Short & Long Question Answers: Exploring Magnets | Short & Long Answer Questions for Class 6 PDF Download
Short Question Answers
Q1. What are magnetic materials?
Ans: Magnetic materials are the materials that are attracted to a magnet, such as iron, nickel, and cobalt.
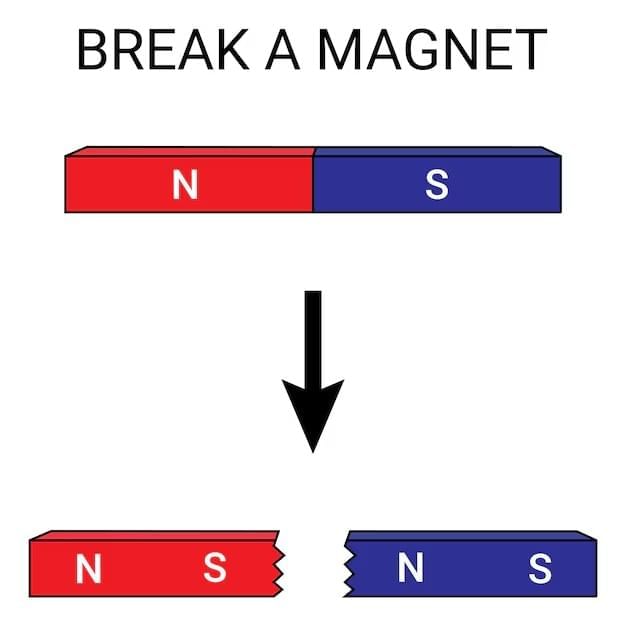
Q2. What happens when a magnet is broken into pieces?
Ans: When a magnet is broken into pieces, each piece has both a North and a South pole, and the poles always exist in pairs.
Q3. What happens when the same poles of two magnets are brought close together?
Ans: When the same poles (North-North or South-South) of two magnets are brought close together, they repel each other.
Q4. What is the direction in which a freely suspended magnet comes to rest?
Ans: A freely suspended magnet comes to rest along the north-south direction, with the North pole pointing north.
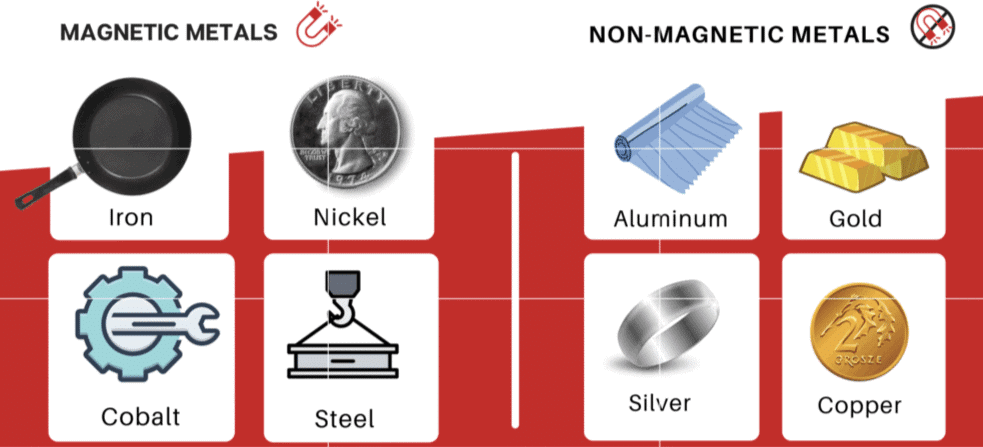
Q5. What is the difference between magnetic and non-magnetic materials?
