Subjective Type Questions: Chemical Kinetics & Nuclear Chemistry- 3 | JEE Advanced | 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE PDF Download
21. Write a balanced equation for the reaction of 14N with aparticle. (1997 - 1 Mark)
Solution:

22. The rate constant of a reaction is 1.5 × 107 s–1 at 50°C and 4.5 × 107 s–1 at 100°C. Evaluate the Arrhenius parameters A and Ea. (1998 - 5 Marks)
Solution: 
23. The rate constant for an isomerisation reaction, A→ B is 4.5 × 10–3 min–1. If the initial concentration of A is 1 M, calculate the rate of the reaction after 1 h. (1999 - 4 Marks)
Solution: 
24.  is radioactive and it emits α and β particles to form
is radioactive and it emits α and β particles to form 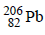 . Calculate the number of α and β particles emitted in this conversion. An ore of
. Calculate the number of α and β particles emitted in this conversion. An ore of  is found to contain
is found to contain  and
and 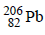 . in the weight ratio of 1:0.1. The half-life period of
. in the weight ratio of 1:0.1. The half-life period of  is 4.5 × 109 years. Calculate the age of the ore. (2000 - 5 Marks)
is 4.5 × 109 years. Calculate the age of the ore. (2000 - 5 Marks)
Solution:
Let the number of α-particles emitted = a
and number of β-particles emitted = b

25. A hydrogenation reaction is carried out at 500 K. If same reaction is carried out in the presence of a catalyst at the same rate, the temperature required is 400 K. Calculate the activation energy of the reaction if the catalyst lowers the activation barrier by 20 kJ mol-1. (2000 - 3 Marks)
Solution:
According to Arrhenius equation k =Ae-Ea/RT
Let Ea of the reaction in absence of catalyst = x kJ mol–1
Therefore Ea of the reaction in presence of catalyst
= x – 20 kJ mol–1
The Arrhenius equations in the two conditions can thus be written as

26. The rate of a first-order reaction is 0.04 mol litre–1 s–1 at 10 minutes and 0.03 mol litre–1 s–1 at 20 minutes after initiation. Find the half-life of the reaction. (2001 - 5 Marks)
Solution:
r2= k1c1 and r2= k2c2
Since rate of first order reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of its reactant,
27. The vapour pressure of the two miscible liquids (A) and (B) are 300 and 500 mm of Hg respectively. In a flask 10 moles of (A) is mixed with 12 moles of (B). However, as soon as (B) is added, (A) starts polymerizing into a completely insoluble solid. The polymerization follows first-order kinetics. After 100 minutes, 0.525 mole of a solute is dissolved which arrests the polymerization completely. The final vapour pressure of the solution is 400 mm of Hg. Estimate the rate of constant of the polymerization reaction. Assume negligible volume change on mixing and polymerization and ideal behaviour for the final solution. (2001 - 10 Marks)
Solution:
Let the number of moles of A left after 100 min = x
Total number of moles after 100 min = x + 12 + 0.525
Pmix = pA+ pB
28. 64Cu (half-life = 12.8 h) decays by β- emission (38%), β+ emission (19%) and electron capture (43%). Write the decay products and calculate partial half-lives for each of the decay processes. (2002 - 5 Marks)
Solution: 
Let the rate constants of the above emission processes be k1, k2 and k3 respectively and the overall rate constant be k. Then

29. For the given reactions, A + B → Products, following data were obtained. (2004 - 2 Marks)

(a) Write the rate law expression
(b) Find the rate constant
Solution:
(a) From the rate law expression, R0= k [A0]a[B0]b and from the table it is clear that :
(i) when the concentration of [A0] is doubled, keeping[B0] constant (see readings 1 and 2), the rate alsodoubles i.e. rate is directly proportional to [A0] or a = 1.
(ii) when the concentration of [B0] is reduced, keeping[A0] constant (see readings 1 and 3), the rate remains constant. i.e. rate is independent of [B0] or b = 0
Thus, rate equation becomes R0= k [A0]
30. Complete and balance the following reactions



Solution:
(i) Sum of atomic masses of reactant = sum of atomic masses of products
(ii) Sum of atomic numbers of reactant = sum of atomic numbers of products
(i) The atomic number of the final stable product = 90 – 7 × 2 + 1 × 6 = 82 & the mass number of the final stable product = 234 – 7 × 4 + 0 = 206.
Thus the element X should be 82Pb206

31. At constant temperature and volume, X decomposes as (2005 - 4 Marks)
2X(g) → 3Y(g) + 2Z(g) ; Px is the partial pressure of X.
| Observation No. | Time (in minute) | P (in mm of Hg) |
| 1 | 0 | 800 |
| 2 | 100 | 400 |
| 3 | 200 | 200 |
(i) What is the order of reaction with respect to X?
(ii) Find the rate constant.
(iii) Find the time for 75% completion of the reaction.
(iv) Find the total pressure when pressure of X is 700 mm of Hg.
Solution:
(i) From the given data, it is evident that the t1/2 (half-life period) for the decomposition of X (g) is constant (100 minutes) therefore the order of reaction is one.

|
347 docs|185 tests
|






















