Speciation, Evolution & Classification - Class 10 PDF Download
Speciation
Biological species concept: A species is a sexually interbreeding group of individuals separated from other species by the absence of genetic exchange. Members of species are capable of breeding with one another and produce living, fertile offspring but are unable to breed with members of other species normally.
Gene pool: Sum of all the genes of all the members of a species.
Speciation occurs when the gene pool of a population is some how reproductively isolated from other sister population of the parent species and gene flow no longer occurs between them. Then population splits into independent species, which becomes reproductively isolated from each other.
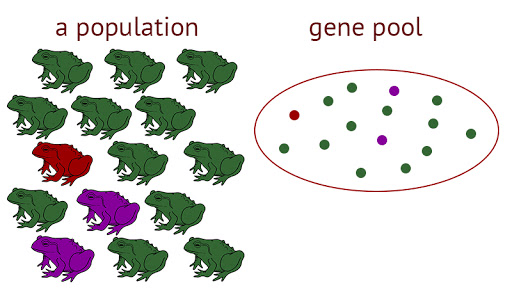 Gene Pool of a Population of FrogsOn basis of period taken in speciation, there are two types of mechanism of speciation.
Gene Pool of a Population of FrogsOn basis of period taken in speciation, there are two types of mechanism of speciation.
Speciation: The process of formation of one or more new species from an existing species is called speciation.
Let us try to understand this concept by taking the example of beetles.

ABOVE EXAMPLE OF SPECIATION SHOWS THAT:
- Large population of beetles occur on a mountain range.
- Few beetles started feeding in neighborhood.
- Gene flow continued in two places.
- They may get isolated at larger distance because of existence of river.
- Gene flow decreases and finally stops.
- Two sub populations change with time because of genetic drifts and natural selection.
- Later they became reproductively isolated.
- Two new species came up.
- This can occur as a result of change in chromosome number.
- Micro evolution is very important. This means that the changes may be small but significant. Speciation due to inbreeding, genetic drift and natural selection will be applicable to all sexually reproducing animals. Geographical isolation does not play any role in the speciation of sexually reproducing animals and self pollinating plants.
EVOLUTION AND CLASSIFICATION
Classification: Classification is the system of arrangement of organism in certain groups or subgroups on the basis of hierarchies of certain characteristics.
The characteristics are the details of appearance from structure, function and behaviour. Phylogenetic taxonomy is a branch of classification on the basis of evolutionary relationship on the basis of common ancestry.
Flow chart of basic characters shared by most of the organisms:

TRACING EVOLUTIONARY RELATIONSHIP
Studies on similarities in structure of different organisms suggests that present forms have evolved through a process of slow and gradual change called evolution. They include the following :
1. Homologous organs : Homologous organs are those structures which are different in appearance and perform different functions but have similar basic structure and developmental origin. This relationship is called homology.
FORELIMB IN VERTEBRATES:
| Seal | Bird | Bat | Horse | Man | |
| Appearance | Flippers | Wings | Patagia | Elongated | Thumb opposability |
| function | Swimming | flying | Support, flying | Running | Grasping |

2. Analogous : Those organs which have different origin and structural plan but appear similar and perform similar functions are called analogous organs. While this relationship is called convergent evolution or analogy.
eg : Wing of an insect and a bird, Hand of man & Trunk of elephant.

Analogy in these organs is due to similar adaptations to perform similar functions rather than their common ancestry.
3. Vestigial organs : Those organs which no longer have a function are called vestigial organs. These organs have reduced structurally as well as functionally. It appears that these organs were once well developed and functional in ancestors and later on due to their less use they became reduced.
eg : Vermiform appendix, ear muscles, third eyelid in man are reduced and function less.

Common ancestry and inter-relationship :
Various organisms are inter connected their resemblance suggest a common ancestry.
Eg :



Connecting links : Some living organisms have characteristics of two groups. They are known as connecting links.
Eg : Lung fish - show connection between fishes and amphibians.

Various connecting links
(i) Virus → Between living and non living
(ii) Euglena → Between plants and animals
(iii) Proterospongia → Between protozoa and porifera
(iv) Neopilina → Between annelida and mollusca
(v) Peripatus → Between annelida and arthopoda
(vi) Archaeopteryx → Between reptiles and birds
(vii) Balanoglossus→ Between non chordates and chordates
(viii) Chimera → Between cartilaginous fish and boney fish
(ix) Lung fish → Between fishes and amphibia
(x) Platypus → Between reptiles and mammals
(xi) Echidina → Between reptiles and mammals

Jurassic period is known as golden age of reptiles.
Dinosaurs of Dromaeosauridae family had feather on body and fore limb.
Huxley called birds as glorified reptiles.
Carnivorous dinosaurs called Velociraptor had a fish bone like birds.
Evidences from embryology:
A comparative study of the stages of embryonic development of animals reveals that in their early stages they were very similar.
These embryonic stages reflect ancestry. The embryological stages of an organism give us an idea about the stages of its evolution.
For example when we study the human embryo, we find that at a certain stage it has gills. This suggests that fish is one of the earliest ancestors in the evolution of mammals including human beings.
FAQs on Speciation, Evolution & Classification - Class 10
| 1. What is speciation? |  |
| 2. How does speciation occur? |  |
| 3. What role does evolution play in speciation? |  |
| 4. How is classification related to speciation? |  |
| 5. What are some examples of speciation? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|


















