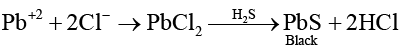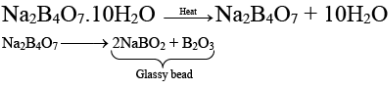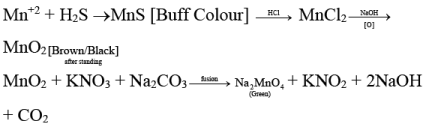Single Correct MCQs: Purification and Characteristics of Organic Compounds | Question Bank for JEE Main & Advanced (350+ Tests) PDF Download
Q.1. In a solution containing Cu2+ and Cd2+, dil. H2SO4 is added followed by iron filings. The solution is warmed and NH4OH is added to reduce the acidity followed by passing of H2S gas. The ppt. obtained will be
(a) CuS
(b) CdS
(c) Both Cu metal and CdS
(d) None of these
Correct Answer is option (c)
Cu+2 ion from solution is removed completely by precipitation with iron filing because iron is more electropositive than copper (Cu+2 + Fe → Fe+2 + Cu). On passing H2S, a yellow ppt. of CdS is obtained. Thus the precipitate contain both Cu metal and CdS.
Q.2. An aqueous solution of a substance gives a white precipitate on treatment with dilute hydrochloric acid, which dissolves on heating. When hydrogen sulphide is passed through the hot acidic solution, a black precipitate is obtained. The substance is a
(a) Hg22+ salt
(b) Cu2+ salt
(c) Ag + salt
(d) Pb2+ salt
Correct Answer is option (d)
Q.3. A glassy bead formed by heating borax on a platinum wire loop is
(a) sodium tetraborate
(b) sodium metaborate
(c) sodium metaborate and boric anhydride
(d) sodium tetraborate and boric anhydride
Correct Answer is option (c)
Q.4. Which of the following element forms dark green coloured salts?
(a) Chromium
(b) Zinc
(c) Barium
(d) Cobalt
Correct Answer is option (a)
Trivalent chromium salts in general have dark green colour.
Q.5. In the second group of qualitative analysis, H2S is passed through a solution acidified with dil. HCl in order to
(a) increase the solubility of H2S.
(b) limit the concentration of S2– ions.
(c) increase the concentration of S2– ions.
(d) make the medium acidic.
Correct Answer is option (b)
HCl suppresses the ionization of H2S and thus, limits the concentration of S2– ions.
Q.6. In the following sequence of reaction, identify the compound (C).
Na2SO4  (A) (white ppt.)
(A) (white ppt.)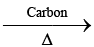 (B)
(B)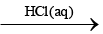 (C) gas
(C) gas
(a) H2S
(b) Cl2
(c) H2
(d) CO2
Correct Answer is option (a)
Q.7. Ammonium salt gives brown colour with alkaline solution of Nessler’s reagent to form iodide of Millon’s base. The formula of this compound is
(a) NH2—Hg—O—Hg—I
(b) NH2—O—Hg—HgI
(c) K2HgI4
(d) NH2—Hg—I
Correct Answer is option (a)
NH3 + 3NaOH + 2K2HgI4 → H2N–Hg–O–HgI + 4KI + 2H2O + 3NaI
Q.8. A coloured ppt. is obtained when H2S gas is passed through an aqueous solution of salt in presence of ammonium hydroxide. The ppt. dissolves in dil. HCl and reacts with NaOH to give white ppt. which on standing turns into brown/black mass. The brown/black mass on fusion with KNO3 and Na2CO3 gives green mass. The cation of the salt is
(a) Co2+
(b) Mg2+
(c) Ni2+
(d) Mn2+
Correct Answer is option (d)
Q.9. The compound (X) on heating gives a colourless gas. The residue is dissolved in water to obtain (Y). Excess CO2 is bubbled through aqueous solution of (Y), (Z) is formed. (Z) on gentle heating gives back (X). The compound (X) is:
(a) CaCO3
(b) Na2CO3
(c) CaSO4.2H2O
(d) K2CO3
Correct Answer is option (a)
It is a reason for the given fact.
Q.10. To an acidified dichromate solution, a pinch of Na2O2 is added and shaken. What is observed?
(a) Blue colour
(b) Red colour changing to green
(c) Copious evolution of oxygen
(d) Bluish-green precipitate
Correct Answer is option (a)
Blue colour is due to the formation of CrO5
Na2Cr2O7 + 4Na2O2 + 5H2SO4 → 2CrO5 + 5Na2SO4 + 5H2O.