Syllogism | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Types of Syllogism |

|
| Rules to Solve Syllogism Questions |

|
| Solved Examples |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
Syllogism is a form of logical reasoning where a conclusion is drawn from two or more given premises (statements). It is widely used in competitive exams like CUET UG to test a candidate's ability to deduce logical conclusions from given information.

Types of Syllogism
1. Basic Categorical Syllogism
It consists of three parts: Major Premise, Minor Premise, and Conclusion.
Example:
All men are mortal. (Major Premise)
Socrates is a man. (Minor Premise)
Conclusion: Socrates is mortal.
2. Conditional Syllogism (Hypothetical Syllogism)
It follows an "If-Then" condition.
Example:
If it rains, the ground gets wet.
It is raining.
Conclusion: The ground is wet.
3. Disjunctive Syllogism
It presents an either-or situation.
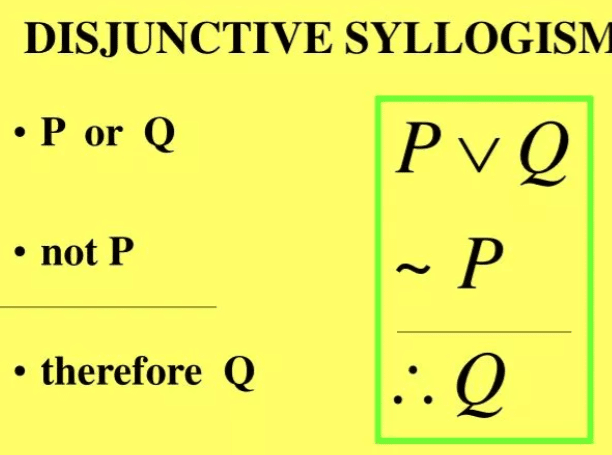
Example:
Either John will go to the party or he will stay home.
John did not go to the party.
Conclusion: John stayed home.
4. Linear Arrangement-Based Syllogism
Used when elements are arranged in a sequence.
Example:
A is taller than B.
B is taller than C.
Conclusion: A is taller than C.
5. Set-Based Syllogism (Venn Diagram Approach)
Venn Diagrams help in solving these problems visually.
Example:
Some apples are red.
All red things are beautiful.
Conclusion: Some apples are beautiful.
Rules to Solve Syllogism Questions
Identify the Key Terms: Analyze the subject and predicate in statements.
Understand the Statement Types:
Universal Affirmative (A-type): All A are B.
Universal Negative (E-type): No A is B.
Particular Affirmative (I-type): Some A are B.
Particular Negative (O-type): Some A are not B.
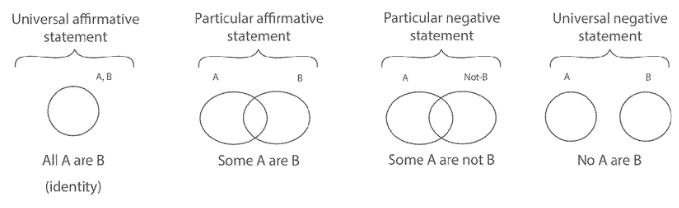
Draw a Venn Diagram (If Necessary): This helps visualize the logical relations.
Check for Immediate Inferences: Validate conclusions step by step.
Avoid Assumptions: Do not assume information that is not explicitly stated.
Solved Examples
Example 1
Statements:
- All cats are animals.
- Some animals are wild.
Conclusions:
- Some cats are wild. (Incorrect)
- Some animals are cats. (Correct)
Explanation:
- The first statement tells us that all cats belong to the category of animals.
- The second statement says that some animals are wild, but it does not specify whether cats are included in those animals. So, we cannot conclude that some cats are wild.
- The second conclusion, "Some animals are cats," is correct because the first statement already establishes that cats are a subset of animals.
Example 2
Statements:
- All birds can fly.
- Penguins are birds.
Conclusions:
- Penguins can fly. (Incorrect)
- Some birds cannot fly. (Correct)
Explanation:
- The first statement is a universal affirmative that says all birds can fly, but in reality, penguins are a known exception. Thus, this contradicts the given statement, making the conclusion incorrect.
- Since penguins are birds, and penguins cannot fly, the conclusion that some birds cannot fly is correct.
Example 3
Statements:
- All students study hard.
- Some students are engineers.
Conclusions:
- Some engineers study hard. (Correct)
- All engineers are students. (Incorrect)
Explanation:
- Since some students are engineers, and all students study hard, it means some engineers must be among those who study hard, making the first conclusion correct.
- However, it is not stated that all engineers are students, so we cannot assume this. Hence, the second conclusion is incorrect.
Example 4
Statements:
- No politician is honest.
- Some honest people are doctors.
Conclusions:
- Some doctors are politicians. (Incorrect)
- No honest person is a politician. (Correct)
Explanation:
- The first conclusion is incorrect because the statements do not establish any relation between doctors and politicians.
