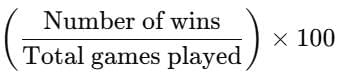Tables: Introduction & Solved Examples | General Aptitude for GATE - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
What is a Table?
A Table is a set of data arranged in rows and columns and is one of the most common ways of putting information across to people.
A Table consists of several boxes with information inside.
- The first row and the first column are generally used to denote the titles.
- While any type of data can be presented in table form, that too in a very accurate manner, interpreting the data in table form is more difficult and time-consuming than the other modes, all of which are basically pictorial or graphical in presentation.
- Tables give values that are organized but not represented visually.
- You may graph the data from the table to compare and see trends. You may create a table from a graph to make calculations easier.
Tips on Solving Table Chart Problems
- Read the data very carefully- The smallest detail may change the question's meaning completely. Similarly, the instructions must be understood carefully to prevent wasting time in calculating data that is not required, and also to find out exactly what the answer is that is sought.
- Understand the data- Before jumping to answer the questions, understand the data properly. The questions are designed to be deceptive, and a proper understanding of the requirements is a must. If the data provided is of the combined variety or if there is more than one data table/chart/graph, try to understand the relation between the given tables.
Example: One table may talk about absolute sales figures, while the other table may talk of sales as a percentage of production. Hence, any question on excess production or Goods in stock will require data from both tables. - Be very careful of the units used: In the tables and the units in which the answers (options) are provided. A mistake in the units may yield an entirely different answer. Also, be careful of whether the answer is required in decimal or percentage. Such errors are common and easily avoidable.
Let's look at some Examples
Example 1: Questions 1−4 are based on the table below, which is a record of the performance of a baseball team for the first seven weeks of the season.
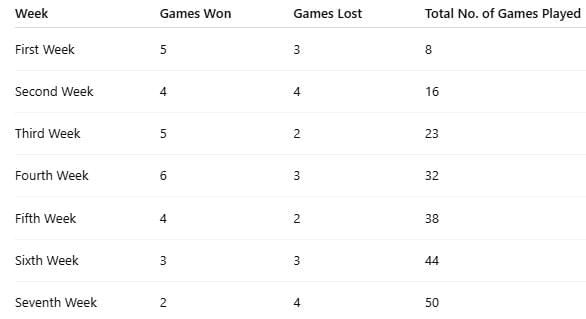 Q.1.1: How many games did the team win during the first seven weeks?
Q.1.1: How many games did the team win during the first seven weeks?
(A) 2
(B) 21
(C) 29
(D) 50
(E) 58
Answer: C
Solution: To find the total number of games won, add the number of games won for all the weeks.
5 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 4 + 3 + 2 = 29
The correct answer is choice (C).
Q.1.2: What percent of the games did the team win?
(A) 21%
(B) 29%
(C) 42%
(D) 58%
(E) 72%
Answer: D
Solution:
Across all seven weeks the team played 50 games (sum of totals) and won 29 of them.
To find the win percentage:
Win percentage =Win percentage =
= 58%
Q.1.3: Which week was the worst for the team?
(A) Second week
(B) Fourth week
(C) Fifth week
(D) Sixth week
(E) Seventh week
Answer: E
Solution:
Let’s look at each week’s winning ratio in words:
In the first week, the team won 5 out of 8 games (about 62.5%).
In the second week, 4 of 16 games (25%).
In the third week, 5 of 23 games (about 21.7%).
In the fourth week, 6 of 32 games (about 18.8%).
In the fifth week, 4 of 38 games (about 10.5%).
In the sixth week, 3 of 44 games (about 6.8%).
In the seventh week, 2 of 50 games (4%).
Since 4% is the lowest win rate, the seventh week was the worst for the team.
Answer: (E) Seventh week
Q.1.4: Which week was the best week for the team?
(A) first week
(B) third week
(C) fourth week
(D) fifth week
(E) sixth week
Answer: B
Solution:
Compare the numbers in the win–loss columns. Since there is more than 1 week with more wins than losses, you need to do a quick calculation.
Method 1
Compare the values of the ratio wins/losses. The greatest value will be the best week.
53 ≈ 1.67
52 = 2.5
63 = 2
42 = 2
The value for the third week is 2.5.
The correct answer is choice (B).
Method 2
Find the percentage of games won using the number of wins and the number of games each week.
58 = 62.5%
57 ≈ 70%
69 ≈ 67%
46 ≈ 67%
The team won 70% of its games in the third week.
The correct answer is choice (B).
Example 2: Here is an example consisting of tabular data:
Q. 2.1: The category receiving the least percentage help from the centre (in the entire data) is:
(A) Category B in 1995
(B) Category C in 1996
(C) Category B in 1996
(D) Category D in 1995
Correct Answer is Option (B).
In this type of question, it is better to examine the alternatives given rather than trying to find the least percentage from the table.
Let us now calculate the required percentage of the given alternatives:
(A) Category B in 1995 =
(Even without calculation, you can eliminate this choice.)
