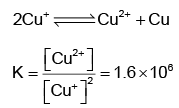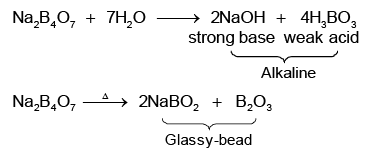Single Correct MCQs: Analytical Chemistry | Question Bank for JEE Main & Advanced (350+ Tests) PDF Download
Q.1. The product of reaction of an aq. solution of Bi3+ salt with sodium thiosulphate gives
(a) Bi2S3
(b) Na3[Bi(S2O3)3]
(c) Na[Bi(S2O3)2]
(d) [Bi2(S2O3)2]Cl2
Correct Answer is option (a)
3Na2S2O3 + BiCl3 = Na3[Bi(S2O3)3] + 3NaCl
Bi2(S2O3)3 + 3H2O = Bi2S3 + 3H2SO4
Q.2. Borax bead test is not given by
(a) an aluminium salt
(b) a cobalt salt
(c) a copper salt
(d) a nickel salt
Correct Answer is option (a)
As only coloured salts gives coloured bead hence B, C D can not be right answers.
Q.3. The ion that cannot be precipitated by both HCl and H2S is
(a) Pb2+
(b) Cu+
(c) Ag+
(d) Sn2+
Correct Answer is option (b)
Cu+disproportionates in the aqueous solution to a very large extent.
Thus, the concentration of Cu+ ion is very small and hence it cannot be precipitated.
Q.4. Aqueous solution of a salt (Y) is alkaline to litmus. On strong heating, it swells-up to give a glassy material. When conc. H2SO4 is added to a hot concentrated solution of (Y), white crystals of a weak acid separates out. Hence, the compound (Y) is
(a) Na2SO4.10H2O
(b) Ca2B6O11.10H2O
(c) Na2B6O11
(d) Na2B4O7.10H2O
Correct Answer is option (d)
(Y) is borax Na2B4O7.10H2O
Na2B4O7 + H2SO4 + 5H2O → Na2SO4 + 4H3BO3
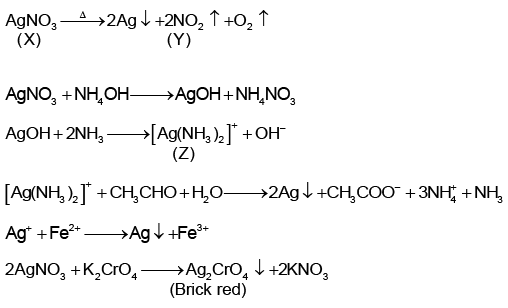
Q.5. A colourless salt (X) is soluble in water and also in alcohols and amines. On strong heating, (X) gives a brown gas (Y) and a grey residue. (X) dissolves in ammonia to give a solution (Z) which gives silver mirror with aldehydes. A solution of (X) is easily reduced by iron (II) sulphate. A solution of (X) also gives a brick red precipitate with potassium dichromate solution. Hence, choose the correct alternative.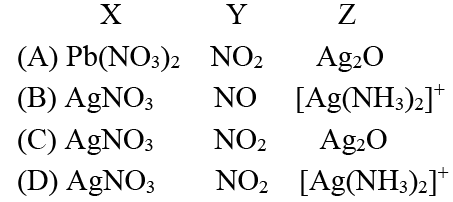
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) d
Correct Answer is option (d)
Hence, D.
Q.6. Which of the following is prepared by heating its hydrated salt?
(a) Anhyd. AlCl3
(b) Anhyd.SnCl2
(c) Anhyd. SnCl4
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is option (d)
All these hydrated salts on heating gets hydrolysed and hence anhydrous salt cannot be prepared by simply heating the hydrated salts.
Q.7. H2SO4 is added while preparing a standard solution of Mohr’ salt to prevent
(a) hydration
(b) reduction
(c) hydrolysis
(d) complex formation
Correct Answer is option (c)
FeSO4 + 2H2O → Fe(OH)2 + H2SO4 Addition of H2SO4 to this solution reverses the hydrolysis of FeSO4.
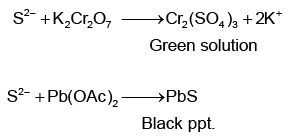
Q.8. Tests on an aqueous solution of sodium salt having an anion Xn– gives the following results.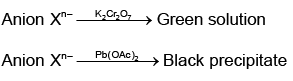
Which of the following could be Xn–?
(a) I–
(b) 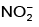
(c) S2–
(d) 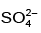
Correct Answer is option (c)
Q.9. When KNO2 is added to Co++ salt in acetic acid medium, yellow ppt is formed. It is due to
(a) K4 [CO(NO2)6]
(b) K3 [CO(NO2)6]
(c) KCO[CO(NO2)6]
(d) None
Correct Answer is option (b)
Na2CrO4 + H2SO4 → Na2Cr2O7
Q.10. Which of the following salt will not produce black ppt. on passing H2S through their aqueous salt solutions in desired medium?
(a) CuSO4
(b) PbCl2
(c) CdSO4
(d) NiCl2
Correct Answer is option (b)
Since, CdS is a yellow solid.