Chemistry: Sample Question Paper- 1, Class 12 | Sample Papers for Class 12 Medical and Non-Medical PDF Download
Section A
Ques 1: A compound contains A atoms at the corners and B atoms at the centres of all faces. What is the formula of the compound? [1]
OR
What kind of attractive forces are present in molecular crystalline solids?
Ans: 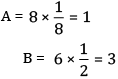
Formula = AB3
OR
Dispersion forces, dipole-dipole interactions and hydrogen bonds.
Ques 2: What are the physical states of the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium of a cloud? [1]
Ans: Dispersed phase: Liquid
Dispersion medium: Gas
Ques 3: Which is the most common oxidation state of lanthanoids? [1]
OR
What is the common oxidation state of Cu, Ag and Au?
Ans: +3 is the most common oxidation state of lanthanoids.
OR
The most common oxidation state of Cu, Ag and Au is +1.
Ques 4: Give the IUPAC name of the following compound: [1]
(CH3)3CCH2Br
Ans: 1-bromo-2, 2-dimethyl propane
Ques 5: Name the monomers of the nylon-2-nylon-6 polymer. [1]
Ans: 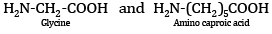
Section B
Ques 6: State Henry’s law. What is the significance of KH? [2]
OR
What would be the value of van’t Hoff factor for a dilute solution of K2SO4 in water?
Ans: Henry’s law: It states that ‘the partial pressure of the gas in vapour phase (p) is proportional to the mole fraction of the gas (x) in the solution’ and expressed as: P = KHx
where KH is Henry’s constant.
Significance of KH: Higher the value of Henry’s law constant KH, lower is the solubility of the gas in the liquid.
OR
In dilute solutions, 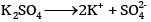
van ' t Hoff Factor, i = 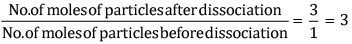
Ques 7: Account for the following: [2]
(a) Alkaline medium inhibits the rusting of iron.
(b) Iron does not rust even if the zinc coating is broken in galvanised iron pipes.
Ans: (a) Alkalinity of the solution prevents the availability of H+ ions.
(b) A galvanised substance is that which has been coated with a layer of zinc to delay corrosion. Zinc gets corroded instead of the substance.
The outer layer of zinc of any galvanised material reacts with the atmospheric oxygen to form zinc oxide (ZnO), which is stronger than zinc. Thus, even if the outer layer of zinc undergoes corrosion, the material is getting coated with a stronger substance (ZnO), and thus is better able to resist corrosion.
Ques 8: Calculate the overall order of a reaction which has the rate expression [2]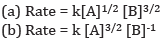
Ans:
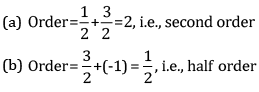
Ques 9: Complete the following chemical reaction equations: [2]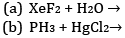
Ans: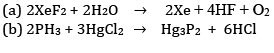
Ques 10: What happens when [2]
(a) Phenol reacts with Br2 in CS2 at 273 K.
(b) Phenol reacts with conc. HNO3.
