Class 7 Science Question Answers - Fibre to Fabric
Short Q & A :
Q1: Define wool.
Ans : Wool is the soft, curly fibres obtained from the fleece of sheep, goat and yak etc., it clothes made from wool keeps us warm.
Q2: What are the different sources of wool?
Ans : The fleece of sheep is the main source of wool .Apart from that, Angora wool is obtained from angora goats. The fur (hair) on the body of camels is also used as wool like Llama and Alpaca.
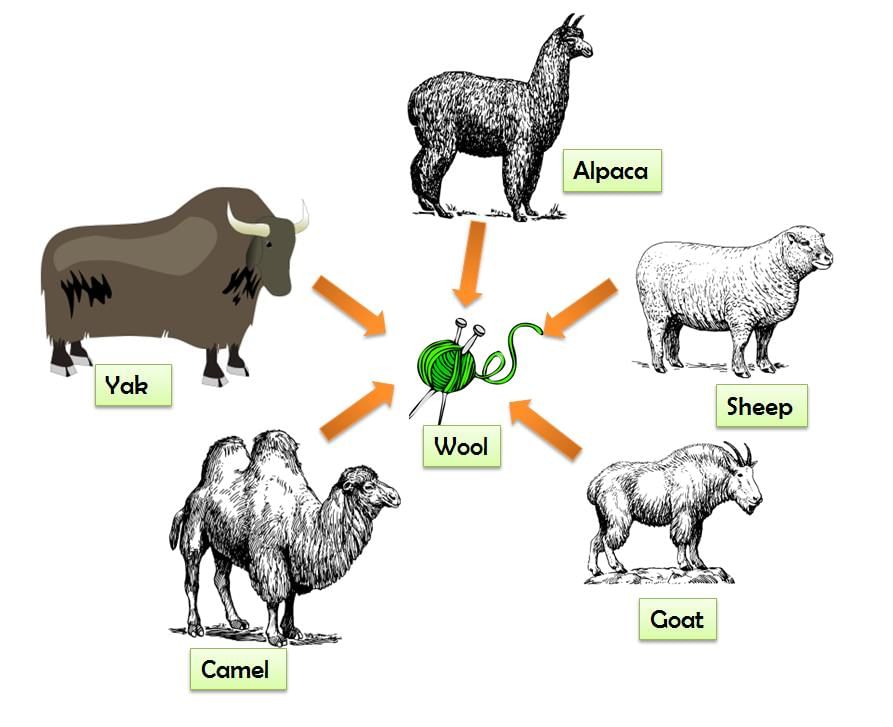 Sources of wool
Sources of wool
Q3: Why sheep have a thick coat of hair on their body?
Ans : The thick coat of hair on their body traps a lot of air. Air is a poor conductor of heat, thus, hair keeps sheep warm.
Q4: Define a fibre.
Ans : A fibre is a long strong thread, which is obtained from natural sources like plants or manmade sources like synthetic fibres, e.g: Rayon
Q5: Explain the two types of fibres.
Ans :
Fibres are classified into two types on the basis of their sources. Plant fibres and animal fibres and synthetic fibres.The fibres, which are obtained from plants and animals are called natural fibres e.g., jute and wool.
Animal fibres are obtained from animals, e.g., silk and wool. Those fibres which are made by the human beings are known as Man-made or Synthetic Fibres, e.g., Rayon
Q6: Why a cotton garment cannot keep us as warm in winter as a woollen sweater does?
Ans : Cotton clothes are thin and do not have spaces in their fabrics through which air can be trapped, to keep us warm thus Cotton clothes do not prevents heat coming out of our body.
Q7: Match the following:
Column I | Column II |
|
|
Ans :
Scouring ---> Cleaning sheared skin
Cocoon ---> Yields silk fibers.
Yak ---> Wool yielding animal
Mulberry leaves ---> Food of silkworm
Q8: Differentiate between natural and man - made fibres.
Ans :
Fibres are classified into two types on the basis of their sources. Plant fibres and animal fibres and synthetic fibres.The fibres, which are obtained from plants and animals are called natural fibres e.g., jute and wool.
Animal fibres are obtained from animals, e.g., silk and wool. Those fibres which are made by the human beings are known as Man-made or Synthetic Fibres, e.g., Rayon.
Q9: Explain the process of making yarn from fiber?
