Geography of South America | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
South America
South America is a long triangular-shaped continent.
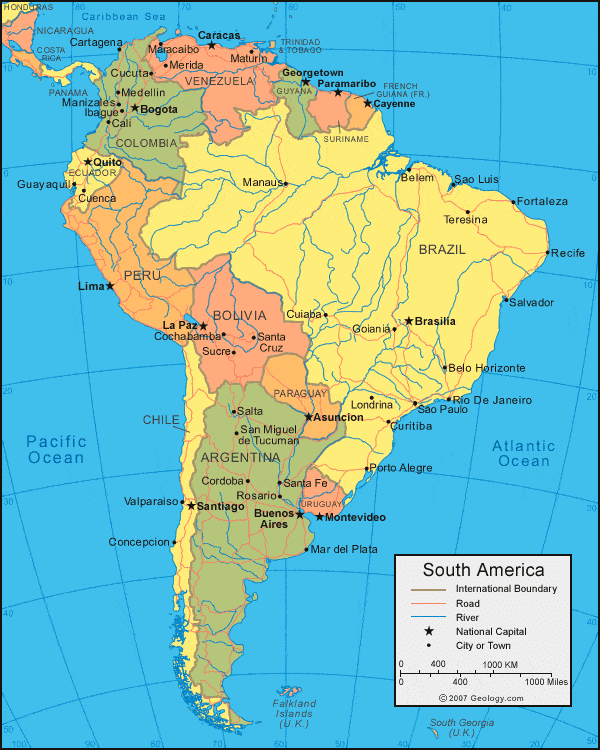
- It stretched from 12°N to 55°S latitude.
- The Equator passes through the northern part of the continent and the Tropic of Capricorn runs roughly through the middle.
- Because of its tapering shape, a major part of the landmass is in the tropics. South America lies on the west of the Prime Meridian. So the time at any place on this continent will be some hours less than or behind the Greenwich Mean Time.
- The 60° meridian divides the continent lengthwise into two halves. It is more to the east compared to North America and is, therefore, closer to Europe and Africa. South America is the fourth largest continent after Asia, Africa, and North America.
- It is two-thirds the size of Africa and six times the size of India. The coastline of South America is smooth with very few inlets except in the extreme southwest where there are fiords and many small islands.
- Fiords are deep inlets of the sea into mountains land. There are a few large islands off the coast of South America.
- The Galapagos Islands near the Equator and the Juan Fernandez Islands near Central Chile are in the Pacific Ocean.
- The Tierra del Fuego is in the Southern Ocean and the Falkland Islands in the South Atlantic Ocean. The island of Trinidad is near Venezuela in the North Atlantic Ocean.
- The Andes is the longest mountain range in the world. South America’s three southern countries – Argentina, Chile, and Uruguay – constitute a region sometimes referred to as the Southern Cone because of its pointed, ice-cream- cone-like shape.
South America includes 14 countries:
1. Argentina
2. Bolivia
3. Brazil
4. Chile
5. Colombia
6. Ecuador
7. Falkland Islands (United Kingdom) i.e. (British Overseas Territories)
8. French Guiana (France)
9. Guyana
