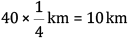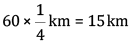Class 7 Science: CBSE Sample Question Paper with Solutions Term I – 1 | Science Class 7 (Old NCERT) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
| Section - D |

|
Section - A
Q 1. Grass eaten by ruminants is stored in the (1 marks)
(a) Rumen
(b) Liver
(c) Gall bladder
(d) Oesophagus
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Grass eaten by ruminants is stored in the rumen. The rumen contains cellulose-digesting bacteria that aid in digesting the carbohydrate cellulose present in grass.
Q 2. Which type of relationship is seen in algae and fungi in lichens? (1 marks)
(a) Predator–prey
(b) Parasitic
(c) Saprophytic
(d) Symbiotic
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Lichens represent a symbiotic relationship between algae and fungi, where both organisms benefit from each other. The alga provides food for the fungus, while the fungus provides shelter for the alga.Lichen
Q 3. Which instrument is used to measure air pressure? (1 marks)
(a) Manometer
(b) Barometer
(c) Hydrometer
(d) Anemometer
Correct Answer is Option (b)
A barometer is specifically designed to measure air pressure.
Q 4. What is biological weathering? (1 marks)
(a) Weathering caused by plant and animal activities
(b) Weathering caused only by plant activities
(c) Weathering caused by the action of air
(d) Weathering caused by the action of water
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Biological weathering is the process by which rocks are broken down into smaller particles due to the activities of living organisms, including both plants and animals.
Q 5. Angora wool is obtained from (1 marks)
(a) Angora sheep
(b) Angora yak
(c) Angora goat
(d) Angora camel
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Angora wool is derived from Angora goats, which are primarily found in hilly regions such as Jammu and Kashmir.
Ques 6: Identify the correct stage of the silkworm life cycle as shown in the picture. (1 marks)
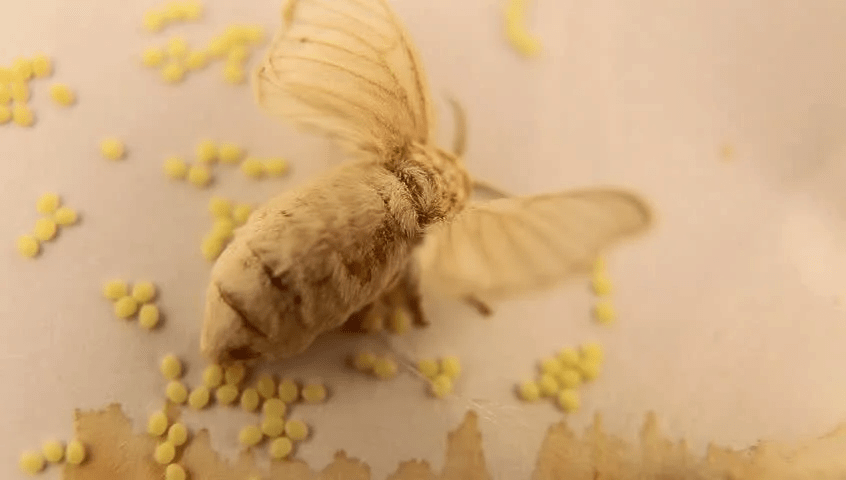

(a) Female laying eggs
(b) Pupa stage
(c) Cocoon stage
(d) Adult stage
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The picture shows a female silk moth laying eggs. A female lays hundreds of eggs at a time.
Q 7. Which microorganism is responsible for the fatal blood disease called sorter's disease? (1 marks)
(a) Virus, Anthrax
(b) Algae, Anthrax
(c) Bacteria, Anthrax
(d) Animal, Anthrax
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Sorters are the people who separate the fleece of sheep into fibres of different quality. The bacterium anthrax causes a fatal blood disease called sorter's disease.
Q 8. Which of the following bases is used as a cleansing agent? (1 marks)
(a) Magnesium hydroxide
(b) Calcium hydroxide
(c) Sodium hydroxide
(d) Ammonium hydroxide
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Ammonium hydroxide is widely used as a cleansing agent due to its effective cleaning properties.
Q 9. Which of the following substances helps in reducing the irritation caused by the sting of an ant? (1 marks)
(a) Vinegar
(b) Lemon juice
(c) Calamine (zinc carbonate)
(d) Orange juice
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Calamine (zinc carbonate) neutralizes the acid present in the ant sting, thereby reducing irritation.