Ans : The process of making yarn from fiber is called spinning. In this process, fibers from a mass of cotton wool are drawn out and twisted. this brings the fibers together to from a Yarn
Q10: Which parts of the black sheep have wool?
Ans : The hairy skin called fleece have wool in black sheep.
Q11: What do you meant by the white fleece of the lamb?
Ans : White fleece means the hairy skin which is white in colour.
Q12: What is selective breeding?
Ans : Certain breeds of sheep have thick coat of hair on their body which yields good quality wool in large quantities. As these sheep are "selectively bred" with one parent being a sheep of good breed. The process of selecting parents for obtaining special characters in their offspring is known as selective breeding.
Q13: What do you mean by shearing and how it is done?
Ans : The process of removing the fleece of the sheep along with a thin layer of skin is from its body is called shearing. It is done by using shearing machine
Q14: Why shearing of wool done only in summer?
Ans : Usually shearing of wool is done only in summer as sheep do not to survive without their protective coat of hair in winter.
Q15: Why wool yelding animals have a thick coat of hair?+
Ans : A thick coat of hair helps in trapping a lot of air. As, air is a poor conductor of heat, it keep these animals warm.
Q16: Does shearing hurts the sheep?
Ans : Shearing does not hurt the sheep because the uppermost layer of the skin is dead. Also, the hair of sheep grows again just as our hair does.
Q17: What do you mean by scouring?
Ans : The sheared skin with hair is thoroughly washed in tanks to remove grease, dust and dirt. This process is known as scouring.
Q18: How do we get wool fibres from sheep?
Ans :
The processing of fibres into wool involves the following steps:
Step I: Shearing: - At first hair are removed using shearing machine
Step II: Scouring : - Hair is washed in tanks to remove grease, dust and dirt. This process is called scouring.
Step III: After scouring, sorting of hair is done on the basic of different textures
Step IV: The small fluffy fibres, called burrs, are picked out from the hair
Step V: The fibres then dyed in various colours, according to choice
Step VI: The coloured fibres are straightened, combed and rolled into yarn.
Q19: What are the main hazards of wool industry?
Ans : Workers in wool industry get infected by a bacterium, anthrax, which causes a fatal blood disease called sorter's disease.
Q20: Explain the process of obtaining silk?
Ans : For obtaining silk, moths are reared and their cocoons are collected to get silk threads. The cocoons are boiled to separate out silk fibres from cocoon. Threads obtain from the cocoon spun into silk threads, which are woven into silk cloth by weavers. The process of taking out threads from the cocoon for use as silk is called reeling the silk
Q21: Why caterpillars need to shed their skin when they grow bigger?
Ans : The caterpillars eat their own shed skin during their growing stage and have no other food option. So they need to shed their skin when they grow bigger enter the next stage of its life history called pupa.
Q22: Why caterpillars should not be collected with bare hands?
Ans : Caterpillars should not be collected with bare hands because skin of caterpillars may cause allergy.
Q23: Why does silk have different varieties?
Ans : Silk-producing moth eats up different kinds of leaves, which accounts for the different varieties of silk. Thus, tassar silk, mooga silk, kosa silk, etc., are obtained from cocoons spun by different types of moths.
Q24: Write short notes on rearing.
Ans : Rearing is raising livestock like goat, cows, sheep etc. for commercial purpose by taking them out in herds for grazing , feeding them on a mixture of pulses, corn, jowar, oil cakes (material left after taking out oil from seeds) and minerals for better growth and yield of produce like meat, milk, wool. Beside this in extreme climatic condition like winter these are also provided shelter and fed on leaves, grain and dry fodder.
Q25: Write short notes on shearing.
Ans : Shearing is the process in which fleece of the sheep along with a thin layer of skin is removed from its body. Machines similar to those used by barbers are used to shave off hair. Generally, the hair is removed during the hot weather which enables the sheep to survive without their protective coat of hair. The hair provides woollen fibres. Woollen fibres are then processed to obtain woollen yarn. Shearing does not hurt the sheep as the uppermost layer of the skin is dead.
Q26: Explain sericulture.
