Subject Verb Agreement | General Aptitude for GATE - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
What is Subject Verb Agreement?
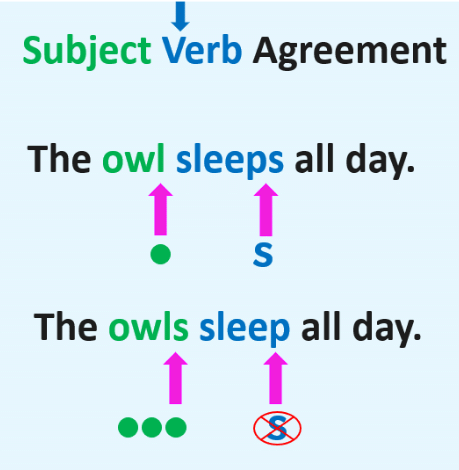
Subject-verb agreement refers to the grammatical concept that the subject of a sentence must align with the main verb of that same sentence.
- Singular subjects take singular verbs and plural subjects take plural verbs.
- If there is more than one noun or pronoun in the subject, identify the head noun, the main subject the verb must agree with. It is not always the noun or pronoun directly before the verb.
This is the head noun and the verb must agree with it. It will not always be the noun or pronoun directly in front of the verb.
- If two nouns are joined by "and", use a plural verb.
- If two nouns are joined by "or" or "nor", use a singular verb.
- Words like each, every and neither take singular verbs.
- Words like several, many and few take plural verbs.
- Words like all, most, any, and some take a singular verb with non-count nouns but a plural verb with plural nouns.
Singular verbs are formed by adding -s or -es to the base form of the verb. For example, leaves and stays are singular verbs.

Basic Rules to Follow
Rule No. 1
A singular subject must have a singular verb.
- He writes.
- She plays.
Rule No. 2
Plural subjects must have plural verbs.
- They write.
- We play.
Rule No. 3
Two subjects joined by ‘and’ will always take a plural verb.
- The doctor and nurse work together.
Rule No. 4
If two subjects express one idea, use a singular verb.
- Bread and butter is a wholesome food.
Rule No. 5
Two singular subjects joined by ‘or’ or ‘nor’ will take a singular verb.
- A doctor or a nurse is working in the hospital.
Rule No. 6
A singular subject and a plural subject joined by ‘or’, ‘either-or’, ‘neither- nor’, ‘none but’, or ‘not only but also’; will take a singular or plural verb depending on which subject is near the verb:
- Neither Deepak nor his friends are joining the tour.
- Neither his friends nor Deepak is joining the tour.
- None but the leaders of our country are responsible for this.
Rule No. 7
If two subjects are joined together by ‘as well as, ‘with’, ‘along with, ‘together with, ‘besides’, ‘in addition to, ‘and not’, ‘rather than, the verb will act according to the main subject:
- Students, as well as the teacher, are playing.
- He, as well as his brothers, is sitting there.
- I, as well as he, am going out of the station for a week.
Rule No. 8
Indefinite pronouns such as someone, somebody, nobody, one, no one, everyone, everybody, either, neither, etc. always take a singular verb.
- Each of my friends calls me once a month.
- Each boy and each girl has come.
- One must tolerate one‘s friend as well as enemy.
Rule No. 9
Indefinite plural pronouns (several, all, few, both, and many) always take plural verbs:
- Both of the books require careful reading.
- Several of the fielders regularly run four or five kilometres a day.
Rule No. 10
The title of the book needs singular verbs:
- ‘Great Expectations’ is a good book.
- ‘Gulliver Travels’ is an interesting book.
Rule No. 11
The subject ‘Many a’ …… is always followed by the singular verb.
- Many a man was drowned in the sea.
Rule No. 12
If the subject is ‘the number of’..…use a singular verb.
- The number of books is very small
- The number of boys in this team is ten.
Rule No. 13
If the subject begins with ‘A number of’, (A large number of, A Great number of, many) use a plural verb:
- A number of books are missing.
Rule No. 14
Some nouns in the plural form represent an amount, a fraction, or an element of time (sum, distance, quantity, and time period) and are considered singular and hence take singular verbs.
- Sixty minutes is enough to finish this work.
Choose the correct form of the verb that agrees with the subject.
Example 1: Annie and her brothers (is, are) at school.
Ans: Annie and her brothers are at school.
Example 2: Either my mother or my father (is, are) coming to the meeting.
Ans: Either my mother or my father is coming to the meeting.
Advanced Tricks
Trick 1
Some indefinite pronouns are considered singular and require singular verb forms.
The following is the list of indefinite pronouns: anyone, anybody, anything, No one, nobody, nothing, someone, somebody, something, everyone, everybody, everything, whatever and whoever.
