.
The Aspirations of women

- Merchant wives played a significant role in family businesses, managing shops or banks in the absence of their husbands.
- The early death of a merchant often forced widows to take on more prominent public roles compared to women from aristocratic backgrounds.
- Cassandra Fedele (1465-1558), a Venetian scholar, challenged the notion that women were incapable of being humanist scholars. She was skilled in Greek and Latin and was honored with orations at the University of Padua.
- Fedele's works and those of other Venetian women writers criticized the limited freedom offered by their society, which prioritized men's desires over women's.
- Isabella d’Este (1474-1539), the Marchesa of Mantua, governed her state during her husband's absences and fostered a court renowned for intellectual achievement.
- Women's writings of the period reflected a desire for economic independence, property rights, and education to achieve a distinct identity in a male-dominated society.
- The presence of intellectually creative women such as Fedele and d’Este highlighted the growing recognition of women’s potential and their contributions to humanist culture.
- The challenge to traditional gender roles was evident as women increasingly voiced their need for greater opportunities and recognition in the intellectual and public spheres.
Debates within Christianity
- Trade and travel, along with military conquest and diplomatic contacts, connected Italian towns and courts with the wider world. This led to the admiration and imitation of new culture by the educated and wealthy, though it rarely reached the ordinary people who were often illiterate.
- In the fifteenth and early sixteenth centuries, scholars in northern Europe were drawn to humanist ideas, focusing on classical texts and Christian holy books. Unlike in Italy, where professional scholars led the movement, in northern Europe, many church members became involved, advocating for a return to ancient Christian texts and condemning unnecessary rituals.
- Christian humanists like Thomas More and Erasmus criticized the Church for its greed and practices like selling indulgences. They used printed translations of the Bible to reveal that such practices were not supported by Christianity, leading to widespread resentment and rebellion against church taxes.
- Peasants across Europe resisted church taxes, while princes disliked clerical interference in state affairs. Humanists exposed the fraudulent nature of the Donation of Constantine, which was used to justify the Church’s judicial and fiscal powers.
- In 1517, Martin Luther challenged the Catholic Church, advocating that faith alone was sufficient for salvation and rejecting the need for priests. This led to the Protestant Reformation, causing churches in Germany and Switzerland to break from the Pope. Reformers like Ulrich Zwingli and Jean Calvin gained support from merchants and had greater appeal in towns, while the Catholic Church retained influence in rural areas.
 Martin Luther
Martin Luther
- Radical reformers like the Anabaptists called for the end of social oppression and the right to choose priests, appealing to oppressed peasants. Although Martin Luther opposed radicalism, calling for the suppression of peasant rebellions, radical ideas persisted and influenced Protestant resistance in France and elsewhere.
- In France, Protestant persecution led to claims of the right to remove oppressive rulers. Eventually, Protestants were allowed to worship freely in many parts of Europe, and in England, the Church broke away from the Pope, making the monarch the head of the Church.
- The Catholic Church responded to these changes by reforming internally. In Spain and Italy, churchmen like Ignatius Loyola founded the Society of Jesus (Jesuits) in 1540 to combat Protestantism, focusing on service to the poor and expanding knowledge of other cultures.
The Copernican Revolution
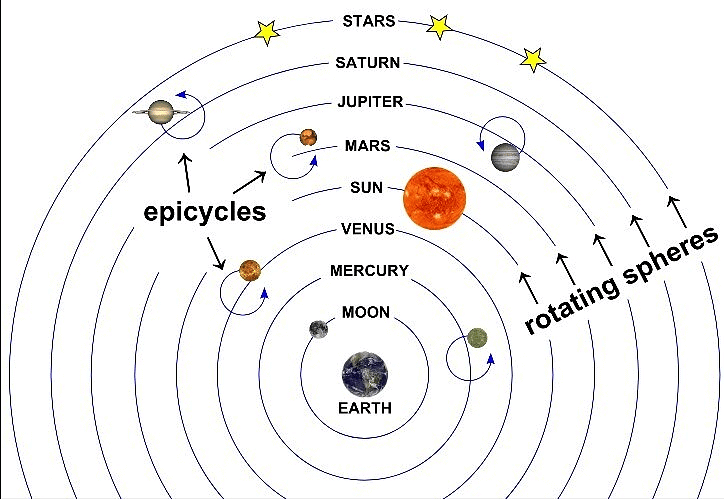
- The Copernican Revolution marked a major shift in European science, challenging the Christian view that the earth was at the center of the universe and immobile due to sin.
