Class 7 Social Science Chapter 12 Question Answers - Understanding Markets
Short Answer Questions
Q1: How do price changes affect the supply and demand of goods in a market?
Ans: If the price is set too high, fewer buyers may purchase, leading to a decrease in demand. On the other hand, if the price is set too low, more buyers will purchase, but the seller may raise the price to earn more, adjusting the supply accordingly. MarketsQ2: What are the main differences between wholesale and retail markets?
MarketsQ2: What are the main differences between wholesale and retail markets?
Ans: Wholesale markets involve large-scale purchases of goods from producers and are typically sold in bulk, while retail markets sell smaller quantities to individual consumers. Retailers buy from wholesalers and sell directly to customers.
Q3: How do government controls, like price ceilings and floors, affect markets?
Ans: Price ceilings prevent sellers from charging excessively high prices, ensuring goods remain affordable for consumers. Price floors prevent prices from falling too low, ensuring producers are fairly compensated, especially in essential sectors like agriculture.
Q4: What is the importance of guilds in ancient markets?
Ans: Guilds were organizations of traders or craftsmen that established rules, standards, and practices for their trade. They ensured fair transactions and supported each other, fostering a cooperative environment for businesses to grow.
Q5: How does the demand and supply model work in a market?
Ans: In the demand and supply model, the price of goods is determined by the interaction between buyers’ demand and sellers’ supply. When demand exceeds supply, prices rise, and when supply exceeds demand, prices fall to balance the market.
Q6: What role do markets play in a country’s economy?
Ans: Markets are essential for the economy as they enable the exchange of goods and services, contributing to economic growth. They facilitate the movement of resources, help create jobs, and ensure that products reach consumers efficiently.
Q7: How does the barter system work, and why was it replaced by money?
Ans: The barter system involves exchanging goods and services directly without using money. It was replaced by money to make transactions more efficient, as money is a universally accepted medium that eliminates the need for a direct exchange of goods.
 Barter System
Barter System
Q8: How did markets evolve with the advent of online platforms?
Ans: Online markets enable transactions to occur remotely through websites or apps, allowing buyers to access a wider range of products and services. These platforms offer convenience, greater variety, and sometimes better prices than physical markets.
Q9: What are domestic and international markets?
Ans: Domestic markets involve trade within a country's borders, while international markets involve the exchange of goods and services between countries. International markets are critical for accessing goods not available domestically and for expanding business opportunities globally.
Q10: How do physical and online markets differ in terms of consumer experience?
Ans: In physical markets, consumers can see, touch, and try goods before buying, offering a direct experience. Online markets, however, provide convenience and a wider selection but lack the ability for consumers to physically inspect items before purchasing.
Q11: What is the role of distributors in the market?
Ans: Distributors play a vital role in connecting wholesalers to retailers, ensuring goods reach their final destinations. They help manage the logistics of large-scale distribution, especially in regions where direct access to retailers is challenging.
Q12: How does government regulation ensure fair pricing and safety in markets?
Ans: The government regulates markets by setting price limits on essential goods, ensuring the quality and safety of products, and protecting consumers. These regulations help avoid exploitation, maintain product standards, and promote consumer trust in the marketplace.
Long Answer Questions
Q1: How do markets contribute to the economy of a country?
Ans:
- Markets play a vital role in the economy by facilitating the exchange of goods and services.
- They ensure that resources are distributed efficiently across the country, promoting trade and stimulating production.
- Markets also help generate employment opportunities, boost income generation, and support businesses by connecting them with consumers.
- \Moreover, taxes collected from markets provide revenue for the government to fund public services.
Q2: Why are price negotiations important in a market?
Ans:
- Price negotiations are important because they allow buyers and sellers to agree on a fair price for goods or services, ensuring both sides benefit from the transaction.
- If the price is set too high, demand decreases, while a price set too low may lead to losses for sellers.
- Through negotiation, the price stabilizes, making the transaction mutually beneficial and maintaining a balance between supply and demand.
Q3: How do government controls on prices affect markets?
Ans:
- Government controls, like price ceilings and floors, are essential to prevent price manipulation and ensure fairness in markets.
- A price ceiling ensures that essential goods, such as medicines or food, remain affordable for consumers.