Q 10. What will happen if a solution of baking soda is put on turmeric paper? (1 marks)
(a) The colour of turmeric paper changes from yellow to blue.
(b) The colour of turmeric paper changes from yellow to green.
(c) The colour of turmeric paper changes from yellow to red.
(d) The colour of turmeric paper changes from yellow to magenta.
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Baking soda is a basic substance and thus changes the colour of yellow turmeric paper to red.
Q 11. The trapped air under the feathers of a bird: (1 marks)
(a) Reduces heat transfer through conduction
(b) Increases heat transfer through conduction
(c) Stops heat transfer by conduction
(d) Does not affect heat transfer through conduction
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The trapped air reduces heat transfer through conduction, helping to keep birds warm.
Q 12. The vacuum present in a vacuum flask reduces heat transfer by _______. (1 marks)
(a) Convection
(b) Radiation
(c) Conduction and convection
(d) Conduction
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The vacuum prevents heat transfer by both conduction and convection.
Q 13. The base/fundamental unit of time is (1 marks)
(a) Minute
(b) Second
(c) Hour
(d) Year
Correct Answer is Option (b)
In the International System of Units (SI), the base unit of time is the second.
Q 14. Average speed = _______ (1 marks)
(a) Half distance travelled/time
(b) Half distance travelled × time
(c) Total distance travelled/total time
(d) Total distance travelled × total time
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Average speed is defined as the total distance traveled divided by the total time taken.
Q 15. A car moves with a speed of 40 km/h for 15 minutes, and then with a speed of 60 km/h for the next 15 minutes. The total distance covered by the car is (1 marks)
(a) 100 km
(b) 25 km
(c) 15 km
(d) 10 km
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Distance covered in first 15 minutes =
Distance covered in second 15 minutes =
Hence, total distance covered = 10 + 15 = 25 km
Section - B
Q 16. How are nutrients replenished in the soil? (2 marks)
Nutrients are replenished in the soil through two primary methods:
- Addition of fertilisers and manures: Fertilisers and manures contain essential plant nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. When these materials are added to the soil, they enrich it with the necessary nutrients.
- Growth of leguminous crops: Leguminous plants host nitrogen-fixing bacteria, such as Rhizobium, in their root nodules. These bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogenous compounds, which then mix with the soil.
Q 17. How do earthworms increase soil fertility? (2 marks)
Earthworms ingest soil, digest the organic matter present in it and excrete soil full of plant nutrients known as worm cast which makes the soil fertile. They make burrows inside the soil and thereby aerate it.
Earth Worms
Q 18. (i) What is the purpose of scouring the sheared skin obtained from sheep?
(ii) How is it done? (2 marks)
(i) Scouring the sheared skin obtained from sheep helps to remove grease, dust and dirt from the fleece of sheep.
(ii) Scouring is done by thoroughly washing the sheared skin and hair in a soap solution and a lot of water to remove all the dirt. It can be done by hands or by machines.
Q 19. Name the base present in milk of magnesia. What is it used for? (2 marks)
Magnesium hydroxide is the base present in milk of magnesia. It is used to neutralise the excess acid present in stomach and is hence used as an antacid.
Q 20. What is an antacid? How does an antacid work? (2 marks)
Antacids are a group of mild bases that have no toxic effects on the body and are used to treat indigestion. Being basic in nature, antacids react with excess acid in the stomach and neutralise it.
Q 21. Your car moves with a speed of 40 km/h for 10 minutes, and then with a speed of 60 km/h for the next 15 minutes. What is the total distance covered by the car? (2 marks)
Distance covered in first 10 min = 40 * (10/60) km = 20/3 km
Distance covered in second 15 min = 60 * (15/60) km = 15 km
Total distance = (20/3) + 15 = 65/3 = 21.66 km
Q 22. A body moves along a path. Its distance–time graph is shown below. How much distance will it cover in 6 hours? (2 marks)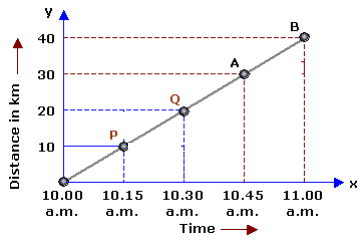
The body starts at 10.00 am, and it covers a distance of 40 km by 11.00 am.