(B) Category C in 1996 =
(C) Category B in 1996 =(Even without calculation, you can eliminate this choice.)
(D) Category D in 1995 =Conclusion: From this, we arrive at the answer (B) since this is the least percentage.
Q. 2.2: The difference between the average costs paid by the Centre during 1995 and 1996 is:
(A) Rs. 6600 lakh
(B) Rs. 132 crore
(C) Rs. 132 lakh
(D) Rs. 13.2 lakh
Correct Answer is Option (C).
Adding all the cost figures in the 1995 column, i.e.
18.4 + 2.6 + 13.0 + 6.6 + 55.0, you get 95.6.The average in 1995:
=95.6Number of categories = 95.65
= Rs. 19.12Similarly, the average in 1996:
= (17.4+1.6+10.0+10.6+62.6)5
= Rs. 20.44The difference = Rs. (20.44−19.12)
= Rs. 1.32 cr
= Rs. 132 lakh (Since, 1 crore = 10 million = 100 lakh)
Q. 2.3: The Monthly cost to the city receiving E category assistance in 1996 is most nearly:
(A) Rs. 1.8 crore less than that in 1995
(B) Rs. 2.1 crore more than that in 1995
(C) Rs. 2.1 crore less than that in 1995
(D) Rs. 1.8 crore more than that in 1995
Correct Answer is Option (B).
Here, straight calculation is only needed. We need to look at the total assistance figures.
In 1995: 216.612 = 18.05
In 1996: 242.812= 20.23
Difference: crores
So, Option (B) is the correct answer.
Q. 2.4: Monthly costs to the city of category D during 1995 and 1996 bear a ratio (most nearly):
(A) 2 : 3
(B) 5 : 3
(C) 3 : 2
(D) 3 : 5
Correct Answer is Option (D).
- Again, we can straightaway determine the answer through simple calculation.
- Since a ratio is required to be calculated, we can avoid the division by 12.
- Directly from the table we have, total assistance in 1995 and 1996 for Category D as 26.4 and 42.6.
- Hence the ratio is 26.4 : 42.6 = 3 : 5 nearly.
Example 3: Directions: Study the table carefully to answer the following questions.
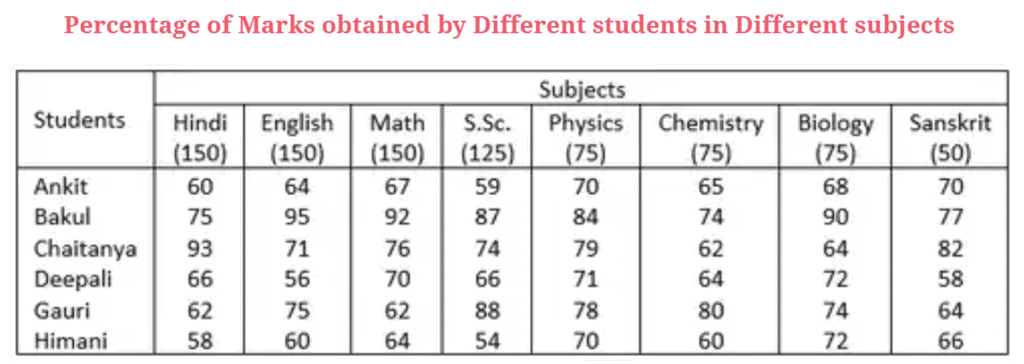
Q. 3.1: How many marks did Himani get in all the subjects together?
A. 505
B. 496
C. 525
D. 601
E. None of these
Correct Answer is Option (C)
Solution:
Required number = (58 x 150)100 + (60 x 150)100 + (64 x 150)100 + (54 x 125)100 + (70 x 75)100 + (60 x 75)100 + (72 x 75)100 + (66 x 50)100
= 87 + 90 + 96 + 67.5 + 52.5 + 45 + 54 + 33 = 525
Q. 3.2: What are the average marks obtained by all students together in Physics?
A. 75.33
B. 56.5
C. 64.25
D. 48.88
E. None of these
Correct Answer is Option (B)
Required average marks obtained = 452 × 75100 × 16 = 56.5
Q. 3.3: How many students have scored the highest marks in more than one subject?
A. Three
B. Two
C. One
D. None
E. None of these
Correct Answer is Option (A)
Bakul, Chaitanya, and Gauri scored the highest marks in more than one subject.
Q. 3.4: Marks obtained by Ankita in Sanskrit is what percent of marks obtained by Gauri in the same subject? (rounded off to two digits after decimal)
A. 91.43
B. 94.29
C. 103.13
D. 109.38
E. None of these
Correct Answer is Option (D)
Required percentage =70 x 10064 = 109.38
Q. 3.5: Who has scored the highest marks in all the subjects together?
A. Chaitanya
B. Himani
C. Deepali
D. Gauri
E. None of those.
Correct Answer is Option (E)
Total marks scored by Ankita = 90 + 96 + 100.5 + 73.75 + 52.5 + 48.75 + 51 + 35 = 547.5
Similarly,
Total marks cored by Bakul = 726.25
Total marks scored by Chaitanya = 647.25
Total marks scored by Deepali =554.75
Total marks scored by Gauri =614.5
Total marks scored by Himani = 525
Thus, highest marks are scored by Bakul.