Ans : Sericulture is the rearing, breeding and management of silkworms for the production of raw silk. For obtaining silk, silk worm moths are reared and their cocoons are collected to get silk threads. Silk yarns come from the cocoon of the silkworm. The caterpillar hatches from a very small egg and is an eating machine. Their diet of continually eating mulberry leaves results in a semi-liquid protein called fibroin. When the silkworms start its spinning process in the cocoon, the worm's head is coated with a gummy protein called sericin. The silkworm rotates its body thousands of times extruding one continuous strand of silk the length of 12 football fields. The silk adheres to itself, forming the cocoon.
Q27: Draw a sketch showing stages in life cycle of silk moth.
Ans : For obtaining silk, moths are reared and their cocoons are collected to get silk threads. The cocoons are boiled to separate out silk fibres from cocoon. Threads obtain from the cocoon spun into silk threads, which are woven into silk cloth by weavers. The process of taking out threads from the cocoon for use as silk is called reeling the silk
Q28: What do you mean by reeling of silk?
Ans : 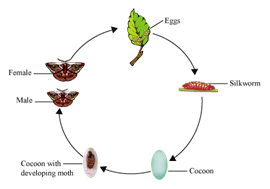
Q29: Write short notes on rearing silkworm.
Ans : Female silk moth lays hundreds of eggs at a time; these eggs are stored carefully on strips of cloth or paper and are sold to silkworm farmers. The eggs are kept in hygienic condition and under suitable temperature and humidity, then the eggs are warmed to suitable temperature and the larva is hatched from the eggs. This is done when mulberry trees bear a fresh crop of leaves. The larvae called caterpillar eat day and night and gets bigger and bigger in size, and are kept on clean bamboo trays along with freshly chopped mulberry leaves. After 25 to 30 days caterpillars stop eating and move to a tiny chamber of bamboo in the tray to spin cocoons. The caterpillar or silkworm spins the cocoon inside which silk moth is developed.
Long Q & A :
Q1: Explain the process involved in obtaining wool.
Ans :
For obtaining silk, moths are reared and their cocoons are collected to get silk threads. The cocoons are boiled to separate out silk fibres from cocoon. Threads obtain from the cocoon spun into silk threads, which are woven into silk cloth by weavers. The process of taking out threads from the cocoon for use as silk is called reeling the silk.
Sericulture is the rearing, breeding and management of silkworms for the production of raw silk. For obtaining silk, silk worm moths are reared and their cocoons are collected to get silk threads. Silk yarns come from the cocoon of the silkworm. The caterpillar hatches from a very small egg and is an eating machine. Their diet of continually eating mulberry leaves results in a semi-liquid protein called fibroin. When the silkworms start its spinning process in the cocoon, the worm's head is coated with a gummy protein called sericin. The silkworm rotates its body thousands of times extruding one continuous strand of silk the length of 12 football fields. The silk adheres to itself, forming the cocoon.
Female silk moth lays hundreds of eggs at a time; these eggs are stored carefully on strips of cloth or paper and are sold to silkworm farmers. The eggs are kept in hygienic condition and under suitable temperature and humidity, then the eggs are warmed to suitable temperature and the larva is hatched from the eggs. This is done when mulberry trees bear a fresh crop of leaves. The larvae called caterpillar eat day and night and gets bigger and bigger in size, and are kept on clean bamboo trays along with freshly chopped mulberry leaves. After 25 to 30 days caterpillars stop eating and move to a tiny chamber of bamboo in the tray to spin cocoons. The caterpillar or silkworm spins the cocoon inside which silk moth is developed.
Q2: Explain the process of obtaining silk from the silk moth.
Ans :
The processing of fibres into wool involves the following steps:
Step I: Shearing: - At first hair are removed using shearing machine
Step II: Scouring : - Hair is washed in tanks to remove grease, dust and dirt. This process is called scouring.
Step III: After scouring, sorting of hair is done on the basic of different textures
Step IV: The small fluffy fibres, called burrs, are picked out from the hair
Step V: The fibres then dyed in various colours, according to choice
Step VI: The coloured fibres are straightened, combed and rolled into yarn.
|
26 videos|32 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Question Answers - Fibre to Fabric
| 1. What is the process of making fabric from fibre? |  |
| 2. What are natural fibres? |  |
| 3. How are synthetic fibres different from natural fibres? |  |
| 4. What is the importance of fibre in the textile industry? |  |
| 5. How can I care for fabrics made from different fibres? |  |






