- The second conclusion is correct because if no politician is honest, it means no honest person can be a politician.
Example 5
Statements:
- Some books are fiction.
- All fiction is interesting.
Conclusions:
- Some books are interesting. (Correct)
- All books are interesting. (Incorrect)
Explanation:
- The first conclusion is correct because some books are fiction, and all fiction is interesting. So, some books must be interesting.
- The second conclusion is incorrect because it generalizes that all books are interesting, whereas we only know that some books (fiction) are interesting.
Example 6
Statements:
- No apple is a mango.
- All mangoes are fruits.
Conclusions:
- No apple is a fruit. (Incorrect)
- Some fruits are not apples. (Correct)
Explanation:
- The first conclusion is incorrect because we are only given information that apples and mangoes are separate, but we do not have any information about apples and fruits in general.
- The second conclusion is correct because since all mangoes are fruits and no apple is a mango, at least those mangoes are not apples. Hence, some fruits are not apples.
Example 7
Statements:
- Some doctors are teachers.
- All teachers are scholars.
Conclusions:
- Some doctors are scholars. (Correct)
- All scholars are teachers. (Incorrect)
Explanation:
- The first conclusion is correct because some doctors are teachers, and all teachers are scholars. So, at least some doctors must also be scholars.
- The second conclusion is incorrect because we only know that all teachers are scholars, but we do not know if all scholars are teachers.
Example 8
Statements:
- All men are humans.
- Some humans are doctors.
Conclusions:
- Some men are doctors. (Incorrect)
- Some doctors are humans. (Correct)
Explanation:
- The first conclusion is incorrect because we do not know if any of the men are doctors, as the given information only tells us that some humans are doctors.
- The second conclusion is correct because since some humans are doctors, and all men are humans, we can infer that some doctors are humans.
Example 9
Statements:
- Some cars are bikes.
- No bike is a truck.
Conclusions:
- Some cars are trucks. (Incorrect)
- Some bikes are not trucks. (Correct)
Explanation:
- The first conclusion is incorrect because there is no direct relationship between cars and trucks in the given statements.
- The second conclusion is correct because since no bike is a truck, it logically follows that some bikes are not trucks.
Example 10
Statements:
- All roses are flowers.
- Some flowers are red.
Conclusions:
- Some roses are red. (Incorrect)
- Some flowers are roses. (Correct)
Explanation:
- The first conclusion is incorrect because although some flowers are red, it is not necessarily stated that those flowers are roses.
- The second conclusion is correct because all roses are flowers, meaning at least some flowers must be roses.
Conclusion
Syllogism is an essential topic for CUET UG and can be mastered through regular practice. Understanding the different types, drawing Venn diagrams, and avoiding assumptions are crucial strategies for solving syllogism questions effectively. With these techniques and examples, students can develop logical reasoning skills and improve their performance in exams.
|
164 videos|800 docs|1160 tests
|
FAQs on Syllogism - General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce
| 1. What is a syllogism and why is it important for the CUET UG exam? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of syllogism that I should be familiar with for the CUET UG? |  |
| 3. What are the key rules to follow when solving syllogism questions? |  |
| 4. Can you provide an example of a syllogism problem and its solution? |  |
| 5. How can I improve my syllogism skills for better performance in the CUET UG exam? |  |















