Stress & Strain | Strength of Materials (SOM) - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Stress |

|
| Tensile Stress |

|
| Hooke’s law |

|
| Poisson’s Ratio |

|
| For bi-axial stretching of sheet |

|
| Elongation |

|
| |

|
| Thermal or Temperature stress and strain |

|
Stress
- When a material is subjected to an external force, a resisting force is set up within the component.
- The internal resistance force per unit area acting on a material or the intensity of the forces distributed over a given section is called the stress at a point.
- It uses the original cross-sectional area of the specimen and is also known as engineering stress or conventional stress.
- Therefore, σ = P / A
 Stress
Stress
- P is expressed in Newton (N), and A, the original area, in square meters (m2). The stress σ will be expressed in N/m2. This unit is called Pascal (Pa).
- As Pascal is a small quantity, multiples of this unit are used in practice.
1 kPa = 103 Pa = 103 N/ m2 (kPa = Kilo Pascal)
1 MPa = 106 Pa = 106N/ m2 = 1 N/mm2 (MPa = Mega Pascal)
1 GPa = 109 Pa = 109 N/ m2 (GPa = Giga Pascal)
- The resultant of the internal forces for an axially loaded member is normal to a section cut perpendicular to the member axis.
- The force intensity on the shown section is defined as the normal stress.
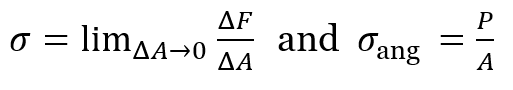 I
I
Tensile Stress
If σ> 0, the stress is tensile. i.e. The fibres of the component tend to elongate due to the external force. The beam is subjected to an external tensile force F, and the tensile stress distribution due to the force is shown in the figure. 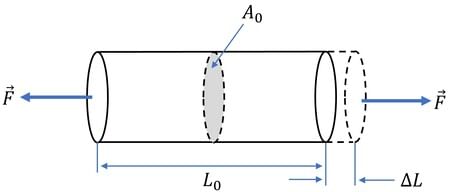 Tensile Stress
Tensile Stress
Compressive Stress (σc)
- If σ < 0, the stress is compressive. i.e. The fibres of the component tend to shorten due to the external force.
- A member subjected to an external compressive force P and compressive stress distribution due to the force is shown in the given figure.
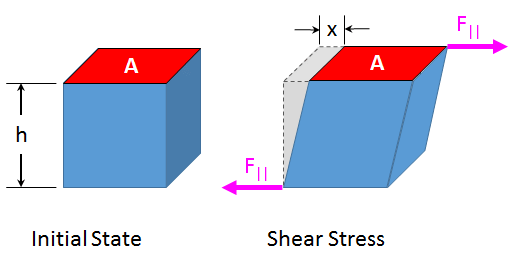
Shear Stress (τ)
- A type of stress that acts coplanar with the cross-section of the material.
- Shear stress acts parallel to the plane of interest.
- The corresponding internal forces act in the plane of the cross-section and are called shearing forces.
- The corresponding average shear stress T = P/A
Strain
- The displacement per unit length (dimensionless) is known as strain.
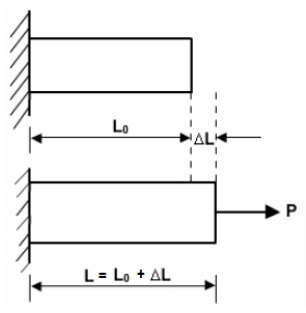
- The formula for strain is: ε = ΔL / L₀, where ε represents strain, ΔL is the change in length, and L₀ is the original length.
- It's a dimensionless quantity representing the ratio of change in length to the original length
Tensile strain
- The elongation per unit length is known as tensile strain.
- εt = ΔL/L0
- It is engineering strain or conventional strain.
- Here we divide the elongation by the original length, notthe actual length (L0ΔL)
 Tensile Strain
Tensile Strain
Compressive strain
- If the applied force is compressive, then the reduction of length per unit length is known as compressive strain.
- It is negative.
- Therefore, εc = (-ΔL)/L0
Shear strain (γ)
When a force P is applied tangentially to the element shown. Its edge displaced to dotted line. Where E is the lateral displacement of the upper face of the element relative to the lower face and L is the distance between these faces.
 Shear StrainThen the shear strain is :
Shear StrainThen the shear strain is : 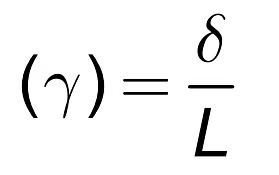
Hooke’s law
