Environmental Chemistry Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 14
Components of Environment:
- Atmosphere: This comprises a blanket of gaseous layer around earth.
- Hydrosphere: This comprises about 96% of earth’s surface & includes all sources of water like oceans rivers lakes, glaciers, ground water etc.
- Lithosphere: It refers to earth’s solid crust containing the outer mineral cover. It comprises soil, minerals, organic matter etc.
- Biosphere: It refers to the domain of living organism in covalent with atmosphere hydrosphere as well as lithosphere.
Environmental Pollution:
Process of contamination of the environment with harmful wastes arising mainly from human activities.
- Pollutant: Any substance or species produced either by a natural source or by human activity, which produces adverse effect on the environment.
- Contaminant: A substance which does not occurs in nature but is introduced by human activity into the atmosphere affecting its composition.
- Source: The site from which the pollution or contaminants originate.
- Sink: The material or medium which consumes or interacts with a long lived pollutant is called sink.
- Receptor : Anything that is affected by the pollutants.
- Threshold limit value (TLV) : This indicates the permissible limit of a pollutant in atmosphere to which a healthy worker is exposed during hours a day or 40 hours a week for life time without any adverse effects. TLV are determined by experimentation on animals, by use of medical knowledge, epidemiology surveys & environmental studies.
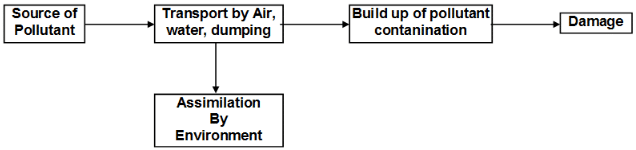
Tropospheric pollution or Air pollution:
It is the atmosphere condition in which the presence of certain concentration produce harmful effects on man and his environment. These substances include:
(i) Gases such as oxides of sulphur, CO, oxide of N2 and hydrocarbons
(ii) Particulate matter such as dust, smoke, fumes etc.
(iii) Radioactive material & many others.
Primary pollutants : These are the pollutants which are emitted directly from the sources.
Some examples are:
Particulate Matter: Such as ash, smoke, dust, fumes etc.
Inorganic gases: Such as sulphur dioxide, carbon monoxide etc.
Secondary Pollutants: These are the pollutants which are formed in the atmosphere by chemical interaction among primary pollutants & normal atmospheric constituents. Some examples are sulphur trioxide, nitrogen dioxide, ozone, aldehyde, ketones, various sulphate & nitrate salts
Pollutant | Source | Sink | Effect |
Carbon monoxide (CO) | (a) Incomplete combustion of carbonaceous matter, automobile engines & also in defective furnaces, Incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, agricultural , slash matter and other carbon 2C + O2 → 2CO (b) Dissociation of carbon dioxide. 2CO2 ⇌ 2CO + O2 (c) Reaction of carbon dioxide with carbon containing compounds at high temperature. CO2 + C ⇌ 2CO | Hydroxyl & perhydroxyl radicals, atomic oxygen & ozone help in the oxidation of atmospheric CO into CO2 . Soil is major sink for CO. Some of the microorganism present in soil remove carbon monoxide from air. | Carbon monoxide is poisonous as it combines with hemoglobin of red blood cells about 300 times faster than O2, thus forming carboxyl hemoglobin. This decreases the transport of oxygen to the body organs & cells. |
Carbon dioxide (CO2) | It is released mainly into the atmosphere by the combustion of fossil fuels (coal, oil etc) in factories & also at homes. CO2 is also produced by biological decay of plants | Ocean is a main sink for CO2. Green plants for photo synthesis. | CO2 causes narcotic effect, stimulation of respiratory center & leads to asphyxiation. The increasing concentration of CO2 also changes climatic conditions especially by raising the general temperature. |
Oxides of sulphur (SOx) | Volcanic eruptions (natural activity) & also through combustion of sulphur bearing fuels such as coal & oil (human activity). This pollutant is also produced during roasting & smelting of sulphide ores (human activity) A part of SO2 undergoes photolytic & catalytic oxidation to form SO3. The SO3, so formed gets converted to H2SO4 in the presence of moisture. This acid comes down from the atmosphere in the form of sulphuric acid rain. | It causes cough, shortness of breath & spasm of larynx, acute irritation to the membrane of gas resulting tears & reduces hearing ability. SO2 irritates the respiratory system of animals & human, produces leaf injuries (called necrotic bloating) to board leaved plants & gases. It also causes deterioration of fabric (cotton, rayon) paper & leather. | |
Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) | NO2 is produced in small amounts by microbiological processes in soil. However significant amount of NO & NO2 are emitted in to the atmosphere by natural activity. | Many natural processes acts as sink for oxides of nitrogen. These oxides are inherently unstable & decompose to N2 & O2 after some time. Therefore, the concentration of nitrogen oxides in the atmosphere tends to remains low. | (i) NO is biologically less active & less toxic than NO2. Like CO it binds hemoglobin & decreases oxygen transport efficiency of blood. (ii) Inhaling of nitrogen oxides by human results in pulmonary odema & hemorrhage. (iii) The oxides of nitrogen cause damage to plants. Exposure of plants to NOx causes leaf spotting & break down of plant tissues. (iv) The sunlight reacts with NO2 to produce highly active oxygen atoms. |
Particulate matter:
- Soot: produced by incomplete combustion of carbonaceous fossils fuels such as coal, fuel oil, natural gas, wood etc in insufficient supply of oxygen.
- Metal particles: These are released by various metal finishing operation. The micro particles of toxic metal & SO2 gas present in the polluted atmosphere get absorbed on the particles rendering them highly toxic.
- Metal oxides : They are generated by combustion of fuels containing metallic compounds.