- On the other hand, price floors guarantee that producers, especially farmers, receive a fair price for their goods, protecting them from market fluctuations.
- These regulations maintain market stability and protect both consumers and producers.
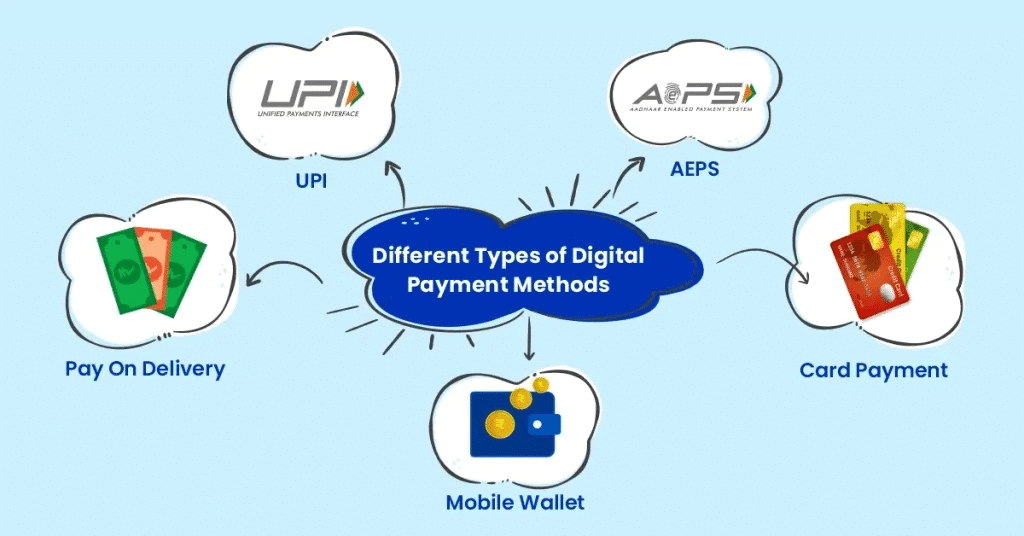 Online Payment Methods
Online Payment Methods
Q4: What is the role of guilds in market transactions and trade?
Ans:
- Guilds were organized groups of traders and craftsmen that regulated trade in ancient markets.
- They set standards for quality, ensured fair pricing, and resolved disputes within the community.
- Guilds provided members with resources, protection, and a network for business opportunities. By promoting cooperation rather than competition, guilds played a critical role in maintaining a stable and efficient market system.
Q5: How have physical and online markets evolved over time?
Ans:
- Physical markets have been around for centuries, where buyers and sellers meet face-to-face to exchange goods. With technological advancements, online markets have emerged, enabling consumers to shop from the comfort of their homes.
- Online platforms offer convenience, a wider range of products, and competitive prices.
- However, physical markets still hold value by providing a direct sensory experience and immediate product availability, and they are ideal for certain services like tailoring or street food.
Q6: What are the differences between wholesale and retail markets in terms of function and trade?
Ans:
- Wholesale markets deal with large quantities of goods bought in bulk from producers and sold to retailers, who then sell smaller quantities to consumers in retail markets.
- Retail markets cater directly to the consumer, making goods available in smaller amounts. While wholesale markets focus on supply chain efficiency, retail markets focus on providing goods to individuals and households, supporting the final step of the distribution process.
Q7: How do markets impact people's lives on a daily basis?
Ans:
- Markets are essential for people's daily needs, providing food, clothing, services, and more.
- They connect producers and consumers, allowing people to access goods they cannot produce themselves.
- Markets also foster relationships and trust, as families often rely on local grocers or tailors for regular purchases. In addition, markets provide economic opportunities and support livelihoods for millions of people involved in production, trade, and services.
Q8: How does the government balance regulation and freedom in markets?
Ans:
- The government regulates markets to ensure fairness, safety, and transparency in transactions.
- This includes setting price controls, ensuring product quality, and protecting consumers from exploitation.
- At the same time, the government allows businesses to operate freely to encourage innovation and competition.
- A balance is necessary to prevent monopolies, protect the environment, and ensure that markets remain efficient and responsive to consumer needs.
|
23 videos|204 docs|12 tests
|
