10. Paraguay
11. Peru
12. Suriname
13. Uruguay
14. Venezuela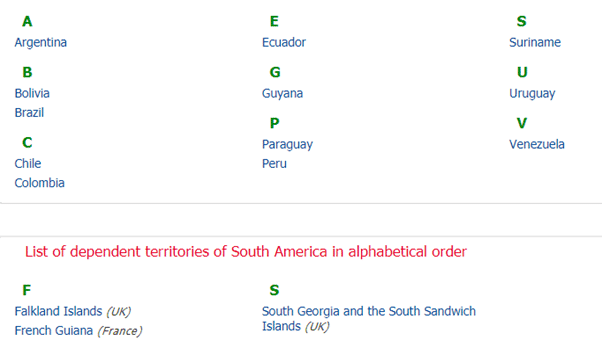
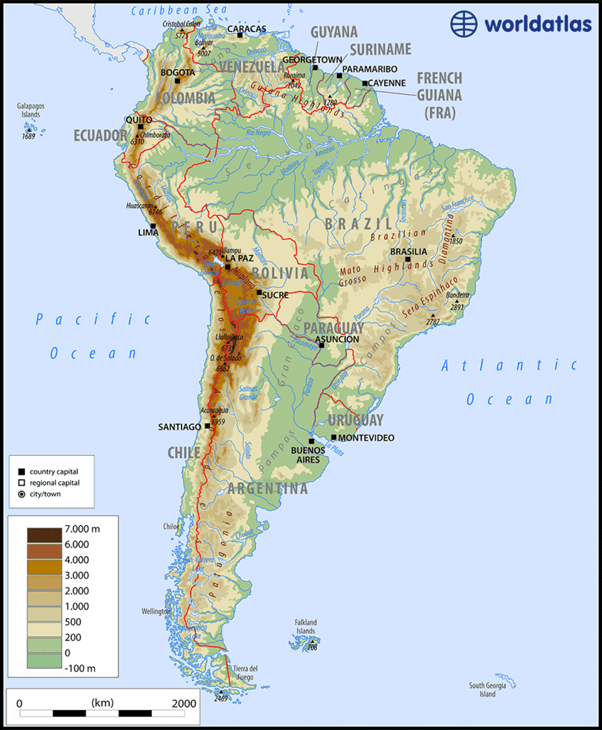
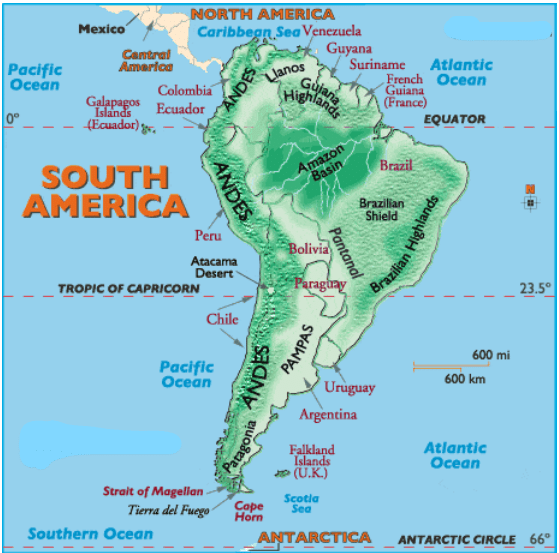
Major Physical Divisions of South America
- The Pacific coastal strip
- Mountain Ranges
- The Central Lowlands
- The Eastern Highlands
The Pacific coastal strip
- It lies in the west, between the ocean and the Andes. It is the longest coastal plain in the Atlantic world.
- In most places, it is about 80 kilometers wide but in some, it is as narrow as 8 meters. The coastline of South America is smooth and regular. At the river mouths, there are inlets that are used as harbors.
- The southwestern coast of the continent has fiords or deep inlets of the sea.
➤ Andes Mountains
- Forms the second-highest mountain systems in the world and is next to the Himalayas
- Mount Aconcagua is an extinct volcano that lies in Argentina
- Mount Ojas del Salado is the highest active volcano in the world of Argentina
- Andes Mountains – A part of seven countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Bolivia, Peru, Chile, Argentina.
Mountain Ranges
- The Andes stretches through the entire continent, running in the north-south direction from the Isthmus of Panama to the Strait of Magellan.
- They are the continuous range of folded mountain systems that cover the entire western coast of South America.
- The Andes is the longest mountain range in the world. The highest mountain of this mountain range is Aconcagua, which stands at 6,962 meters (22,841 feet) and straddles the Argentina-Chile border.
- They form a chain of ranges and knots with enclosed intermontane plateaus namely in Ecuador and Bolivia.
- Being part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, there are many volcanoes and frequent earthquakes in this region. Mount Cotopaxi and Mount Chimborazo are active volcanic peak, which is the highest peak in South America.