Ans: (a) When phenol reacts with Br2 in CS2 at 273 K, a mixture of o- and p-bromophenol is formed in which p-bromophenol is the major product.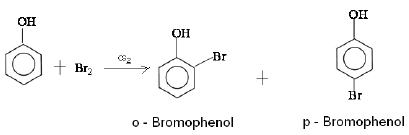
(b) When phenol reacts with conc. HNO3, 2,4,6-trinitrophenol is formed. 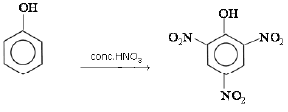
Ques 11: Out of acetophenone and benzophenone, which gives the iodoform test? Write the reactions involved. [2]
OR
Draw the structures of the following compounds:
(a) 3-methyl butanal
(b) 4-chloropentan-2-one
Ans: Acetophenone (C6H5COCH3) contains the group (–CH3CO) and hence gives the iodoform test, while benzophenone does not contain this group and hence does not give the iodoform test: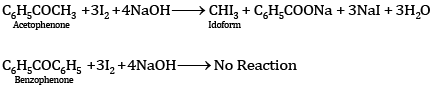
OR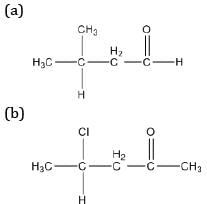
Ques 12: Write the structure of the monomers of the following polymers: [2]
(a) PVC
(b) Polypropene
Ans:
| Polymer | Monomer | Structure of the monomer |
| (a) PVC | Vinyl chloride | CH2=CH=Cl |
| (b) Polypropene | Propene | CH3-CH=CH2 |
Section C
Ques 13: Chromium crystallises in BCC structure. If its atomic diameter is 245 pm, find its density. Atomic mass of Cr = 52 amu and NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol−1. [3]
Ans: Diameter = 245 pm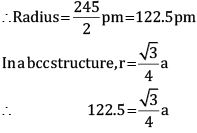

Ques 14: A solution is made by dissolving 30 g of a non-volatile solute in 90 g of water. It has a vapour pressure of 2.8 kPa at 298 K. The vapour pressure of pure water is 3.64 kPa. Calculate the molar mass of the solute. [3]
OR
Calculate the freezing point of depression expected for 0.0711 m aqueous solution of Na2SO4. If this solution actually freezes at −0.320ͦC , then what would be the value of van’t Hoff factor? (Kf = 1.86ͦC)
Ans: According to Rault’s law,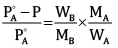
Here, 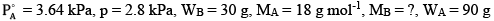
Substituting the values in the above equation, we get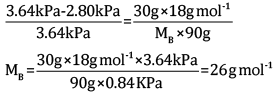
OR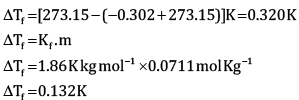
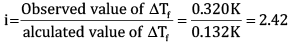
Ques 15: The decomposition of Cl2O7 at 400 K in the gas phase to Cl2 and O2 is a first-order reaction. [3]
(a) After 55 s at 400 K, the pressure of Cl2O7 falls from 0.062 to 0.044 atm. Calculate the rate constant.
(b) Calculate the pressure of Cl2O7 after 100 s of decomposition at this temperature.
Ans: (a) For a first-order reaction,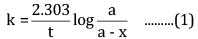
Here, a = 0.062 atm
a - x = 0.044 atm
t = 55 s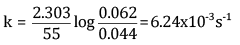
(b) To calculate a - x when t = 100 s, a = 0.062 atm
Putting the values in the above equation,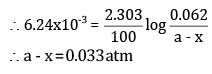
Ques 16: (a) Why are deltas formed at places where the river meets the sea?
(b) List two characteristics of catalysts.
(c) What are macromolecular colloids? Give an example.[3]
Ans: (a) River water is muddy and contains charged colloidal particles of clay, sand and many other materials. Sea water contains in it a number of dissolved electrolytes. When sea water and river water come in contact with each other, the electrolytes present in sea water coagulate the suspended colloidal particles which ultimately settle at the point of contact. Thus, a delta is formed at the point where the river enters the sea.
(b) Characteristics of catalysts:
(i) Catalysts are highly selective. A catalyst is able to direct a reaction to give a particular product.
(ii) Catalysts are highly active. A catalyst is able to increase the rate of a chemical reaction.
(c) A colloid in which the particles of dispersed phase are sufficiently big in size to be of colloidal dimensions is called a macromolecular colloid. Example: Starch
Ques 17: State briefly the principles which serve as the basis for the following operations in metallurgy: [3]
(a) Froth flotation process
(b) Zone refining
(c) Refining by liquation
Ans: (a) The principle of the froth flotation process is that sulphide ore particles are preferentially wetted by oil, whereas gangue particles are wetted by water.
(b) Zone refining is based on the principle that the impurities are more soluble in the melt than in the solid state of the metal.
(c) The principle of refining by liquation is that the impurities whose melting points are higher than the metal are left behind on melting the impure metal. Hence, pure metal separates out.
