Wastewater story Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 13
What is Wastewater?
The water which gets contaminated after various works; like washing, bathing, mopping, etc. is called wastewater. Wastewater includes all effluent from homes, hospitals, business organizations and institutions, industries, and so on.
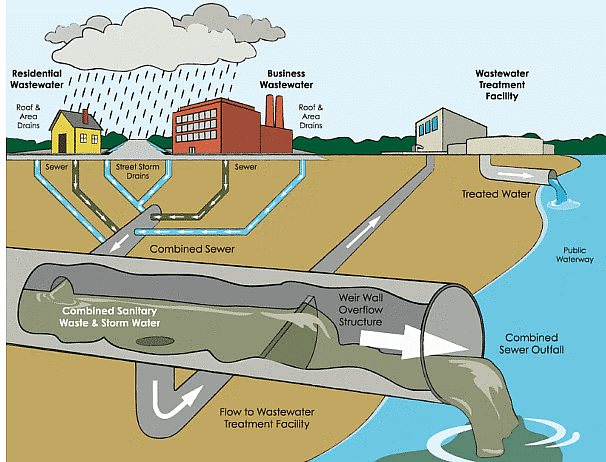 Wastewater
Wastewater
World Water Day: 22nd March
International Decade for Action on Water for Life: 2005 – 2015. It was declared by the General Assembly of the United Nations. Its main goal was to reduce the number of people who do not have access to safe drinking water, by half.
Sewage Treatment: The process of removing impurities from waste water before it can be reused or sent to the water bodies is called sewage treatment or cleaning of water.
Sewage: The liquid waste which has water as its largest component; along with various types of impurities; is called sewage.
Sewers: The pipes which carry wastewater.
Sewerage: The network of sewers.
Manhole: These are the holes made in sewers at frequent intervals, so that timely inspections and cleaning of sewers can be done through them. The manhole is covered with a hard lid so that people and traffic can easily move over it.
Wastewater Treatment Plant

Wastewater treatment is a process used to remove contaminants and make the water usable.
The sewage treatment involves physical, chemical and biological processes to remove impurities from the wastewater :-
1. Physical Processes:
- Filtration: The wastewater is passed through bar screen. Large objects; like rags, sticks, plastic bags, cans, etc. are removed in this process.
- Grit and Sand Removal: The wastewater is slowly passed through the sedimentation tank. Grit, sand and pebbles settle down at the bottom.
- Sedimentation: Water is sent to the sedimentation tank. Solids; like faeces settle at the bottom. Floatable impurities; like oil and grease float on the surface. A scraper removes the faeces from the water. The impurity thus collected is called sludge; which is sent to the sludge tank. The sludge can be used to produce biogas or to produce manure. A skimmer removes the floatable impurities. Now, the water is called clarified water.
2. Biological Process
- Aeration: Air is pumped into clarified water so that bacteria can proliferate. Bacteria consume the human waste. It leaves food waste, soap and other unwanted materials in the water. The microbes settle down at the bottom after several hours. Water is then removed from the top. This water is fit for irrigation and can be used for that purpose.
3. Chemical Process
- Chlorination: Water purified through aeration is not fit for human consumption. It needs to be treated with chlorine. For this, bleaching powder is added to the water. The chlorine kills whatever germs may be left in the water. After chlorination, the water is fit for drinking.
Maintaining Sanitation
Better Housekeeping Practices to Maintain Sanitation:
- Do not throw cooking oil and fat in the drain. This can block the drain. The fat and oil clogs the pores in the soil; in open drains. This reduces the filtering capacity of soil.
- Do not throw chemicals; like paint, insecticides, medicines, etc. into the drain. They kill the bacteria which otherwise help in cleaning the water.
- Do not throw used tea leaves, solid food, soft toys or napkins in the drain. They can clog the drain and do not allow oxygen to enter the sewage water. Oxygen is important for the natural process of decomposition.
Sanitation and Disease
Maintaining overall cleanliness in the home and in surroundings is called sanitation. Sanitation is important for the health of a person and that of the community.
- Many people have the habit of defecating in the open. Uncovered human excreta attract flies and other insects. These insects carry the germs of many dangerous diseases; like cholera, typhoid and jaundice. With constant public awareness campaign, the practice of open defecation can be stopped.
- Poor sanitary condition also contaminated the groundwater because contaminants percolate down the ground.
- Stagnant water is a perfect breeding ground for mosquitoes. Mosquitoes are the carriers of several diseases; like malaria, dengue, chikungunya and filaria.
Alternative Arrangements for Sewage Disposal
In the absence of a sewerage system, arrangements for onsite sewage disposal can be made. For example; septic tanks are built in which human excreta are collected. In due course of time, the human excreta get decomposed into compost.
- Composting pits can be made to dump waste and to make manure from them. Sewage can be collected into biogas plants to produce useful biogas.
- Chemical toilets are new discoveries. They do not require much water for the disposal of human excreta and are environment friendly. Such toilets are ideal for the trains.
Sanitation at Public Places
 Avoid littering 1. Use trash bins: Always dispose of waste in the designated bins to keep the area clean.
Avoid littering 1. Use trash bins: Always dispose of waste in the designated bins to keep the area clean.
2. Wash Hands Regularly: Use soap and water especially after using restrooms or touching shared surfaces.
3. Avoid littering: Never throw garbage on the ground; keep the environment clean.
4. Report unclean areas: Inform authorities or maintenance staff about any unhygienic spots.
5. Use Toilets Properly: Ensure that you flush toilets after use and keep restroom areas tidy.
6. Respect Public Property: Avoid vandalizing public amenities, which helps in maintaining cleanliness and order.
Practice Questions:
Q1. What is sewer?
Answer: The pipe which carries the wastewater is called sewer.
Q2. What is sewerage?
Answer: The network of sewers is called sewerage.
Q3. Which process during the wastewater treatment results in proliferation of bacteria?
Answer: Aeration
Q4. Which process during the wastewater treatment kills the germs?
Answer: Chlorination
|
112 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Wastewater story Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 13
| 1. What is wastewater and why is it a concern? |  |
| 2. How is wastewater treated before being released back into the environment? |  |
| 3. What are some common pollutants found in wastewater? |  |
| 4. What are the potential risks associated with untreated wastewater? |  |
| 5. How can individuals help reduce the impact of wastewater pollution? |  |






