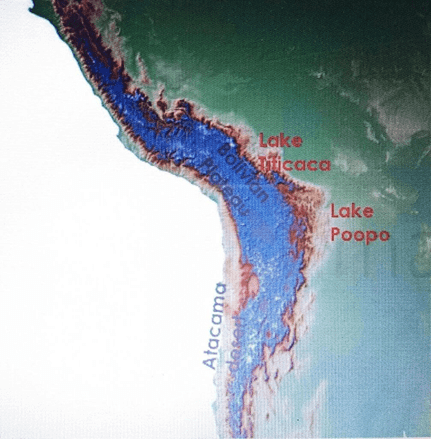 Intermontane plateau – Bolivian plateau
Intermontane plateau – Bolivian plateau
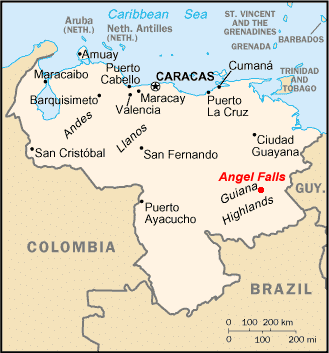
➤ Guiana Highlands
- An abundance of rain, tropical rainforest, gold, diamond, and iron ore reserve. World’s highest fall – Angel’s fall on the Caroni River.
➤ Plateau of Mato Grosso
- Ancient erosional plateau, savannah, cattle raising, gold, and diamond reserve.
➤ Plateau of Borborema
- Semi-arid, deciduous-thorny scrub
- Brazilian highlands:
- Lava plateau, Minas Garais region- iron and gold reserve.
The Central Lowlands
- They are formed by two great river systems – the Amazon- the Orinoco and the Parana-Paraguay. The vegetation of the lowlands is given special names.
- The Orinoco Basin has dense tropical forests. The northern part is a plain covered with savanna grass called the Llanos.
- The equatorial jungle of the Amazon Basin is called the selvas, a typical tropical rain forest.
- The rich temperate grasslands around the mouth of the Parana-Paraguay is the pampas.
- At the source of these rivers is a region scrub forest called the Gran Chaco.
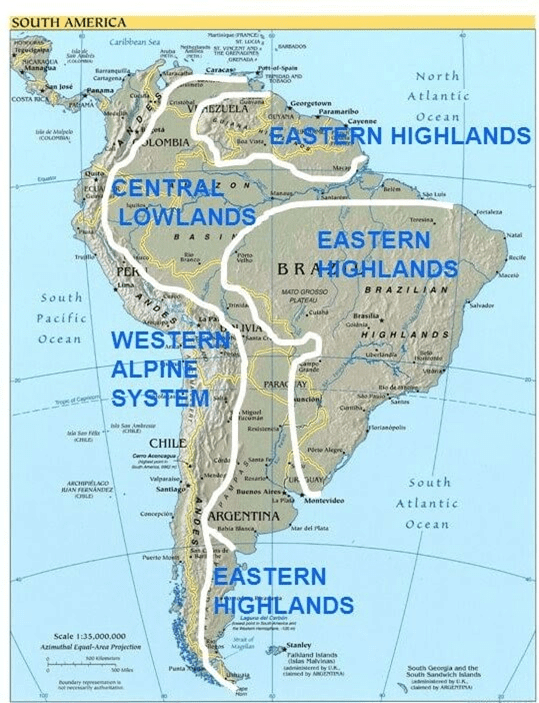
The Eastern Highlands
- These are plateaus made up of hard old rocks.
- The River Amazon separates them into the Guiana Highland to the north and the Brazilian Highland to the south.
- They have been worn down by wind, rain, and rivers. They have steep cliffs along the east coast and slope gently towards the Central Plains.
- The savanna grasslands of the Brazilian Highlands are the Campos.
- Towards the Central Lowlands, it is known as the plateau of Matogrosso.
- The Eastern highlands consists of Igneous and Metamorphic rocks.
Highlands are split into three regions:
1. Brazilian Highlands
2. Guiana Highlands
3. Patagonian Plateau
➤ Guiana Highlands
- It is a geographically stunning part of Planet Earth, over 1,000 miles in length, the Highlands stretch from southern Venezuela across the northern edge of South America to the tip of Brazil.
- It consists of a vast plateau, one marked by deep gorges, tropical rain forests, numerous rivers, and waterfalls. It’s famed for the highest waterfall in the world (Angel Falls) at 3,212 ft (979 m) high. The highest point is Mt. Roraima on the borders of Brazil, Guyana, and Venezuela at 2,810 m.
