Short & Long Answer Questions: Redox Reactions | Physical Chemistry for NEET PDF Download
Q1. The blue colour of copper sulphate solution is discharged when a rod of zinc is dipped in it. Explain.
Ans: Zinc lies below copper in the electrochemical series and can therefore, release electrons to the 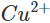 ions. As a result, Zn is oxidised while
ions. As a result, Zn is oxidised while 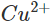 ions are reduced. Since the concentration of
ions are reduced. Since the concentration of 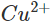 ions in the solution decreases, the blue colour of the solution is slowly discharged.
ions in the solution decreases, the blue colour of the solution is slowly discharged.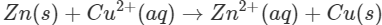
Q2. Why cannot oxidation occur without reduction?
Ans: Oxidation involves the loss of electrons while the reduction involves the gain of electrons. Energy is needed when a species loses electrons and is released when it accepts electrons. This means that a species can gain energy only at the cost of electron releasing species. In other words, oxidation cannot occur without reduction or oxidation and reduction go side by side.
Q3. Articles of iron are generally coated with zinc. Explain.
Ans: Iron gets easily rusted in the presence of moist air. Formation of rust (Fe2O3. x H2O) is a redox reaction in which Fe is oxidised to 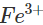 ions. Since zinc is more reactive than iron (placed below iron in the activity series), it is oxidised to
ions. Since zinc is more reactive than iron (placed below iron in the activity series), it is oxidised to 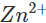 ions instead of iron when coated over the surface of iron. Thus, zinc takes part in the redox reaction while surface of iron remains intact.
ions instead of iron when coated over the surface of iron. Thus, zinc takes part in the redox reaction while surface of iron remains intact.
Q4. Why is anode negatively charged in an electrochemical cell?
Ans: Anode is negatively charged in an electrochemical because electrons are released at this electrode.
Q5. Why is standard hydrogen electrode called reversible electrode?
Ans: A standard hydrogen electrode is called reversible electrode because it can act both as anode as well as cathode in an electrochemical cell.
Q6. Check the feasibility of the following redox reaction with the help of electrochemical series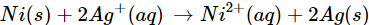
Ans: The E° value of 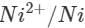 is 0.25V while that of
is 0.25V while that of 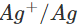
is +0.80 V. This means that nickel is placed below silver in the series and can easily reduce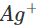 ions to silver by releasing electrons. The redox reaction is therefore, feasible.
ions to silver by releasing electrons. The redox reaction is therefore, feasible.
Q7. What will happen when chlorine is passed through an aqueous solution of potassium bromide?
Ans: The solution will acquire an orange colour due to the vapours of bromine that are evolved. Actually, chlorine is a stronger oxidising agent than bromine and oxidises 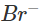 ions (in KBr) to Br2 and itself is reduced to
ions (in KBr) to Br2 and itself is reduced to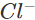 ions.
ions.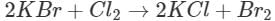
Q8. What is the source of electrical energy in a galvanic cell?
Ans: In a galvanic cell, the redox reaction is of spontaneous nature. The energy as free energy 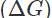 is released in the reaction. This gets converted into the electrical energy.
is released in the reaction. This gets converted into the electrical energy.
Q9. Knowing that: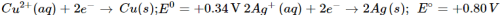
Ans: A solution of an electrolyte can be stored in a particular vessel only in case there is no chemical reaction taking place with the material of the vessel. Now if silver nitrate solution is to be kept in copper vessel, the probable reaction will be:
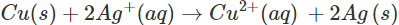
Since copper is placed below silver in the activity series, this means that it can lose electrons to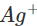 ions and the chemical reaction will occur. Therefore, silver nitrate solution cannot be kept in copper vessel. Now, when copper sulphate solution is placed in silver vessel, the likely chemical reaction is:
ions and the chemical reaction will occur. Therefore, silver nitrate solution cannot be kept in copper vessel. Now, when copper sulphate solution is placed in silver vessel, the likely chemical reaction is:
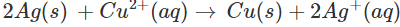
Since Ag is placed above copper in the activity series, the chemical reaction will not take place. As a result, copper sulphate can be easily stored in silver vessel.
Q10. Determine the oxidation number of the element in the bold in the following species
(i) SiH4
(ii) BH3
(iii) BF3
(iv)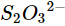
(v)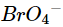
(vi)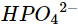
Ans: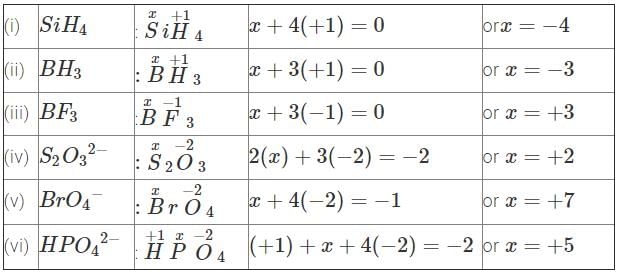
Q11. Identify the oxidants and reductants in the following reactions
(a)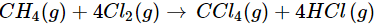
(b)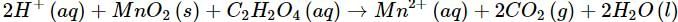
(c)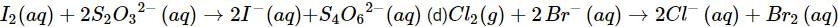
Ans:
(a) Let us write the oxidation numbers of all the atoms of the reactants and products taking part in the reaction. CH4 is reductant (reducing agent) and Cl2 is oxidant (oxidising agent).
(b) Let us write the oxidation numbers of all the atoms of the reactants and products taking part in the reaction. C2H2O4 is reductant (reducing agent) and MnO2 is oxidant (oxidising agent).
(c) Let us write the oxidation numbers of all the atoms of the reactants and products taking part in the reaction.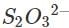 is reductant (reducing agent) and I2 is oxidant (oxidising agent).
is reductant (reducing agent) and I2 is oxidant (oxidising agent).
(d) Let us write the oxidation numbers of atoms of all the reactants and products taking part in the reaction.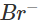 is reductant (reducing agent) and Cl2 is oxidant (oxidising agent).
is reductant (reducing agent) and Cl2 is oxidant (oxidising agent).
Q12. Write the O.N. of all the atoms in the following well known oxidants:
(i) KMnO4
(ii) K2Cr2O7
(iii) KClO4
Ans:
(i) KMnO4: K(+1); Mn(+7); O(-2)
(ii) K2Cr2O7: K(+1); Cr(+6); O(-2)
(iii) KClO4: K(+1); Cl(+7); O(-2)
Q13. What is oxidation according to electronic concept?
Ans: Oxidation involves loss of one or more electrons by a species during a reaction.
Q14. Define reducing agent.
