Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Question Answers - Light: Shadows and Reflections
Short Question Answer:
Q1: What is the difference between luminous and non-luminous objects?
Answer: Luminous objects are those that emit their own light, such as the Sun, stars, and fireflies. Non-luminous objects do not emit light; they reflect light from luminous objects. The Moon is an example of a non-luminous object because it only reflects sunlight.
Q2: How does light travel?
Answer: Light travels in a straight line, as demonstrated by various activities where light passes through holes or is blocked by objects. This straight-line travel is known as the rectilinear propagation of light.
Q3: What happens when light passes through transparent materials?
Answer: When light passes through transparent materials, like glass or clear water, it passes almost completely through them, allowing us to see through the material clearly. Transparent materials allow most of the light to pass through without scattering.
Q4: How does the Moon produce light?
Answer: The Moon does not produce its own light. It is a non-luminous object that reflects the light of the Sun. This reflected light is what we see as moonlight. The surface of the Moon reflects sunlight, but because the surface is rough, the light is scattered.
Q5: What is lateral inversion in mirrors?
Answer: Lateral inversion refers to the reversal of left and right in an image formed by a plane mirror. When you look into a mirror, the image appears reversed, such as your left hand appearing as the right hand in the reflection.
Q6: Why do opaque objects create shadows?
Answer: Opaque objects block the path of light, and as a result, a dark area forms on the opposite side of the object. This dark area is the shadow. Since opaque objects completely block light, they create the darkest shadows.
Q7: What happens when light is reflected by a mirror?
Answer: When light strikes a mirror, it changes direction and is reflected. The angle at which light hits the mirror (angle of incidence) is equal to the angle at which it is reflected (angle of reflection). This is known as the law of reflection.
Q8: How do you form a shadow using a torch?
Answer: To form a shadow, you need a light source (like a torch), an opaque object to block the light, and a screen (like a wall or a cardboard). When the object blocks the light, the shadow forms on the screen in the shape of the object.
Q9: How does a periscope work?
Answer: A periscope allows you to see objects that are out of your direct line of sight by using two mirrors placed at 45° angles inside a box. Light entering the periscope is reflected off both mirrors, allowing you to see over obstacles or around corners.
Q10: What is the role of mirrors in forming images?
Answer: Mirrors form images by reflecting light. The image formed in a plane mirror is virtual, meaning it cannot be captured on a screen. The image is always upright, of the same size as the object, and laterally inverted (left-right reversal).
Long Question Answer
Q1: Explain how light travels and what happens when it hits different objects.
Answer: Light travels in a straight line. This is known as the rectilinear propagation of light. When light strikes different materials, it behaves in different ways:
Transparent materials, like glass and clear water, allow light to pass through them completely. This means we can see through them clearly.
Translucent materials, like tracing paper or frosted glass, let some light pass through but not all. They cause the light to scatter, so objects on the other side are not clearly visible.
Opaque materials, like cardboard or wood, block light completely. No light passes through opaque objects, which is why we can't see through them.
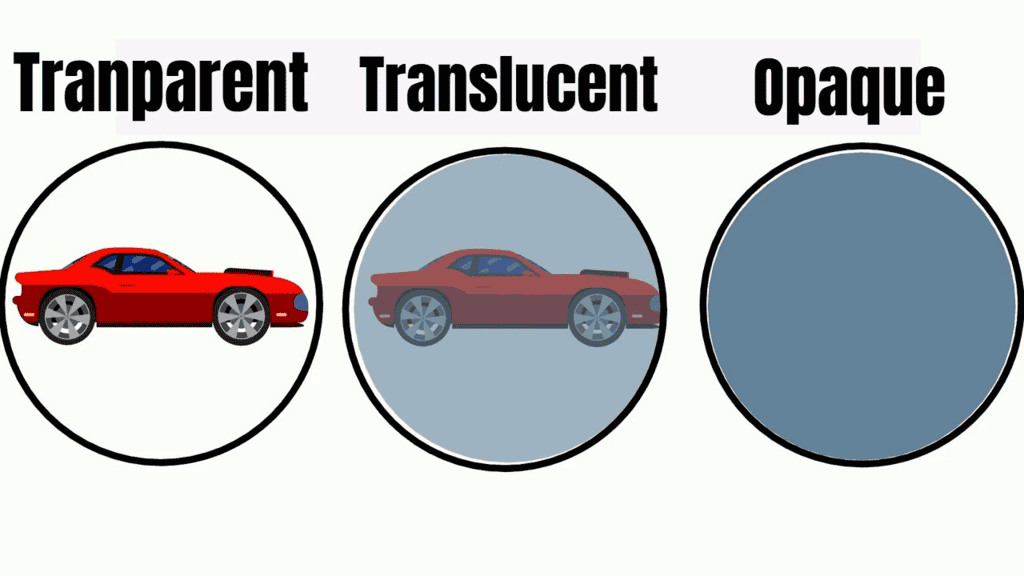 In experiments, when you place objects in the path of a torch beam, you can observe that light passes through transparent materials but either partially or completely blocks through translucent and opaque materials.