Ans: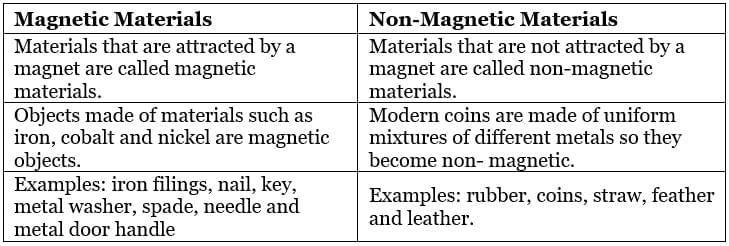
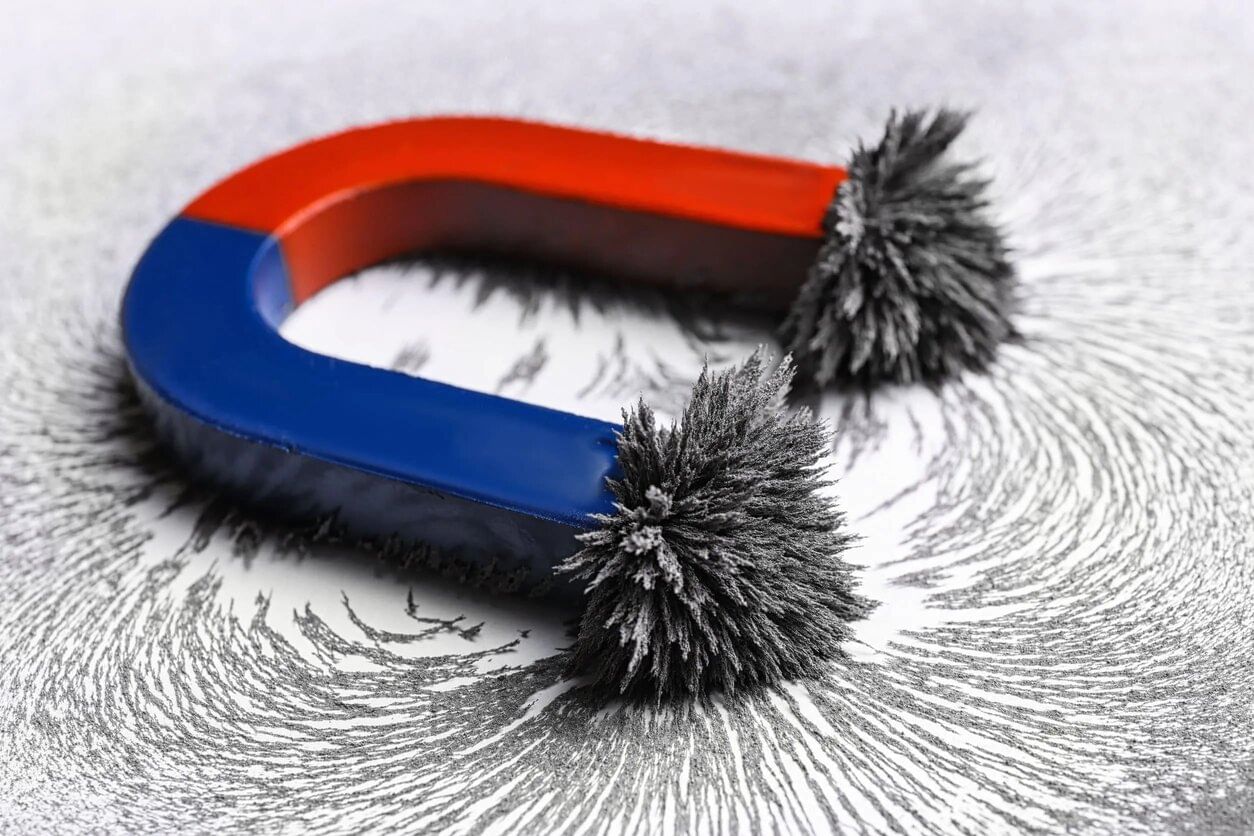
Q6. Why do iron filings stick more at the poles of a magnet?
Ans: Iron filings stick more at the poles of a magnet because the magnetic field is strongest at the poles.

Long Answer Questions
Q1. Explain the concept of magnetic poles and how they behave when magnets are brought together.
Ans: A magnet has two poles: the North pole and the South pole. When two magnets are brought close together, opposite poles (North-South) attract each other, while like poles (North-North or South-South) repel each other. This behaviour demonstrates the fundamental properties of magnets, where poles always exist in pairs, and a single pole cannot exist alone.
Q2. Describe how you can create a simple magnetic compass and how it works.
Ans: To create a simple magnetic compass, you need a small iron needle, a permanent bar magnet, a cork, and a bowl of water. First, magnetise the needle by rubbing it with one pole of the magnet. Then, place the magnetised needle through the cork and float it in the bowl of water. The needle will rotate and come to rest in the north-south direction. The end of the needle pointing towards the north is called the North-seeking pole, and the other end is the South-seeking pole.
Q3. What is the importance of magnets in navigation? Explain how a magnetic compass helps sailors find directions.