Thus, the speed at B = Distance/Time = 40/1 = 40 km/hr
∴ the distance covered in 6 hours is given by
Distance = Speed * Time = 40 * 6 = 240 km
Section - C
Q 23. (i) How is the camel adapted to survive in deserts?
(ii) How do rats and snakes survive in deserts? (4 marks)
(i) The following adaptations of camel help it to survive in deserts
- It has long legs which prevent it from coming in contact with hot sand.
- It drinks excess amounts of water in one go.
- It excretes less amount of urine.
(ii) Rats and snakes avoid the high temperature of the day by residing in burrows during the day time and become active at night. They remain inactive and show lowered metabolic rate in response to high temperature and arid conditions (undergo aestivation).
Q 24. (i) Which soil horizon/section has the highest mineral content and why?
(ii) How is soil important for plant growth? (4 marks)
(i) The B-horizon of the soil has the highest mineral content, because when rainwater seeps through the topsoil, it dissolves minerals and deposits them in this layer.
(ii) Soil is important for plant growth because
- It provides mechanical support to the plants.
- It provides water and nutrients to the plants.
Q 25. (i) Why do muscle cells respire anaerobically?
(ii) Why do muscle cramps arise after heavy physical exercise? (4 marks)
(i) Our muscle cells respire anaerobically for a short period of time whenever there is a temporary deficiency of oxygen. When we do heavy physical exercise for several hours or do heavy weightlifting, the demand for energy increases. However, the supply of oxygen to produce the required energy is limited. So, anaerobic respiration takes places in the muscle cells to fulfil the increased energy demands of the body.
(ii) Muscle cramps occur when muscle cells respire anaerobically. The partial breakdown of glucose produces lactic acid. The accumulation of lactic acid causes muscle cramps.
Q 26: Give reasons for the following: (4 marks)
(i) Wool burns with a bad smell.
(ii) Wool is used for making winter clothing.
(iii) The quality of wool depends on the breed of sheep.
(iv) Shearing does not cause any pain to the sheep.
(i) Wool is a proteinaceous fibre and hence burns with a bad smell.
(ii) Wool fibre is extremely porous. The air in the pores acts as an insulator and does not allow the body heat to escape. Hence, wool is used for making winter clothing.
(iii) The quality of wool is judged on the basis of its thickness, length, shine, strength and colour of the fibre, which in turn, depends on the breed of sheep.
(iv) In shearing, the hair of sheep along with a thin layer of skin called fleece is removed from the body of sheep. Shearing does not cause any pain to the sheep because the uppermost thin layer of their skin is dead.
Q 27. (i) Define sericulture.
(ii) What is a cocoon?
(iii) Explain the process of obtaining silk thread from the cocoon. (4 marks)
(i) The process of rearing of silkworms for obtaining silk is called sericulture.
(ii) The covering of silk fibres inside which the caterpillar covers itself is called a cocoon.
(iii) The cocoons of silk moth are used to obtain silk fibres. The cocoons are kept under the Sun or boiled or exposed to steam. The silk fibres are then separated out. This process of separating the silk fibres from the cocoon is called reeling.Cocoon
Q 28. Differentiate between acids and bases (four points). (4 marks)
Q 29. (i) An iron ball at 40°C is dropped in a mug containing water at 40°C. What will be the passage of flow of heat in the system? Explain.
(ii) How does heat flow in a body having one end cool and the other at high temperature? (4 marks)
(i) There will be no flow of heat either from the iron ball to water or from water to the iron ball because both are at the same temperature, so heat transfer will not take place.
(ii) Heat flows from higher temperature to lower temperature. So, heat will go from the hotter end to the colder end.
Q 30. (i) What is a laboratory thermometer?
(ii) Which thermometer is used to measure high temperatures?
(iii) Stainless steel pans are usually provided with copper bottoms. Why? (4 marks)
(i) A laboratory thermometer is a thermometer used to measure temperatures in the range −10°C to 110°C.
(ii) A pyrometer is used to measure high temperatures.
(iii) Stainless steel pans are usually provided with copper bottoms because copper is a better conductor of heat than stainless steel, and hence, food can be cooked at a faster rate.
Q 31. (i) Give two examples of periodicity observed in nature.
(ii) A bike moves with a speed of 60 km/h and covers 25 km, and then with a speed of 50 km/h covers 20 km to reach the destination. What is the total time taken by the bike to reach the destination? (4 marks)
(i) Example 1: Revolution of the Earth around the Sun causes the change in season on a periodic basis.
