Class 12 Geography Short Questions with Answers - Transport and Communication
Q. 1. Define the term ‘Transport Network’.
Ans. Several places (nodes) joined together by a sense of routes (links) to form a pattern which permits vehicular movement or flow of some commodity is called transport network.
Q. 2. What is the meaning of ‘transport’?
OR
Define the term ‘transport’.
Ans. Transport is a service or facility for carrying persons and goods from one place to the other using humans, animals and different kinds of vehicles.
Q. 3. On what factors does the navigability of inland waterways depend?
Ans. The navigability of inland waterways depends on the width by stabilizing the river banks and increasing depth by regular dredging. Building dams and barrages also regulates the flow of water.
Q. 4. Name the western terminal station of Trans Canadian Railway.
Ans. Vancouver.
Q. 5. Name any one major seaport of Africa.
Ans. Cape town/ Durban/ Mombasa/ Suez.
Q. 6. Name any one international airport of Australia.
Ans. Perth/ Sydney/ Darwin.
Q. 7. Explain any two characteristics of the Volga Inland Waterway.
Ans. The Volga inland waterway:
(i) It connects various industrial regions of Russia.
(ii) It connects various navigable canals.
Q. 8. Mention one reason for the least development in rail facilities in West Asia.
Ans. Reasons for least development in rail facilities in West Asia are:
(i) Vast desert area
(ii) Sparsely populated region (Any one point to be mentioned)
Q. 9. Name the navigational canal that serves as a gateway of commerce for both the continents of Asia and Europe.
Ans. Suez Canal.
Q. 10. Name the terminal stations of the Trans-Siberian Railway.
Ans. It extends from St. Petersburg in European Russia to Vladivostok in Asian Russia.
Q. 11. How is the importance of a seaport judged?
Ans. The significance of a seaport is measured by the number of ships handled and how much cargo it receives.
Q. 12. In which country are motorways called ‘autobahns’?
Ans. Germany
Q. 13. Mention the two principal modes of land transportation.
Ans. The two principal mode of land transport are railways and road transport.
Q. 14. Differentiate between a node and a link.
Ans. Difference between a node and a link: A node is the meeting point of two or more routes. A link is a road that joins two nodes.
Q. 15. Mention the two principal modes of transportation other than land transportation.
Ans. Waterways and pipelines.
Q. 16. Name two terminals of the Orient Express.
Ans. Paris and Istanbul.
Q. 17. Which material is transported by the ‘Big Inch’ pipeline?
Ans. Petroleum oil and natural gas.
Q. 18. Name the two regions of the world having very dense network of airways.
Ans. North Eastern America and Western Europe.
Q. 19. Name the most important inland waterway of Germany.
Ans. The Rhine Waterways.
Q. 20. Name the seaports on each end of the Suez Canal.
Ans. (i) Port Said on its North.
(ii) Port Suez on its South.
Q. 21. Which is the busiest sea route in the world?
Ans. Northern Atlantic Sea route.
Q. 22. Name the famous petroleum pipeline which connects the oil wells in the Gulf of Mexico to the North Eastern states in USA.
Ans. Big Inch.
Q. 23. Name the most important rail route of Russia.
Ans. Trans-Siberian Railway line.
Q. 24. State any two advantages of air transport in the international trade.
Ans. Two advantages of air transport in the international trade:
(i) Air transport is the fastest means of transport.
(ii) Valuable cargo can be moved rapidly on a worldwide scale.
(iii) It has brought connectivity revolution even reaching inaccessible areas.
(iv) Highly suitable for handling perishable goods over long distances.
Q. 25. Name the important inland waterway that passes through Germany and the Netherlands.
Ans. The Rhine waterway passes through Germany and the Netherlands.
Q. 26. Name the ‘Highway ’ which connects the South American countries with Canada.
Ans. The Pan-American Highway connects the South American countries with Canada.
Q. 27. Name the terminal stations of the Australian TransContinental Railway.
Ans. Perth and Sydney.
Q. 28. Define the term ‘Trans-Continental Railway ’.
Ans. It is a contiguous network of railroad trackage that crosses a continental landmass with terminals at different oceans or continental borders.