➤ Brazilian Highlands
- This highlands region is about 800 miles in length and runs through the Brazilian states of Minas Gerais, Goias, Bahia, and Sao Paulo in southeastern Brazil. The magnificent landscape includes varied mountain ranges, namely the Serra de Mantiquiera, Serra do Paranapiataba, Serra Geral, and Serra do Mar.
Patagonian Plateau
- It is located between the Andes and the Atlantic Ocean, and about 1,000 miles in length; Patagonia stretches south from the Rio Negro river in southern Argentina to Tierra del Fuego and the Strait of Magellan. It’s mostly rugged, barren land, famed for its beauty and striking scenery.
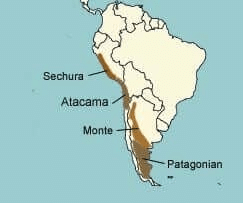
Deserts of South America
- Patagonian Desert – the largest desert by area located in Argentina
- La Guajira Desert – a desert in northern Colombia and some of northwestern Venezuela
- Atacama – a desert in Chile, the driest place on Earth.
- Sechura Desert – a desert located along a portion of the northwestern coast of South America
- Monte Desert – in Argentina, a smaller desert above the Patagonian desert.
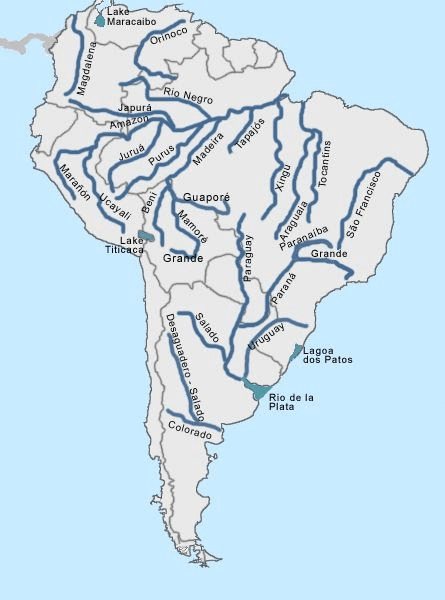
Drainage System of South America
- The Amazon Basin
- The Rio de Plata Basin
- The Orinoco Basin
- The Sao Francisco Basin
The Amazon Basin
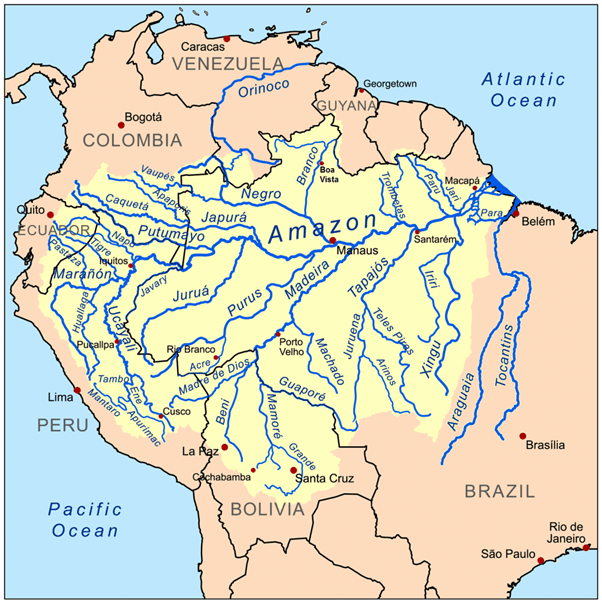
- It is the basin of River Amazon.
- Its length is second to that of the Nile river of Africa.
- It has the largest flow of water in the world.
- The river drains nearly 40 percent of the area of South America.
- The major tributaries of the Amazon river are the Caqueta, the Jurua, the Madeira, the Negro, etc.
- Equatorial rainforest
- Navigable till Manaus
- Petroleum at mouth
- Natural Rubber
- Amazon rainforest – deforestation due to cattle ranching and soya beans field.
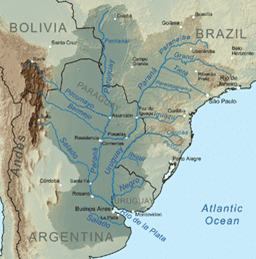
The Rio de Plata basin
- This basin is second in size to that of the Amazon.
