Solutions of Carbon And Its Compounds (Page No - 265) - Chemistry Lakhmir Singh, Class 10 | Extra Documents, Videos & Tests for Class 10 PDF Download
Question 46:
(a) When ethanoic acid reacts with sodium hydrogencarbonate, then a salt X is formed and a gas Y is evolved.
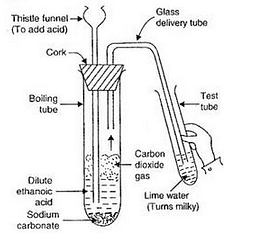
Name the salt X and gas Y. Describe an activity with the help of a labelled diagram of the apparatus used to prove that the evolved gas is the one which you have named. Also write the chemical equation of the reaction involved.
(b) Give any two uses of ethanoic acid.
Solution :
(a)Salt X is sodium ethanoate, CH3COONa; Gas Y is carbon dioxide, CO2
Activity: Take a boiling tube and put about 0.5 g of sodium carbonate in it. Add 2 ml of dilute ethanoic acid to the boiling tube (through a thistle funnel). We will observe that brisk effervescence of carbon dioxide gas is produced. Let us pass this gas through lime water taken in a test tube. We will find that lime water turns milky. Only carbon dioxide gas can turn lime water milky. So, this experiment proves that when ethanoic acid reacts with sodium carbonate, then carbon dioxide gas is evolved.
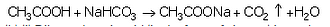
(b)(i) Dilute ethanoic acid (in the form of vinegar) is used as a food preservative in the preparation of pickles and sauces.
(ii) It is used in the manufacture of acetone and esters used in perfumes.
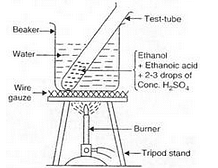
(a) Activity:
(i) Take 1 ml of pure ethanol (absolute alcohol) in a test-tube and add 1 ml of glacial ethanoic acid to it. Then add 2 or 3 drops of concentrated sulphuric acid to the mixture.
(ii) Warm the test-tube containing above reaction mixture in hot water bath (a beaker containing hot water) for about 5 minutes.
(iii) Pour the contents of the test-tube in about 50 ml of water taken in another beaker and smell it.
(iv) A sweet smell is obtained indicating the formation of an ester.
Reaction:
(c) Uses of esters:
(i) Esters are used in making artificial flavours and essences. These are used in cold drinks, ice-creams, sweets and perfumes.
(ii) Esters are used as solvents for oils, fats, gums, resins, cellulose, paints, varnishes, etc.
(iii) Pour the contents of the test-tube in about 50 ml of water taken in another beaker and smell it.
(iv) A sweet smell is obtained indicating the formation of an ester.
Reaction:

Question 48:
(a) Name the reaction which is usually used in the conversion of vegetable oils to fats. Explain the reaction
involved in detail. Write a chemical equation to illustrate your answer.
(b) What is saponification ? Write the chemical equation of the reaction involved in this process. Name all the substances which take part in this process and also those which are formed.
(c) Why does micelle formation take place when soap is added to water ? Will a micelle be formed in other solvents like ethanol also ?
Solution :
(a) Catalytic hydrogenation is usually used in conversion of vegetable oils to fats. Hydrogenation of oils: Vegetable oils are unsaturated fats having double bonds between some of their carbon atoms and can undergo addition reactions. When a vegetable oil (like groundnut oil) is heated with hydrogen in the presence of finely divided nickel as catalyst, then a saturated fat called vegetable ghee (or vanaspati ghee) is formed. This reaction is called hydrogenation of oils and it can be represented as follow.

(b) The process of making soap by the hydrolysis of FatcrCl + Scdiumhydroxlde Scep + Glycerd fats and oils with alkalis called saponification.

(c) Soap are sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids. When soap is added to the water, the hydrophilic end (acid end) will align along the surface of water and the hydrophobic tail (carbon chain) remains out of water. When a soap is dissolved in water, it forms a colloidal suspension in water in which the soap molecules cluster together to form spherical aggregates called micelles. In a soap micelle, soap molecules are arranged radially Wth hydrocarbon ends directed towards the centre and ionic ends directed ounvards.
No, micelle will not be formed in other solvents such as ethanol because hydrocarbon chains of soap molecules are soluble in organic solvents like ethanol.
Question 49:
(a) What is a soap ? Name one soap.
(b) Describe the structure of a soap molecule with the help of a diagram.
(c) Explain the cleansing action of soap. Draw diagrams to illustrate your answer.
Solution :
(a) A soap is the sodium salt (or potassium salt) of a long chain carboxylic acid (fatty acid) which has cleansing properties in water.
Example: Sodium stearate, C17H35COO–Na+
(b) A soap molecule has two parts: the long chain organic part and the ionic part containing the -COO–Na+group. It has to be remembered that this is not an ion, the atoms are all covalently bonded, the electrical charges show how the charges get polarized in the group. A soap molecule has a tadpole like structure shown below:
(c) Cleaning action of soap has been explained with the help of the image below:
Soaps are molecules in which the two ends have differing properties, one is hydrophilic, that is it dissolves in water, while the other end is hydrophobic, that is it dissolves in hydrocarbons. When soap is at the surface of water, the hydrophobic ‘tail’ of soap will not be soluble in water and the soap will align along the surface of water with the ionic end in water and the hydrocarbon ‘tail’ protruding out of water.
Inside water, these molecules have a unique orientation that keeps the hydrocarbon portion inside the water. This is achieved by forming clusters of molecules in which the hydrophobic tails are in the interior of the cluster and the ionic ends are on the surface of the cluster. This formation is called a micelle. When a dirty cloth is put in water containing dissolved soap, then soap in the form of a micelle is able to clean. The hydrocarbon ends of the soap attach to the oily dirt particles and entrap them at the centre of the micelle. the ionic ends in the micelles remain attached to water. When the dirty cloth is agitated in soap solution, the oily dirt particles entrapped by soap micelles get dispersed in water and the cloth gets cleaned.
|
5 videos|292 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Solutions of Carbon And Its Compounds (Page No - 265) - Chemistry Lakhmir Singh, Class 10 - Extra Documents, Videos & Tests for Class 10
| 1. What is the importance of carbon in compounds? |  |
| 2. How does carbon form covalent bonds with other elements? |  |
| 3. What are hydrocarbons? |  |
| 4. How do carbon compounds contribute to global warming? |  |
| 5. What are some examples of carbon compounds? |  |
|
5 videos|292 docs|59 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|

