Ans: Magnets play a crucial role in navigation, particularly through the use of a magnetic compass. A magnetic compass has a magnetised needle that aligns itself with the Earth's magnetic field, pointing towards the magnetic North and South poles. This allows sailors to determine the direction even when stars or other natural indicators are not visible, such as during overcast skies or storms. By observing the direction of the needle, sailors can find the North-South axis and navigate accurately.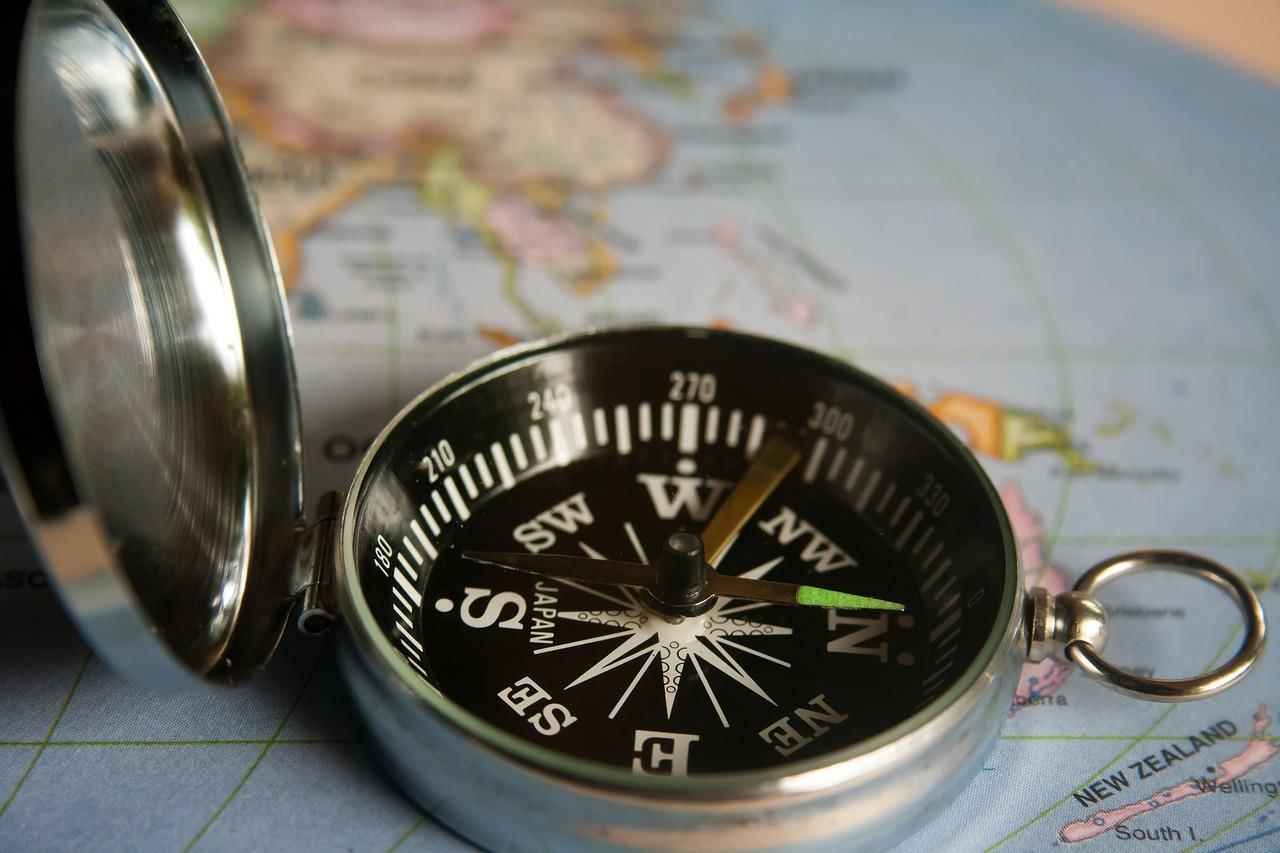
Q4. Explain the concept of attraction and repulsion between magnets with examples.
Ans: Attraction and repulsion are the primary interactions between magnets. When the opposite poles of two magnets (North-South) are brought close together, they attract each other. For example, if the North pole of one magnet is brought close to the South pole of another, they will pull towards each other. Conversely, when like poles (North-North or South-South) are brought near each other, they repel. For instance, two North poles will push away from each other, demonstrating repulsion.

Q5. Describe an activity to explore magnetic materials and how to identify them.
Ans: One activity to explore magnetic materials is to collect a variety of objects made from different materials and use a magnet to test their attraction. The objects can be made from wood, plastic, glass, iron, or other materials.

By bringing the magnet near each object, you can observe which materials are attracted to the magnet.

Magnetic materials, such as iron, nickel, and cobalt, will stick to the magnet, while non-magnetic materials, such as plastic or wood, will not. This experiment helps identify which materials are magnetic.
FAQs on Short & Long Question Answers: Exploring Magnets - Short & Long Answer Questions for Class 6
| 1. What are magnets and how do they work? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of magnets? |  |
| 3. How can we use magnets in our daily life? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between magnetic and non-magnetic materials? |  |
| 5. How can we test if an object is magnetic? |  |

