- The main rivers which form the Basin of Rio de Plata are the river Paraguay, the Parana, and the river Uruguay.
- River Parana (4,879 km) rises from Minas Gerais from a water divide Carino.
The Orinoco basin
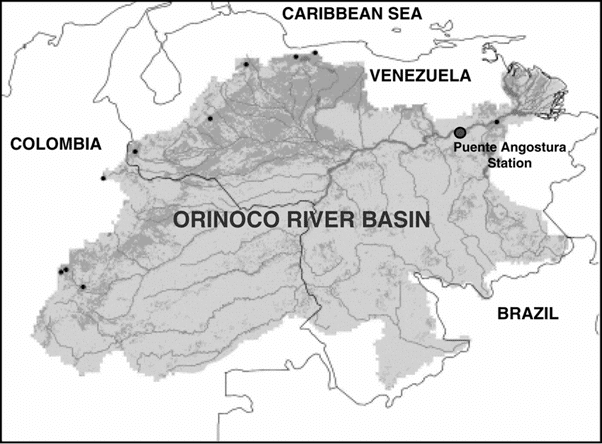
- This is considered to be the third-largest drainage system of South America.
- It rises in the Southern end of Sierra Parima near Mount Delgado Chalboud at a height of 1000 meters.
- It traverses 2,740 km to meet the Atlantic ocean.
- The word the Orinoco means ‘a place to paddle’, i.e. a river where navigation is possible.
- In the North, the Orinoco river passes through a zone called ‘Region of Rapids’ where there are enormous granite boulders.
- The world’s highest waterfall Angel (979 m) is situated on the river Churun which is a tributary of river Caroni which is further a tributary of river Orinoco.
- The Orinoco flows through the llanos (savanna grasslands) of Venezuela into the (North Atlantic Ocean).

➤ Parana river system
- From source to its junction with Paraguay – known as Alto Parana
- Numerous waterfalls in alto Parana – then navigable
- Useful for HEP, irrigation
- Wheat cultivation in the Pampas region
➤ Uruguay river system
- Joins Parana river – to form Rio de la Plata estuary
- Important for irrigation and HEP
- Not useful for navigation due to numerous rapids
The Sao Francisco basin
- The fourth-largest river system of South America is the river Sao Francisco which is about 2,914 km in length. It flows within Brazil.
- It originates North-west of the city of Belo Horizonte.
Rivers of South America
- Amazon River
- Orinoco River
- Magdalene River
- Parana-Rio de la Plata
- Tocantins-Araguaia
- Sao Francisco River
- Paraguay and Uruguay Rivers.
 |
Download the notes
Geography of South America
|
Download as PDF |
Important Lakes and Islands

 Galapagos Islands
Galapagos Islands
Pantanal Wetlands
- It is the world’s largest tropical wetland.
- It sprawls across three South American countries i.e. Bolivia, Brazil, and Paraguay, and supports millions of people there, as well as communities in the lower Rio de la Plata Basin.
- The Pantanal derives its name from the Portuguese word for ‘swamp’.
- It has the largest concentration of crocodiles in the world.
- Jaguars, the largest feline in the Americas, hunt caiman in the Pantanal, which has one of the highest density of jaguars anywhere in the world.
- The Pantanal is also home to the biggest parrot on the planet, the hyacinth macaw.
- The areas that are protected include parts that fall under an agreement called Ramsar that requires national governments to conserve and wisely use wetlands and some that are UNESCO World Heritage Sites and Biosphere Reserves.
- The Pantanal is bounded by the Chiquitano dry forests to the west and northwest, by the Arid Chaco dry forests to the southwest, and the Humid Chaco to the south.
- Less than 5% of the Pantanal is protected, with parts that fall under an Ramsar agreement, and some that are UNESCO World Heritage Sites and Biosphere Reserves.
- Around 95% of the Pantanal is under private ownership, the majority of which is used for cattle grazing.
Latin America
Reference – Britannica
- Latin America is generally understood to consist of the entire continent of South America in addition to Mexico, Central America, and the islands of the Caribbean whose inhabitants speak a Romance language.