- Nicolaus Copernicus (1473-1543) proposed that planets, including Earth, revolve around the sun rather than the Earth being the center of the universe. Despite his devout Christian faith, he was initially hesitant to publish his theory due to potential backlash from traditionalist clergy.
- De Revolutionibus (The Rotation), Copernicus’s manuscript, was only published posthumously by his follower Joachim Rheticus. The idea faced slow acceptance and was developed further over time.
- Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) and Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) advanced the Copernican theory. Kepler’s work, Cosmographical Mystery, demonstrated that planets orbit the sun in ellipses rather than circles, while Galileo’s The Motion confirmed the dynamic nature of celestial bodies.
- The Copernican Revolution culminated with Isaac Newton’s theory of gravitation, which provided a comprehensive explanation of the forces governing planetary motion, solidifying the sun-centered model of the universe.
Reading the Universe
Galileo Galilei suggested that while the Bible guides spiritual life, it does not explain the workings of the heavens. This highlighted a shift towards relying on observation and experiments for knowledge.
 Galileo Galilei
Galileo Galilei
- The Scientific Revolution emerged as thinkers developed new methods in physics, chemistry, and biology based on empirical evidence and experimentation.
- As science advanced, some people began to see Nature as the source of creation rather than God, leading to a shift from a directly intervening God to a more distant deity.
- Scientific societies, such as the Paris Academy (established in 1670) and the Royal Society (formed in 1662), played a key role in popularizing these new ideas. They organized lectures and experiments for public viewing, fostering a new scientific culture.
 |
Download the notes
Revision Notes - Changing Cultural Traditions
|
Download as PDF |
Was there a European ‘Renaissance’ in the Fourteenth Century?
- The idea of the Renaissance as a sharp break from the past and a rebirth of Greek and Roman ideas is questioned. Recent scholars, like Peter Burke, argue that this view, popularized by Burckhardt, exaggerates the contrast between the Renaissance and earlier periods.
- Scholars in the twelfth and thirteenth centuries were already familiar with Greek and Roman cultures, and religion remained central. The contrast between the Renaissance and the Middle Ages as periods of drastic change is seen as an oversimplification.
- Elements of Renaissance culture can be traced back to earlier periods, such as the ninth-century literary and artistic developments in France. The Renaissance was not solely a revival of classical civilization but was also influenced by advances from other cultures.
- The Renaissance was shaped by knowledge and technologies from Asia, including India, Arabia, Iran, Central Asia, and China. The expansion of Islam and the Mongol conquests facilitated trade and learning, connecting Europe with these regions. This global exchange was not fully acknowledged in early European-centric historical accounts.
- During this period, there was a growing distinction between the ‘private’ and ‘public’ spheres of life. Individuals began to be recognized for their personal achievements rather than merely their social roles. Additionally, Europe started to develop distinct regional identities based on language, moving away from the unified Roman and Christian heritage.
Timeline
 The Fourteenth and Fifteenth Centuries
The Fourteenth and Fifteenth Centuries The Sixteenth and Seventeenth Centuries
The Sixteenth and Seventeenth Centuries
Conclusion
The Renaissance was a complex blend of innovation and continuity. It combined the revival of classical ideas with new global influences and evolving individual identities. Rather than a stark departure from the past, it was an expansion of cultural and intellectual progress that set the foundation for modern Europe.
|
3 videos|687 docs|659 tests
|
FAQs on Changing Cultural Traditions Revision Notes - NCERT Textbooks (Class 6 to Class 12) - CTET & State TET
| 1. What was the significance of the Renaissance in shaping modern culture? |  |
| 2. How did Italian cities contribute to the Renaissance? |  |
| 3. What is humanism, and how did it impact education during the Renaissance? |  |
| 4. What were the contributions of Arab scholars to Renaissance science and philosophy? |  |
| 5. In what ways did the Renaissance change the perception of women in society? |  |