State-Wise List of Governors of India | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
Introduction
In India, Governors serve as the constitutional heads of state, appointed by the President under Article 154 of the Constitution. They oversee state governance, acting on the advice of the Chief Minister and council of ministers. Their role mirrors the President’s at the national level, ensuring constitutional integrity and state stability.
Current List of Governors in India (State-Wise)
The table below lists the Governors of each state in India, reflecting their vital role in upholding the Constitution and supporting state administration.
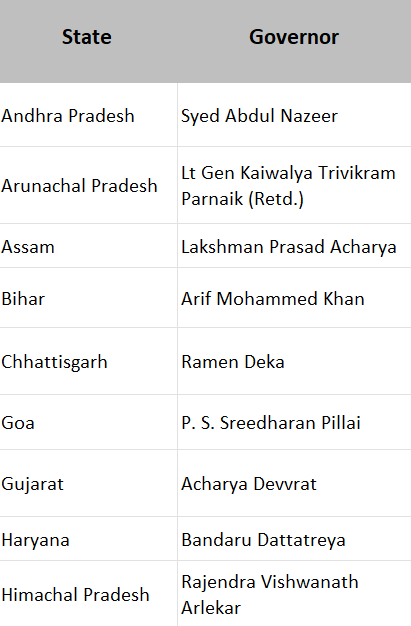
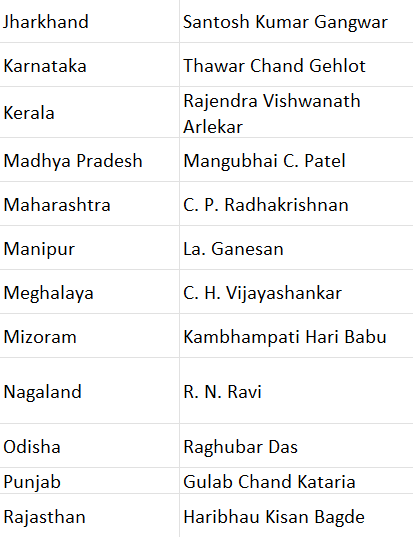
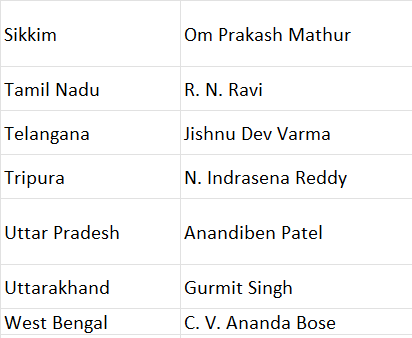
The above table represents the names of Governors of different states in India who play a significant role in protecting Indian constitutional laws and providing better facilities for the country’s people. The Governor is appointed as ahead of the state government and the Chief Minister is required to obtain permission of the Governor before formulating laws and administrative action.
Did You Know?
The Governor of a state can also serve as the administrator of a Union Territory if appointed by the President, showcasing the flexibility of their constitutional role.
Conclusion
Governors in India act as custodians of state governance, facilitating the smooth functioning of laws and administration under their nominal leadership. Though they rely on the elected government’s advice, their presence ensures a vital link between the state and the union, preserving sovereignty and unity. Their role, while ceremonial in many aspects, remains essential to India’s federal structure.
|
164 videos|800 docs|1160 tests
|
FAQs on State-Wise List of Governors of India - General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce
| 1. Who is the current Governor of Maharashtra? |  |
| 2. How are Governors appointed in India? |  |
| 3. Can Governors be removed from their position? |  |
| 4. How long is the term of a Governor in India? |  |
| 5. Are Governors involved in the day-to-day governance of a state? |  |
