Example 2 : Rotation of the Earth around its own axis causes days and nights periodically.
(ii) Time = Distance/Speed
= (25/60) + (20/50)
= (5/12) + (2/5)
= [(5 * 5) + (12 * 2)]/(12 * 5)
= [25 + 24]/60
= 49/60 h = 49 min
Section - D
Q 32. (i) What is the role played by the stomata in plants?
(ii) How do snakes respire? (5 marks)
(i) Air containing carbon dioxide enters the plant through small openings called stomata. This air is used during photosynthesis and respiration. Oxygen produced during photosynthesis exits the plant through the stomata. Even the excess of water vapour is released into the atmosphere through these pores by the process of transpiration.
(ii) In this picture of a DEADLY black mamba you can see the breathing tube at the bottom of the mouth.
They breathe through this opening just behind the tongue called the glottis, which opens into the trachea, or windpipe.Through this opening snakes take breathe.
Snakes don't have a diaphragm so they use muscles along their sides to expand and contract their lungs. Most snakes have only one main, functional lung to obtain oxygen.
When a snake is feeding on a large prey item it can also push its trachea (windpipe) off to the side so it can still breathe with a mouth full of food.
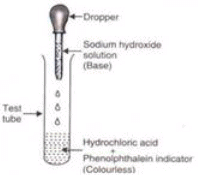
Q 33. (i) What is neutralisation? How is a neutralisation reaction represented?
(ii) Describe the neutralisation reaction between sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid with the help of an activity. (5 marks)
(i) The reaction in which an acid reacts with a base to form salt and water is called neutralisation. A neutralisation reaction can be represented as:
Acid + Base → Salt + water
The salt formed during a neutralisation reaction depends on the acid and the base which are reacted with each other. Some heat is always evolved (or produced) in a neutralisation reaction.
(ii) Sodium hydroxide is a base and hydrochloric acid is an acid. So, when sodium hydroxide is treated with hydrochloric acid, a neutralisation reaction takes place to form sodium chloride (salt) and water. This can be written as:
- We take 5 ml of dilute hydrochloric acid solution in a test tube. The hydrochloric acid solution is colourless. Add 2 or 3 drops of phenolphthalein indicator to the acid in the test tube. Shake the test tube gently. Phenolphthalein indicator is colourless. There is no change in the colour of the phenolphthalein indicator on adding it to the hydrochloric acid solution.
- Take sodium hydroxide solution (base) in a dropper. Add this sodium hydroxide solution to hydrochloric acid in the test tube drop wise (stirring the test tube gently after each addition). Continue to add sodium hydroxide solution drop by drop (while stirring) till a light pink colour just appears in the solution in the test tube. We then stop adding more of sodium hydroxide solution.
- At this stage, all the hydrochloric acid taken in the test tube has been completely neutralised by the sodium hydroxide base. Thus, a neutralisation reaction has taken place in the test tube. The completion of neutralisation reaction is indicated by the fact that when all the acid has been neutralised, a little excess of the base changes the colour of the phenolphthalein indicator to pink. This makes the solution in the test tube light pink.
Q 34. (i) What is a simple pendulum? Define the time period of a simple pendulum.
(ii) State whether the following statement is true or false: The time period of a given pendulum is not constant.
(iii) In an experiment to measure the time period of a simple pendulum, the time for 20 complete oscillations was found to be 36 s. What is the time period of this pendulum? (5 marks)
(i) A simple pendulum consists of a small metal ball (called bob) suspended by a long thread from a rigid support such that the bob is free to swing back and forth. The time of a simple pendulum is the time taken by the pendulum bob to make one complete oscillation.
(ii) False. For a particular pendulum, the time period remains constant throughout.
(iii) Time for 20 complete oscillations = 36 s
Time for 1 complete oscillation = 36/20 = 1.8 s
So, the time of the pendulum = 1.8 s
|
112 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science: CBSE Sample Question Paper with Solutions Term I – 1 - Science Class 7 (Old NCERT)
| 1. What is the CBSE Class 7 Science Sample Question Paper? |  |
| 2. How can I download the CBSE Class 7 Science Sample Question Paper? |  |
| 3. What is the format of the CBSE Class 7 Science examination? |  |
| 4. How should I prepare for the CBSE Class 7 Science examination? |  |
| 5. Are there any tips for answering the CBSE Class 7 Science examination? |  |