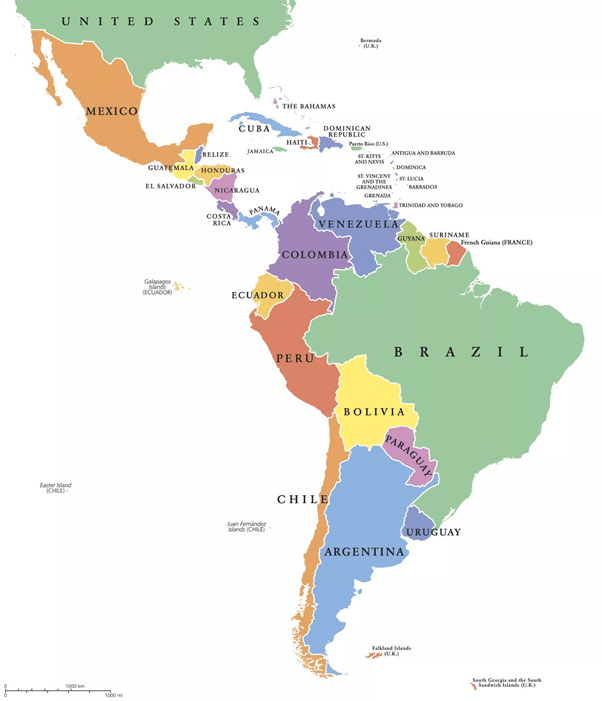
North and Central America
- Belize
- Costa Rica
- El Salvador
- Guatemala
- Honduras
- Mexico
- Nicaragua
- Panama
South America
- Argentina
- Bolivia
- Brazil
- Chile
- Colombia
- Ecuador
- French Guiana (département of France)
- Guyana
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Suriname
- Uruguay
- Venezuela
Caribbea countries
- Cuba
- Dominican Republic
- Haiti
Dependencies and constituent entities
- Guadeloupe
- Martinique
- Puerto Rico
- Saint-Barthélemy
- Saint-Martin
Lithium Triangle
Lithium Triangle is an intersection of Chile, Bolivia, and Argentina, known for high-quality salt flats.
Salar de Uyuni in Bolivia, Salar de Atacama in Chile, and Salar de Arizaro in Argentina contain over 45%of known global lithium reserves.
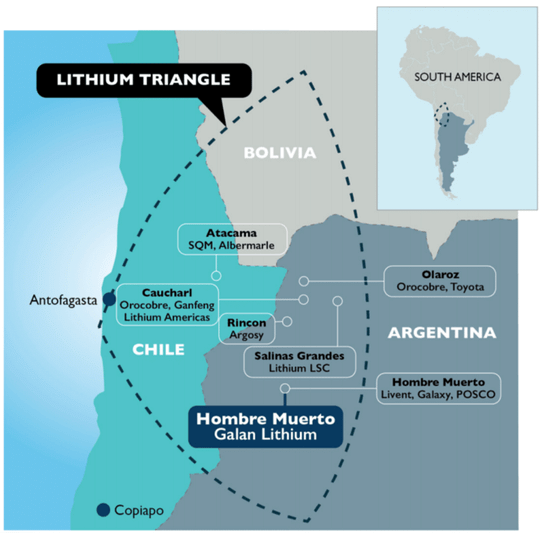
- Beneath Salar de Uyuni, the world’s largest salt flat lies the world’s greatest lithium deposits.
- Bolivia, one of South America’s poorest countries, envisions development by harvesting lithium on an industrial scale from underground saltwater brines.
- It can be mined from rock or processed from brine.
- Lithium dissolved in underground saline aquifers called “brine”, pumped to the surface by wells and then allowed to evaporate in vast knee-deep ponds.
- Demand for electric vehicles and smart devices powered by lithium-ion batteries gives an opportunity for development.
|
180 videos|485 docs|193 tests
|
FAQs on Geography of South America - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the major physical divisions of South America? |  |
| 2. What deserts are found in South America? |  |
| 3. How does the drainage system of South America work? |  |
| 4. What are some important lakes and islands in South America? |  |
| 5. What is the Pantanal Wetlands and why is it significant? |  |