Hydrogen Class 11 Notes Chemistry
HYDROGEN ELEMENT
- Atomic number = Mass Number = 1
- Isotopes of hydrogen:
- 1H1 : Protium , Most abundant in nature
- 2H1: Deuterium (D), Component of heavy water.
- 3H1 : Tritium (T) , Radioactive in nature
DIHYDROGEN
(a) Laboratory preparation:
Reaction of metals with acids. Zn + H+→ Zn2++H2
(b) Commercial Preparation:
- Electrolysis of acidified water
- Electrolysis of warm aqueous Ba(OH) 2 between nickel electrodes.
- By-product in the manufacture of NaOH and Cl2 by electrolysis of brine solution.
- Reaction of steam and hydrocarbons at high temperatures
(c) Properties:
- Reaction with halogen: H2 +X2→ 2HX
[X= F, Cl, Br, I] - Reaction with oxygen: H2(g) +O2(g) + Δ → 2H2O(l)
ΔH0 = -285.9 kJ mol-1 - Reaction with nitrogen: 3H2(g) +N2(g) + Δ → 2NH3(l)
ΔH0 = -92 kJ mol-1 - Reaction with alkali metals: 3H2(g) +2M(g) + Δ → 2MX(s)
Uses of Hydrogen:
- Used for synthesis of ammonia and vanaspati fat and many other products.
- Used as rocket fuel.
- Used in hydrogen fuel cells.
Hard Water:
(a) Water containing carbonate, chloride and sulphate salts of calcium and magnesium.
Temporary hardens is due to the presence of carbonate salts and can be removed by boiling or by adding lime water.
Ca(HCO3)2 + Ca(OH)2 → 2CaCO3↓+2H2O
Ca(HCO3)2 + Δ → 2CaCO3↓+2H2O +CO2↑
Permanent hardness is due to presence of sulphate and chloride salts and can be removed by treatment with washing soda.
MCl2 + Na2CO3 → MCO3 ↓ + 2NaCl ( M= Mg, Ca)
MSO4 + Na2CO3 → MCO3 ↓ + Na2SO4 ( M= Mg, Ca)
(b) Hard water forms scum/precipitate with soap: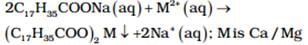
Heavy water:
- Molecular formula: D2O
- 10.68% denser than ordinary water
- Freezing point 3.8 0C
- Unfit for drinking and causes sterility.
HYDROGEN PEROXIDE
(a) Preparation:
Lab Method
Na2O2 (s) + H2SO4(aq) → H2O2(aq) + Na2SO4(s)
BaO2.8H2O + H2SO4(aq) → H2O2 (aq) + BaSO4(s)
Anhydrous barium oxide is not used because the precipitated BaSO4 forms a protective layer on the unreacted barium peroxide and thus prevents its further participation in the reaction. However it can be overcome by using phosphoric acid.
By Electrolysis: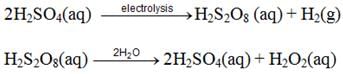
By the auto-oxidation of 2-ethyl anthraquinol. The net reaction is a catalytic union of H2 and O2 to yield hydrogen peroxide.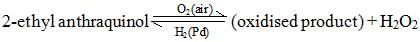
(b) Properties:
(i) Unstable liquid, decomposes to give water and dioxygen and the reaction is slow in the absence of catalyst. It is catalysed by certain metal ions, metal powders and metal oxides.
2H2O2 (l) → 2H2O (l) + O2 (g)
(ii) It is a very powerful oxidising agent and poor reducing agent.
As oxidising agent
In acidic medium: H2O2 + 2H+ + 2e- → 2H2O
In basic medium :H2O2 + OH- + 2e- → 3OH-
As reducing agent
In acidic medium: H2O2 → 2H+ + O2 + 2e-
In basic medium : H2O2 + 2OH- → 2H2O + O2 + 2e-
2Fe2+ + H2O2 + 2H+ → 2Fe3+ + 2H2O
2MnO4- + 5H2O2 + 6H+ → 2Mn2+ + 8H2O + 5O2
Mn2+ + H2O2 → Mn+4 + 2OH-
2Fe3+ + H2O2 + 2OH- → 2Fe2+ + 2H2O + O2
The oxidising property of hydrogen peroxide is put to use in the restoration of old paintings, where the original white lead paint has been converted to black PbS by the H2S in the atmosphere. Hydrogen peroxide oxidises the black PbS into white PbSO4.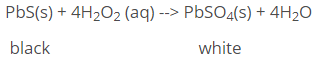
(c) Tests:
- It liberates iodine from potassium iodide in presence of ferrous sulphate
- Acidified solution of dichromate ion forms a deep blue colour with H2O2 due to the formation of CrO5.
Cr2O72- + 4H2O2 + 2H+ → 2CrO5 +5H2O - With a solution of titanium oxide in conc.H2SO4, it gives orange colour due to the formation of pertitanic acid.
Ti4+ + H2O2 + 2H2O → H2TiO4 + 4H+
|
357 docs|100 tests
|
FAQs on Hydrogen Class 11 Notes Chemistry
| 1. What is hydrogen and why is it important? |  |
| 2. How is hydrogen used in energy production? |  |
| 3. What are fuel cells and how do they work? |  |
| 4. Can hydrogen be used as a replacement for fossil fuels? |  |
| 5. How is hydrogen produced and stored? |  |





