Ques 18: Complete the following chemical equations: [3]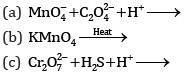
Ans:
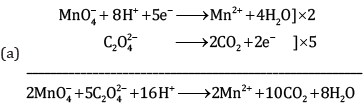
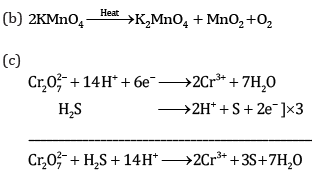
Ques 19: (a) Give the IUPAC name of K3[Cr(C2O4)3]. [3]
(b) What is the number of unpaired electrons in [CoF6]3− and [Co(NH3)6]3+?
(c) Name the isomerism exhibited by the following pair of compounds:
[Co(en)2(H2O)Cl]Cl2 and [Co(en)2Cl2]Cl.H2O]
Ans: (a) Potassium trioxalatochromate (III)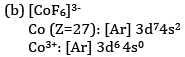
F− is a weak field ligand and therefore does not cause pairing of electrons.
There are four unpaired electrons.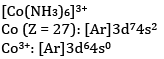
NH3 is a strong field ligand and causes pairing of electrons. Hence, there are no unpaired electrons.
(c) Hydrate isomerism
Ques 20: Answer the following questions: [3]
(a) What is meant by chirality of a compound? Give an example.
(b) Which of the following compounds is more easily hydrolysed by KOH and why?
CH3CHClCH2CH3 or CH3CH2CH2Cl
(c) Which one undergoes SN2 substitution reaction faster and why?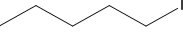
and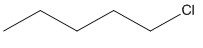
OR
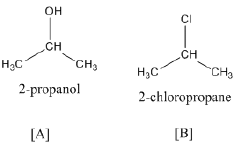
(a) Give a chemical test to distinguish between chlorobenzene and benzyl chloride.
(b) Identify A, B, C and D: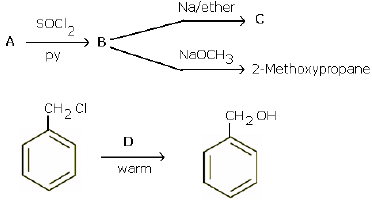
Ans: (a) Chiral molecules are those molecules which are non-superimposable on their mirror images, and this property is known as chirality. Butan-2-ol is an example of a chiral molecule.
Due to the –I effect of alkyl groups, the secondary carbanion ion 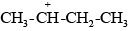 derived from secondary butyl chloride is more stable than the primary carbanium ion
derived from secondary butyl chloride is more stable than the primary carbanium ion 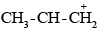 derived from n-propyl chloride. Therefore, the secondary butyl chloride gets hydrolysed more easily than n-propyl chloride under SN1 conditions.
derived from n-propyl chloride. Therefore, the secondary butyl chloride gets hydrolysed more easily than n-propyl chloride under SN1 conditions.
(c) As iodine is a better leaving group because of its large size, it will be released at a faster rate in the presence of incoming nucleophiles.
OR
(a) Add a small amount of aqueous KOH to both compounds. Acidify with dil. HNO3 and add AgNO3. Benzyl chloride gives white precipitate, while chlorobenzene does not.
(b)
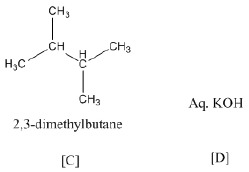
Ques 21: Give the equation of the following reactions: [3]
(a) Oxidation of propan-1-ol with alkaline KMnO4 solution.
(b) Bromine in CS2 with phenol.
(c) Dilute nitric acid with phenol.