Example 4: Directions: Answer the questions based on the information given below.
The given table shows the data regarding the number of air conditioners and air coolers sold by a shop in 5 different months and also percentage of those installed.
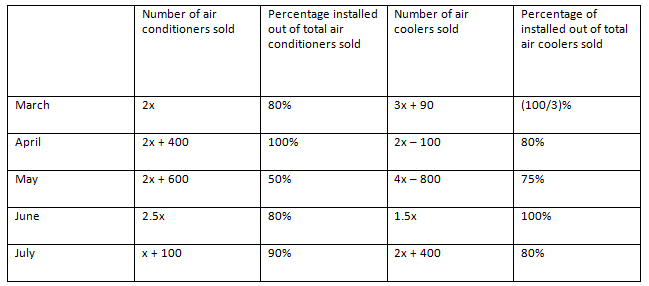
If total number of air conditioners installed in all the months together is 1540 units, then find out the number of air coolers installed in the month of June.
A – 120
B – 170
C – 140
D – 210
E – 150
Solution
In March, Number of air conditioners installed = 2x × 0.8 = 1.6x
Number of air coolers installed = (3x + 90) × 13 = x + 30
Similarly, we can find out the number of air conditioners and air coolers installed in the given 5 months.
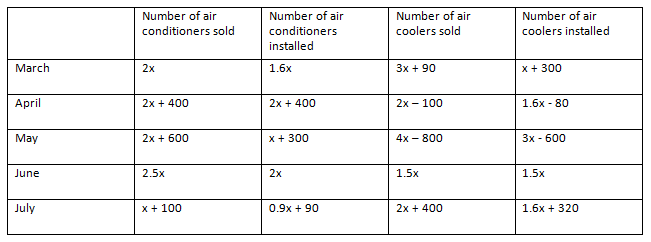
Total number of air conditioners installed in all the months together
= (1.6x) + (2x + 400) + (x + 300) + 2x + (0.9x + 90)
= 7.5x + 790
According to the question,
7.5x + 790 = 1540
Or, 7.5x = 750
Or, x = 100
Number of air coolers installed in the month of June = 1.5 x 100 = 150
Hence, option E.
Example 5: Directions: Answer the questions based on the information given below.
The given table shows the data regarding the number of air conditioners and air coolers sold by a shop in 5 different months and also percentage of those installed
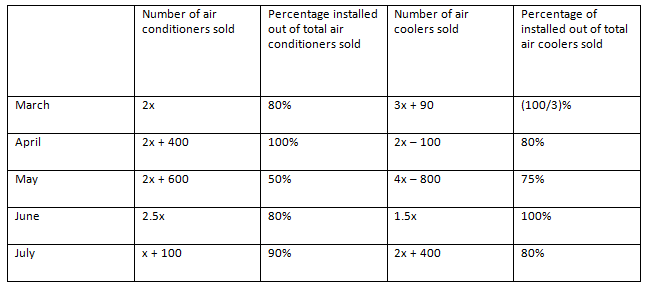
Find the difference between number of air conditioners installed in April and June together and the number of air coolers installed in March and May together.
A – Can’t be determined
B – 970
C- 870
D – 210
E – 530
Solution
In March, Number of air conditioners installed = 2x × 0.8 = 1.6x
Number of air coolers installed = (3x + 90) × 13 = x + 30
Similarly, we can find out the number of air conditioners and air coolers installed in the given 5 months.
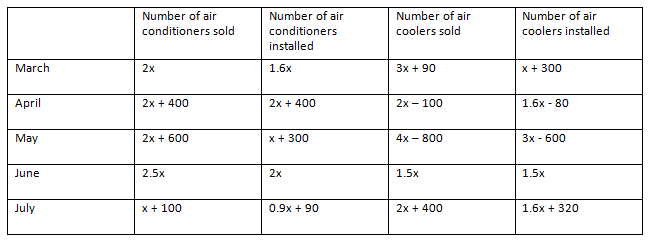
Number of air conditioners installed in April and June together = (2x + 400) + 2x = 4x + 400
Number of air coolers installed in March and May together = (x + 30) + (3x – 600) = 4x – 570
Required difference = (4x + 400) – (4x – 570) = 970
Hence, option B.
|
193 videos|169 docs|152 tests
|
FAQs on Tables: Introduction & Solved Examples - General Aptitude for GATE - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What is a table in data representation? |  |
| 2. How can I effectively solve table chart problems in exams? |  |
| 3. What are some common types of tables used in data analysis? |  |
| 4. Can you provide an example of a table and explain its components? |  |
| 5. What strategies can I use to interpret data from a table effectively? |  |