- Lead salts: Their source is lead tetraethyl (Pb(C2H5)4) which is added to gasoline to improve its antiknock property. In order to avoid deposition of PbO suitable amounts of C2H4Cl2 & C2H4Br2 are added to gasoline along with Pb(C2H5)4.
- Fly ash: It originates from the combustion of high ash fossil. It contains partially burnt particles of the fuels.
- Asbestos dust: It originates from industrial units manufacturing asbestos sheets, gaskets ropes etc. Asbestos flowing & asbestos insulations also contribute towards asbestos dust in the atmosphere.
- Solid Hydrocarbons: These are emitted from petroleum refineries & comprise of paraffins, olefins & aromatics.
- Dust Particulates: Originate from natural, domestic, industrial or agricultural sources. These are thrown into atmosphere by volcanic eruptions, blowing of dust by wind, mining operations etc.
- Acid mist : Sulphuric acid mist is produced when SO3 present in the atmosphere comes in contact with moisture. Nitric acid mist is produced when oxides of nitrogen, viz, NO & NO2, undergo the series of reactions in the atmosphere.
Harmful effects of particulates
- Effect on human beings: Affect the human respiratory system & cause several respiratory illnesses. The particles with small size are more harmful in this context. The particulates in fact, become the carriers of the toxic substances from the atmosphere to the human & cause big health hazards.
- Effect on visibility: Particulates in the atmosphere cause scattering & absorption of sunlight & reduce the visibility.
- Effect on Materials : The adverse effect of particulates on materials include corrosion of metals (when the atmosphere is humid), erosion & soiling of building, sculptures & painted surfaces & soiling of clothes & draperies.
Stratospherical Pollution: (ozone layer & its depletion):
Role of Ozone Layer: protecting earth from the UV radiation coming from the sun.
Depletion of Ozone Layer : The equilibrium between formation & destruction of ozone has been upset by influx of several substances into the atmosphere which react with ozone to destroy it.
Effect of Depletion of Ozone layer: The influx of UV radiation reaching the surface of earth would increase which would increase in risk to skin cancer due to exposure to UV radiation, UV radiations also tend to damage the immune system.
Acid Rain:
SO2, nitrogen oxides & acidic soots. Sulphurdioxide & nitrogen dioxide interact with water vapours in presence of sunlight to form sulphuric acid & nitric acid units.
Green House Effect & Global Warming:
The green house gases (CO2, CH4, O3, CFC’S ) in the atmosphere form a thick cover around the earth. About 75% of the solar energy reaching the earth is absorbed by the earth surface. The IR radiations coming from sun are not absorbed by atmospheric gases but Earth absorbs these IR radiations of short wavelength. As a result of this the temperature of earth stands rising. Eventually, earth starts emitting infrared radiations of longer wavelengths. The partially radiated infrared radiations from the earth are absorbed by the greenhouse gases. This results in excessive heating of Earth’s atmosphere. Thus the greenhouse gases add to the heating of atmosphere. This causes global warming. The atmosphere traps the sun’s heat near earth’s surface and keeps it warm. The reemission of the earth’s energy absorbed by CO2 and other greenhouse gases present near the earths surface and its radiation back to the earth is called green house effect.
Advantages of green house effect :
- It is necessary for evaporation of water, formation of clouds, rainfall etc.
- The warm atmosphere helps in rapid growth of plants, trees etc.
Harmful effects of green house effect :
- High temperature of atmosphere may melt polar ice caps which are likely to raise the level of sea thereby sinking most of the coastal areas and causing large scale destruction.
- The high temperature may reduce crop product.
- The high temperature will reduce work efficiency of human being.
- Tropical rains and hurricane will become more frequent and also stronger causing more devastation.
- The change in ocean temperature will adversely affect the warm life.
Water Pollution:
Pollutant | Source |
Microorganism | Domestic sewage |
Organic wastes | Domestic sewage, animal waste, decaying animals, plants and discharge from food processing factories |
Plant nutrients | Chemical fertilizers |
Toxic heavy metals | Industries and chemical factories |
Sediments | Erosion of soil by agriculture and strip mining |
Pesticides | Chemical used for killing insects, fungi & weeds |
Radioactive substances | Mining of Uranium containing minerals |
Heat | Water used by industrial plants which is discharged as hot water |
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) : The measure of the total contamination caused by compounds which can be oxidised in the presence of microorganisms. The BOD is taken as a realistic measure of water quality – clean water would have a BOD value of less than 5 ppm whereas highly polluted river water could have a BOD value of 17 ppm or more.
Land Pollution :
Caused by pesticides and other chemicals which are added to the soil to grow better crops.
Insecticides are the pesticides used to Control of insects by insecticides helps to curb disease and protect crops. Organo chlorines are a group of compounds which have been developed and used as insecticides.Examples: DDT (dichlorodiphenyl trichloro ethane) organo chlorines are stable in the environment, toxic to insects in small amounts, but much less go to humans, and because they are organic compounds not very soluble in water. The advantage of these insecticides is that, bring persistent.
Fungicides are the pesticides used to check the growth of fungi. Fungi, are plants without chlorophyll, they cannot use solar energy for preparing their food. They live as saprophytes on decaying organic matter or as parasites at the expense of living organisms. Hence they are considered to be a threat to human interests.
|
357 docs|100 tests
|
FAQs on Environmental Chemistry Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 14
| 1. What is environmental chemistry? |  |
| 2. How does environmental chemistry contribute to solving environmental issues? |  |
| 3. What are the main sources of pollution in the environment? |  |
| 4. How does environmental chemistry help in water purification? |  |
| 5. What are the potential risks associated with environmental pollution? |  |
