Q. 29. Mention any three features of the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Seaway.
Ans. Features of the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Seaway:
(i) The Great Lakes of North America–Superior, Huron, Erie, Ontario are connected by 500 Canal and Well land Canal to form an inland waterway.
(ii) The estuary of St. Lawrence River, along with the Great Lakes forms a unique commercial waterway in the northern part of North America.
(iii) The ports on this route are well equipped with all facilities of ocean ports.
Q. 30. How does the ‘Suez Canal’ serve as a gateway of commerce for both the eastern and western worlds? Explain with suitable examples.
Ans. Suez Canal Characteristics:
(i) It connects Mediterranean Sea with Red Sea.
(ii) It gives Europe a new gateway to the Indian Ocean.
(iii) It reduces distance between Liverpool and Colombo.
(iv) It is sea level canal without locks.
(v) As the tolls are heavy, some find it cheaper to go by the longer Cape Route whenever the consequent delay is not important.
Q. 31. Explain the three major factors which affect the development of inland waterways in the world.
OR
List the factors which affect the inland water transport.
Ans. The development of inland waterways is dependent on the following factors:
(i) Navigability, width and depth of the channel
(ii) Continuity in the water flow
(iii) Transport technology in use
Q. 32. Name the canal that connects the Atlantic Ocean in the East to the Pacific Ocean in the West. Write any four characteristics.
Ans. Panama Canal 1 Features of the Panama Canal:
(i) It connects Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
(ii) Constructed across Panama Isthmus between Panama City and Colon.
(iii) It involves deep cutting.
(iv) It has six locks system.
(v) It shortened the distance between the East and the West Coast of USA.
(vi) It has also given a boost to the economy of Latin America.
Q. 33. Why is road transport considered better than rail transport?
Ans. Road transport is considered better than rail transport because:
(i) Construction and maintenance is cheaper than railways.
(ii) Road transport provides door to door services.
(iii) Roads can be constructed over undulating terrain.
Q. 34. Describe any three advantages of pipelines as a means of transport in the world.
Ans. Advantages of pipelines as a means of transport in world are:
(i) It is safe and reliable mode of transport system.
(ii) It is an economical and dependable mode of transport system particularly to the sensitive and strategic areas.
(iii) It provides a long term infrastructural option.
Q. 35. Study the map given below and answer the questions that follow: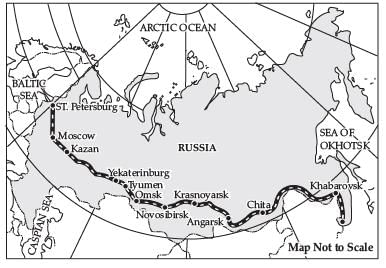
1. Identify and name the railway line shown on the map.
2. Name the continents linked by this rail route.
3. Explain how this railway line is helpful for the promotion of trade in this region.
Ans. 1. Trans-Siberian railway
2. It connects Asian countries with European countries.
3. It helps Asian region to market their products in European region.
Q. 36. Study the map given below and answer the questions that follow: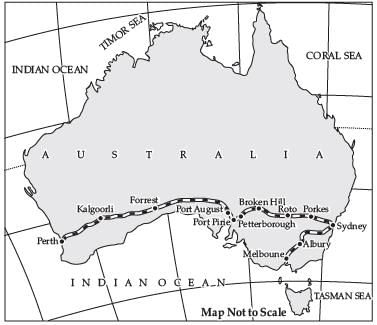
1. Name the railway line shown in the given map.
2. Which are the terminal stations of this railway line?
3. Name the ports located on the coast of Spencer Gulf through which this railway line passes
Ans. 1 Australian Trans-Continental Railway.
2 Perth and Sydney.
3 Port Augusta and Port Pirie.
Q. 37. Mention the famous oil pipeline of the USA. How are pipelines one of the most convenient modes of transport? Explain any four points.
Ans. Big Inch is the famous pipeline of the USA which carries petroleum from the oil wells of the Gulf of Mexico to the North-eastern States. Pipelines are considered as one of the most convenient modes of transport due to the following benefits by them:
(i) Large volume transportation, for example 60 million litres per day.
(ii) Excellent safety with fewer than two incidents per 10,000 kilometres of pipeline per year.
(iii) Secure supply, unaffected by weather conditions.