- According to Hooke’s law, the stress is directly proportional to strain i.e., normal stress (σ) ∝ normal strain (ε), and shearing stress (τ) ∝ shearing strain (γ).
i.e. σ = Eε and τ = Gγ, where E is Young's modulus of elasticity - The co-efficient E is called the modulus of elasticity i.e. its resistance to elastic strain. The co-efficient G is called the shear modulus of elasticity or modulus of rigidity.
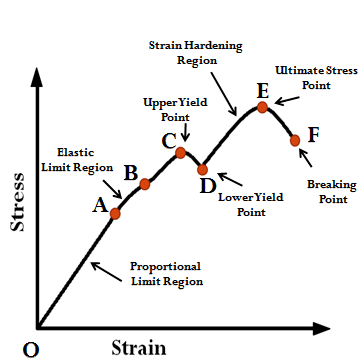
Volumetric Strain
A relationship similar to that for length changes holds for three-dimensional (volume) change.
For volumetric strain(εv),
The relationship is (εv) = (V-V0)/V0 or (εv) = ΔV/V0
- Where V is the final volume, V0 is the original volume, and ΔV is the volume change.
- Volumetric strain is a ratio of values with the same units, so it is also a dimensionless quantity.
- ΔV/V= volumetric strain = εx + εy + εz= ε1 + ε2 + ε3
Poisson’s Ratio
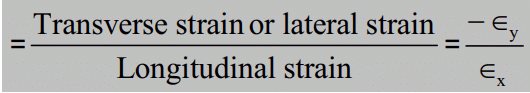 Poisson's ratio
Poisson's ratio
- Poisson's ratios are in the range from -1 to 1/2.
- Poisson's ratio in various materials is given below:
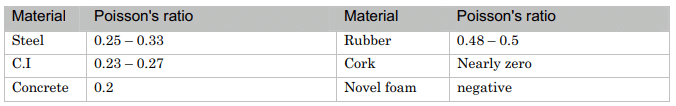 Ratios of various material
Ratios of various material
- We use cork in a bottle as the cork is easily inserted and removed, yet it also withstands the pressure from within the bottle. Cork with a Poisson's ratio of nearly zero is ideal in this application.
For bi-axial stretching of sheet
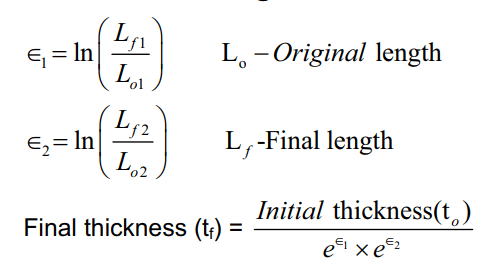 Ratio
Ratio
Elongation
- A prismatic bar loaded in tension:
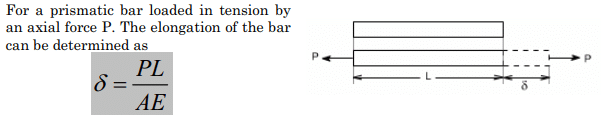 Elongation for a bar
Elongation for a bar
Elongation of composite body:
 Elongation of a composite body
Elongation of a composite body
- Elongation of a tapered body:
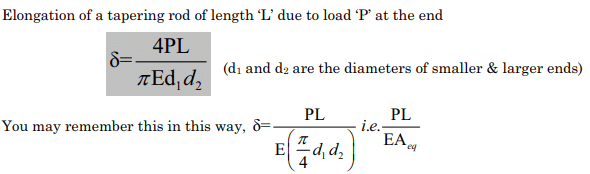 Elongation of a tapered body
Elongation of a tapered body
- Elongation of a body due to its self weight
 Elongation due to self-weight
Elongation due to self-weight
Thermal or Temperature stress and strain
- When a material undergoes a change in temperature, it either elongates or contracts depending upon whether temperature is increased or decreased of the material.
- If the elongation or contraction is not restricted, i. e. free then the material does not experience any stress despite the fact that it undergoes a strain.
- The strain due to temperature change is called thermal strain and is expressed as,
ε = α(ΔT)
- Where α is the coefficient of thermal expansion, a material property, and ΔT is the temperature change.
- The free expansion or contraction of materials, when restrained, induces stress in the material, and it is referred to as thermal stress.
σt = αE(ΔT)
where, E = Modulus of elasticity
- Thermal stress produces the same effect in the material similar to that of mechanical stress. A compressive stress will be produced in the material with an increase in temperature, and the stress developed is tensile stress with a decrease in temperature.
[Intext Question]
|
37 videos|106 docs|48 tests
|
FAQs on Stress & Strain - Strength of Materials (SOM) - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What is the difference between tensile stress and compressive stress? |  |
| 2. How is strain defined in materials science? |  |
| 3. What is Hook's Law and how does it relate to stress and strain? |  |
| 4. What is Poisson's Ratio and why is it important in material science? |  |
| 5. What are true stress and true strain, and how do they differ from engineering stress and strain? |  |





