Example: Everyone wants to watch a movie. (Notice the singular verb 'wants' in this case).
A sentence that uses 'want' in the plural form is: Ram and Sham want to watch the movie.
Trick 2
Five indefinite pronouns can be either singular or plural, depending on the usage.
Which are these pronouns? These are the SANAM pronouns: Some, Any, None, All, More / Most. You can use this handy mnemonic, SANAM, to keep this in mind.
Now, the important thing is the basis on which we decide whether the noun is singular or plural. There is one simple rule that is followed here:
- If the noun is a countable noun (nouns for which the plural form exists), then the verb is plural.
- If the noun is an uncountable noun (nouns for which only the singular forms exist), then the verb is singular.
Let's take up some example sentences to understand how this works.
Examples using Countable Nouns:
Sentence 1: Some of the girls are going out.
Sentence 2: Most of the glasses were broken.
We can see in both these cases that the nouns are plural in nature (girls and glasses), and therefore, the verb is plural in nature (are and were). Now, let's take up the example of uncountable nouns.
Examples using Uncountable Nouns:
Sentence 1: Some water is needed.
Sentence 2: Most of the money was lost.
In this case, we can see that water and money are uncountable nouns (these cannot be counted, and the plural form does not exist for these words). Considering this, the verbs are singular in nature.
Trick 3
After many/a great many/a good many, etc., the noun is always plural, which is followed by a plural verb.
Example: A great many girls are following fashion trends these days. (Here, the plural noun 'girls' is followed by the plural verb are.)
Trick 4
After 'a number of/a large number', the noun and verb in the sentence are always plural.
Example: A number of soldiers have lost their lives on the border. (Here, the noun 'soldiers' is used in the plural form, and the verb 'have lost' is also plural in nature.)
A good number of students __________ studying for the exam.
Trick 5
After 'the number', the noun is plural, but the verb is singular.
Example: The number of soldiers at the border is large.
This time, even though the noun soldiers is plural, the verb in the sentence, 'is', is singular in nature. The reason for this is that we are referring to a singular number in this case.
Trick 6
Collective nouns may take either a singular or a plural verb, depending on their use in the sentence.
If collective nouns are acting as a unit, use a singular verb. If the sentence implies that the individual members are taking up different actions, we use a plural verb.
Before we understand this rule, let's understand what collective nouns are. A collective noun is the name we give to a group of nouns to refer to them as one entity. Some examples of collective nouns are:
- A class of students.
- An army of soldiers.
Now that you know what collective nouns are, let's take two sentences to understand how they operate.
Sentence 1: The committee is discussing the issue of safety in the neighbourhood.
Sentence 2: The committee are disagreeing on the issue of installing street lamps.
We can see from the above examples that even though we have used the same collective noun, we end up using a different verb. The reason for this is very simple. In the first sentence, the collective action of the collective noun is the same; there is no division among the members of the collective noun. In the second case, this is not so. There is a disagreement, and the members of the collective noun have different actions.
Collective nouns like family, community and majority take a singular verb if their focus is on the whole entity. However, they take a plural verb if the focus is on individual members of the entity.
- Some words appear to be plural but are actually singular, so they take a singular verb (e.g. politics, athletics, news).
- You cannot make plurals out of some commonly used academic words (e.g. evidence, information).
Trick 7
Some words, such as news, measles, mumps, physics, etc. are extremely deceptive. They end in -s and appear to be plural but are really singular and require singular verbs.
Examples:
- The news from across the border is not encouraging.
- Physics is a fascinating subject.
- We can see that each of these uses a singular verb.
Trick 8
The verb in the subjunctive mood always takes the plural verb, even if the subject is singular in nature.
The plural verb 'were' replaces 'was' in sentences that express an unfulfilled wish, desire or condition. These sentences are built using if, as if, as though, I wish, etc.
The obvious question in your mind should be: What is the subjunctive mood of the verb? The subjunctive mood of the verb expresses an unfulfilled wish, desire, or condition. Generally, these sentences are built using if, as if, as though, I wish, etc. Let's take up some sentence examples to understand this rule:
- If I were the mayor of the city, I would have done so much for the poor.
- I wish I were a king.
|
193 videos|169 docs|152 tests
|
FAQs on Subject Verb Agreement - General Aptitude for GATE - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What is subject-verb agreement? |  |
| 2. What are the basic rules to follow for subject-verb agreement? |  |
| 3. Why is subject-verb agreement important in writing? |  |
| 4. How can subject-verb agreement errors affect the meaning of a sentence? |  |
| 5. What are some common examples of subject-verb agreement errors to watch out for? |  |






