Ans: (a) 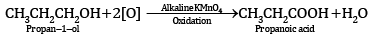
(b)
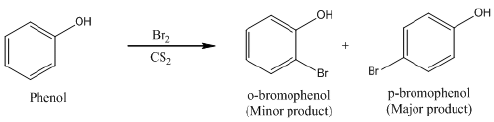
(c)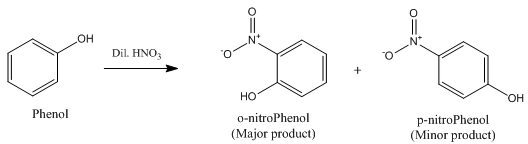
Ques 22: In the following cases, rearrange the compounds as directed: [3]
(a) In the increasing order of basic strength: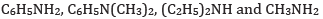
(b) In the decreasing order of basic strength:
Aniline, p-nitroaniline and p-toluidine
(c) In the increasing order of pKb value: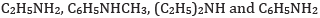
Ans: (a) In increasing order of basic strength: 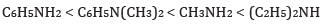
(b) In decreasing order of basic strength: 
(c) In increasing order of pKb value: 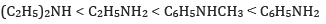
Ques 23: Name three fat-soluble vitamins, their source and the diseases caused by their deficiency in the diet. [3]
OR
Explain the following terms:
(a) Peptide linkage
(b) Pyranose structure of glucose
(c) Glycosidic linkage
Ans:
| Name of fatsoluble vitamins | Source | Deficiency Diseases |
| Vitamin A | Fish liver oil, carrots, milk | Xerophthalmia, night blindness |
| Vitamin D | Exposure to sunlight, fish and egg | Rickets and osteomalacia |
| Vitamin E | Vegetable oils like wheat germ oil, sunflower oil | Sterility and muscular atrophy |
OR
(a) Peptide linkage: The 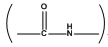 bond formed between two amino acid molecules with loss of water in a polypeptide linkage.
bond formed between two amino acid molecules with loss of water in a polypeptide linkage.
(b) Pyranose structure of glucose: The six-membered cyclic structure of glucose is called the pyranose structure (α- or β-), in anology with the heterocyclic compound pyran.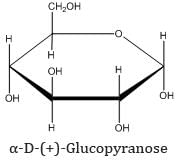
(c) Glycosidic linkage: The linkage between two monosaccharide molecules through oxygen atom in a disaccharide or polysaccharide is known as a glycosidic linkage.
Ques 24: Give reason for the following: [3]
(a) Sulpha drugs work like antibiotics, but they are not antibiotics.
(b) Aspirin helps in the prevention of heart attack.
(c) Soaps are biodegradable, whereas detergents are non-biodegradable.
Ans: (a) This is because sulpha drugs are purely prepared synthetically. Antibiotics may be either wholly or partially obtained from microorganisms.
(b) Aspirin helps in the prevention of heart attack because of its anti-blood clotting action.
(c) Soaps are biodegradable because their molecular structure has a straight chain which is easy to break and degrade by bacteria present in sewage water, whereas the molecules of detergents have a branched chain which is difficult to break. The branched chain may or may not be attacked by bacteria. Hence, detergents are non-biodegradable.
Section D
Ques 25: (a) Name two transition elements which show +1 oxidation state.
(b) Name the transition element which does not exhibit variable oxidation state.
(c) Transition elements show catalytic properties. Why?
(d) Explain why Cu+ ion is not stable in aqueous solutions.
OR
(a) Write the steps involved in the preparation of
(i) Na2CrO4 from chromite ore
(ii) K2MnO4 from pyrolusite ore
(b) What is the effect of increasing pH on K2Cr2O7 solution?
(c) Draw the structure of dichromate ion indicating the bond angles and bond lengths.
Ans: (a) Au and Hg can show +1 oxidation state.
(b) Scandium
(c) Transition elements exhibit variable oxidation state and can form complexes.
(d) Due to low charge density, Cu+ has low enthalpy of hydration. Cu+ in aqueous solution undergoes disproportionation.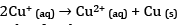
The EӨ value for this is positive and the reaction is favourable.
OR
(a) 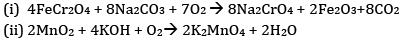
(b)On increasing pH, the solution turns yellow due to the formation of chromate ion.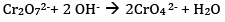
(c)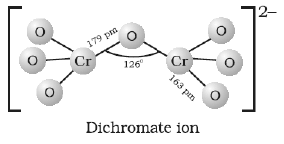
Ques 26: The emf of the cell reaction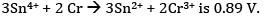
Calculate:
(a) Δθ for the reaction.
(b) Equilibrium constant for the reaction relating to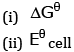
OR
Given: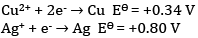
(a) Write the cell reaction.