(iv) Cost efficiency for medium and long haul transportation, with no need for handling operations.
Q. 38. What are the problems of road transport in mountainous, desert and flood prone regions?
Ans. The problems of road transport in mountainous, desert and flood prone regions are: (i) High cost of construction of roads: Due to shortage of funds and poor terrains it becomes difficult to construct and maintain roads in mountain and desert regions. In flood prone regions there are high chances of the roads getting washed out.
(ii) High rate of accidents: Due to uneven terrain, the safety level is very low due to which the rate of road accidents is high in mountainous and desert areas.
(iii) Limited land area: In mountainous regions, desert areas and flood prone regions there is very limited space left for the construction of proper and safe roads.
Q. 39. Which are the major regions of the world having a dense network of airways?
Ans. Dense network of airways exists in Eastern USA, Western Europe and Southeast Asia. USA alone accounts for 60 per cent of the airways of the world. New York, London, Paris, Amsterdam, Frankfurt, Rome, Moscow, Karachi, New Delhi, Mumbai, Bangkok, Singapore, Tokyo, San Francisco, Los Angeles and Chicago are the nodal points where routes converge or radiate to all the continents.
Q. 40. Describe any three major problems of road transport in the world.
Ans. Major problems of road transport in the world are:
(i) Roads are unusable during the time of natural calamity and bad weather conditions.
(ii) Road network cannot cope with the demands of traffic as a result congestion occurs.
(iii) Road construction requires heavy investment in construction and maintenance.
(iv) Any other relevant point.
Q. 41. What is ‘satellite communication’?
Ans. Communication via satellite is known as satellite communication. We know that satellites are means of transferring information between the sender and receiver. In this process, the signal which is basically beam of modulated microwaves is sent towards the satellite.
Q. 42. On the basis of configuration and purpose, compare the two satellite systems in India.
Ans. I ndian National Satellite System (INSAT) and Indian Remote Sensing Satellite System (IRS)
Q. 43. What is the meaning of ‘Cyberspace’?
Ans. Cyberspace refers to the virtual computer world and more specifically, is an electronic medium used to form a global computer network to facilitate online communication.
Q. 44. Why were all forms of transport referred to as lines of communication?
Ans. All forms of transport were referred to as lines of communication as they both are complimentary to each other.
Q. 45. Discuss how the various most important means of communication have evolved over the years.
Ans. Human beings have used different methods of longdistance communications of which the telegraph and the telephone were important.
The telegraph was instrumental in the colonisation of the American West.
The telephone also became a critical factor in the urbanisation of America. Today there is a phenomenal pace of development. The first major breakthrough is the use of optic fibre cables (OFC).
With the digitisation of information in the 1990s, telecommunication slowly merged with computers to form integrated networks termed as Internet.
Communication through satellites emerged as a new area in communication technology since the 1970s after USA and former USSR pioneered space research.
Cyberspace is the world of electronic computerised space. It is encompassed by the internet such as the World Wide Web (www).
It is also referred to as the internet. Cyberspace exists everywhere. It may be in an office, sailing boat, flying plane and virtually anywhere.
Q. 46. What are the modes by which cyberspace will expand the contemporary economic and social space of humans.
Ans. As billions use the internet each year, cyberspace will expand the contemporary economic and social space of humans through e-mail, e-commerce, e-learning and e-governance. Internet together with fax, television and radio will be accessible to more and more people cutting across place and time.
It is these modern communication systems more than transportation, which has made the concept of global village a reality.
Q. 47. What is satellite communication? How has it brought revolutionary changes in the field of communication in the world? Explain.
Ans. A communication satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Communication satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. Revolutionary changes in the field of communication in the world:
(i) Making mobile communication available everywhere.
(ii) Connecting people that have never been connected.
(iii) It helps to spread messages from one place to another very quickly.
(iv) The whole world has become one global village.
|
50 videos|273 docs|37 tests
|
FAQs on Class 12 Geography Short Questions with Answers - Transport and Communication
| 1. What are the different modes of transportation? |  |
| 2. How does communication contribute to the development of society? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of using public transportation? |  |
| 4. How has technology transformed transportation and communication? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges faced in the transportation and communication sector? |  |

