In experiments, when you place objects in the path of a torch beam, you can observe that light passes through transparent materials but either partially or completely blocks through translucent and opaque materials.
Q2: Describe the process of shadow formation.
Answer: Shadows are formed when an object blocks the path of light. Since light travels in a straight line, when it hits an opaque object, the area behind the object will not receive light. This creates a shadow. The size, shape, and sharpness of the shadow depend on the position of the object, the light source, and the screen where the shadow is cast.
Opaque objects create darker shadows because they block most or all of the light.
Translucent objects create lighter shadows because some light passes through them.
Even transparent objects, like clear plastic, can create faint shadows, as they only slightly allow light to pass through.
When you move the object closer to the light source, the shadow becomes larger. If you move the object further away, the shadow becomes smaller. The position of the object also affects the sharpness of the shadow—closer objects create sharp shadows, while distant objects create blurry ones.
Q3: How do mirrors reflect light?
Answer: Mirrors reflect light by changing the direction of the light that falls on them. When light hits a mirror, it bounces off the surface. This reflection allows us to see an image of objects placed in front of the mirror. The reflection follows a law called the law of reflection, which states that the angle at which the light hits the mirror (angle of incidence) is equal to the angle at which it reflects off (angle of reflection).
In experiments with mirrors:
If you direct light onto a flat, shiny surface (like a mirror), it will reflect in a straight line to another surface or wall.
If the mirror is tilted, the direction of the reflected light will change, but the angle of incidence will always equal the angle of reflection.

The images formed in a plane mirror are:
Erect (not upside down),
Same size as the object,
Laterally inverted (left and right are reversed),
Cannot be projected on a screen because they are virtual.
Q4: Explain how the Moon reflects light.
Answer: The Moon does not produce its own light. It is a non-luminous object, which means it doesn’t emit light. Instead, the Moon reflects the light of the Sun that falls on its surface. This reflected light is what we see as moonlight.
The Moon's surface is rough and uneven, so the light it reflects is scattered. This is why moonlight is not as bright as sunlight. During the day, we can’t see the moon's light because the sunlight is much brighter. But at night, when the Sun’s light is not in the sky, the moon’s reflection becomes visible to us.
This phenomenon of reflection is similar to how mirrors work. The only difference is that the Moon’s surface reflects light unevenly due to its craters and rough texture, which is why the moonlight we see is softer and more diffused than sunlight.
Q5: How can we create a periscope and how does it work?
Answer: A periscope is a simple device that allows you to see things that are hidden from direct view. It works by using two mirrors arranged at an angle to each other. Here's how to make a simple periscope:
Take a rectangular box and cut two holes on opposite sides.
Place two plane mirrors inside the box at an angle of 45° to each other.
Through one hole, you can look into the periscope, and through the other hole, you can see the image reflected by the mirrors.
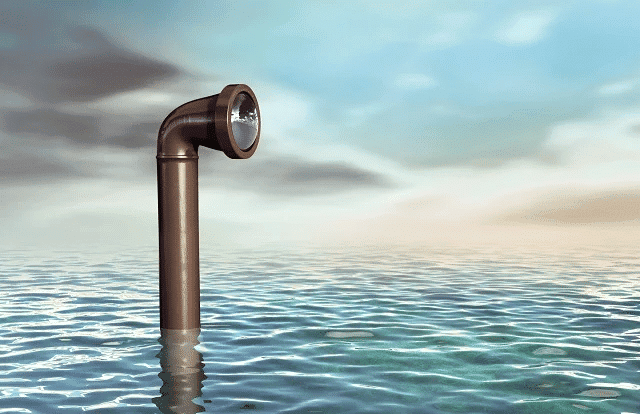

When light enters through the first hole, it strikes the first mirror and is reflected onto the second mirror. The second mirror then reflects the light to the second hole, allowing you to see objects that are outside the direct line of sight.
Periscopes are often used in submarines, tanks, or by soldiers to observe the surroundings without exposing themselves. They are useful for seeing over obstacles or around corners.
|
80 videos|224 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Question Answers - Light: Shadows and Reflections
| 1. What is the difference between shadows and reflections? |  |
| 2. How are shadows formed? |  |
| 3. Can shadows change size? If so, how? |  |
| 4. What materials can create reflections? |  |
| 5. How do we see a reflection? |  |





