(b) Construct the galvanic cell.
(c) For what concentration of Ag+ ions will the emf of the cell be zero at 25°C if the concentration of Cu2+ is 0.01 M?
Ans: (a)The cell reaction is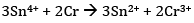
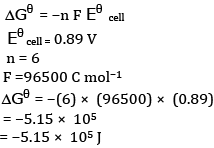
(b)Calculation of K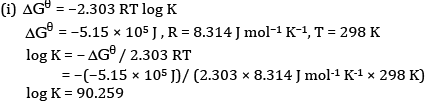
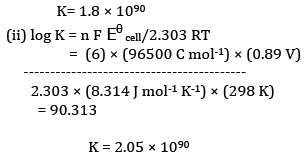
OR
(a) Since the reduction potential of Ag+/Ag is more than that of Cu2+/Cu, Ag+ gets reduced to Ag at the cathode and Cu gets oxidised to Cu2+ at the anode.
At the cathode: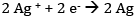
At the anode: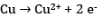
Therefore, the net reaction is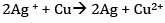
(b) The cell is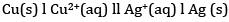
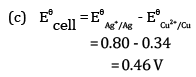
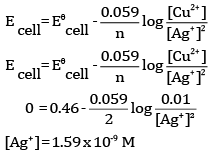
Ques 27: (a) Ethanol reacts with acetic acid in the presence of conc. H2SO4 to give a sweet smelling substance. Give the equation involved in the reaction. [5]
(b) Write a note on
(i) Rosenmund’s reduction
(ii) Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction
OR
(a) Complete the equations: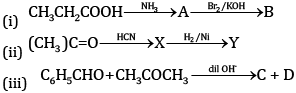
(b) Semicarbazide contains two NH2 groups, but only one participates in the reaction with carbonyl compounds. Why?
(c) Which of the two will give a yellow precipitate with iodine and sodium hydroxide: pentan-2-one or pentan-3-one?
Ans: (a) 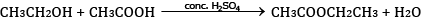
(b) (i) In Rosenmund’s reaction, acid chlorides are subjected to catalytic hydrogenation in the presence of Pd supported over BaSO4 to yield corresponding aldehyde. The catalyst is poisoned by S or quinoline. 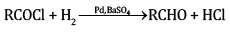
(ii) In the Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction, carboxylic acids react with chlorine or bromine in the presence of a small amount of P to give α-halogenated carboxylic acids. The reaction requires the presence of α-hydrogen in the acid.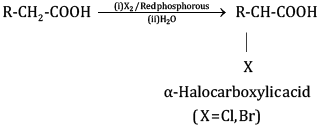
OR
(a) (i) 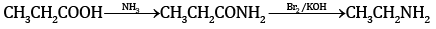
(ii)
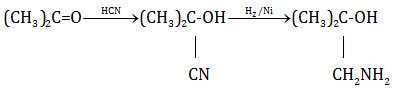
(iii)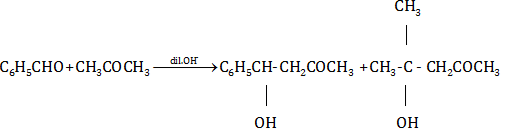
(b) NH2CONHNH2, semicarbazide contains two NH2 groups, but the one next to the CO group is involved in resonance with C=O and is thus not available.
(c) Pentan-2-one will give a yellow precipitate with iodine and sodium hydroxide because it contains the group
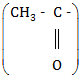
|
159 docs|4 tests
|
FAQs on Chemistry: Sample Question Paper- 1, Class 12 - Sample Papers for Class 12 Medical and Non-Medical
| 1. What is the importance of sample question papers for Class 12 Chemistry exams? |  |
| 2. How can sample question papers be used effectively for Class 12 Chemistry exam preparation? |  |
| 3. Are sample question papers enough for Class 12 Chemistry exam preparation? |  |
| 4. Can solving sample question papers guarantee success in Class 12 Chemistry exams? |  |
| 5. Where can I find sample question papers for Class 12 Chemistry exams? |  |





















