Tense - 1 | English Grammar Basic - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Tense |

|
| Types of Tenses |

|
| The Present Tense |

|
| Present Continuous Tense |

|
| Present Perfect Tense |

|
| Present Perfect Continuous Tense |

|
Tense
Tense is that form of a verb which shows the time and state of an action or event.

Let us take three sentences:
- I sing this song to please you.
- I sang the song in her very presence.
- I shall sing another song for her tomorrow.
In the first sentence, the verb sing refers to present time.
In the second sentence, the verb sang refers to past time.
In the third sentence, the verb shall sing refers to future time.
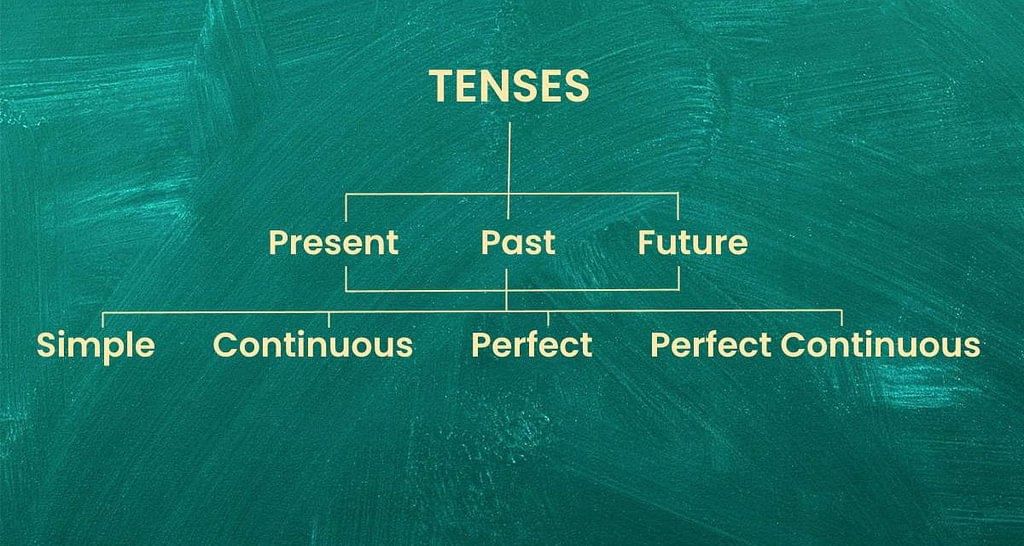
Types of Tenses
There are three main types of tenses:
- The Present Tense.
- The Past Tense.
- The Future Tense.
Present Tense: Describes actions happening now or regularly.
Past Tense: Refers to actions that occurred in the past.
Future Tense: Indicates actions that will happen later.
Each of the three above-mentioned tenses can further be divided into four subparts. These subparts include:
- Simple
- Continuous
- Perfect
- Perfect Continuous
Now, we will study all types of present tenses. Below a table is given consisting of structures and examples of all types of present tenses.
Present Tense Chart
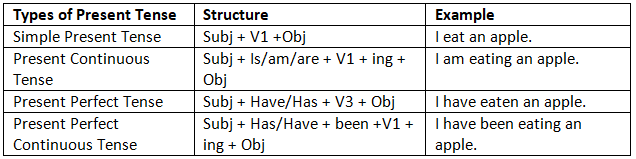
Now, let us study the present tense in detail. In each example sentence, the verb form, along with helping verbs, is highlighted.
The Present Tense
Present Indefinite Tense
The Present Indefinite or Simple Present Tense is used :
(i) To express a habitual action.
As,
- The cock crows every morning.
- I get up everyday at 6.o' clock.
- He goes to school everyday.
(ii) To express general truths.
As,
- The earth is round.
- Slow and steady wins the race.
- The sun sets in the west.
(iii) In exclamatory sentences beginning with here and there to express what is actually taking place in the present.
As,
- Here comes the tram!
- There goes the ball!
- There he goes!
(iv) In vivid narrative, as substitute for the simple past.
As,
- The officer now comes forward and tells the staff to complete all the work by 6 pm.
- Immediately the minister hurries to the capital.
- Sachin now makes quick runs to save the follow on.
(v) To indicate a future event that is part of a plan or arrangement.
As,
- We leave for Delhi next Wednesday.
- We go to Bangkok next week.
- When does the school reopen?
(vi) Simple Past is also used to introduce quotations.
As,
- Rousseau says, "Every man is born free, but everywhere he is in chains today."
(vii) Simple Past is used instead of the Simple Future Tense, in clauses of time and of condition.
As,
- I shall sing till you sleep.
- If it rings, I shall pick up the receiver.
He ___ to the gym every morning.
Present Continuous Tense
The Present Continuous Tense is used:
(i) For an action going on at the time of speaking.
As,
- He is reading.
- The boys are playing cricket.
(ii) For a temporary action which may not actually be happening at the time of speaking.
As,
- I am reading 'Romeo and Juliet'.
- He is reading 'Illyus and the Odyssey'.
[In both cases, none is reading at this moment].
(iii) For an action that is planned or arranged to take place in the near future.
As,
- I am going to the party tonight.
- My father is arriving day after tomorrow.
Exception: Certain verbs are generally not used in continuous forms when they describe states rather than actions.
(a) Verbs of Perception (when describing involuntary perception): see, hear, smell, notice, recognise.
Example: I see a bird (not "I am seeing a bird").
(But when used actively, some can be continuous: "She is smelling the flowers.")
(b) Verbs of Appearance: appear, look, seem.
Example: He looks tired (not "He is looking tired").
(But "He is looking at the painting" is correct.)
(c) Verbs of Emotion (when expressing feelings rather than actions): want, wish, desire, feel, like, love, hate, hope, refuse, prefer.
Example: I love music (not "I am loving music").
(But "I am feeling cold" is correct.)
(d) Verbs of Thinking (when referring to states of mind): think, suppose, believe, agree, consider, trust, remember, forget, know, understand, imagine, mean, mind.
Example: I know the answer (not "I am knowing the answer").
(But "I am thinking about the problem" is correct.)
(e) Verbs of Possession & Existence: have, own, possess, belong to, contain, consist of, be.
Example: She has a car (not "She is having a car").
(But "She is having lunch" is correct.)
These verbs may take continuous forms when their meanings change to describe temporary or active situations.
Present Perfect Tense
The Present Perfect Tense is used:
(i) To indicate complete activities in the immediate past.
As,
- He has just finished the work.
- The train has just started.
(ii) To express past actions whose time is not given and not definite.
As,
- I have never known him to be pessimistic.
- Mr John has been to Europe.
(iii) To describe past events when we think more of their effect in the present than of the action itself.
As,
- I have finished my homework.
- Mohan has drunk all the milk.
(iv) To denote an action beginning at some time in the past and continuing up to the present moment.
As,
- I have known him for a long time.
- He has been ill since last week.
- We have lived here for five years.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense is used for an action which began at some time in the past and is still continuing.
As,
- I have been watering the plants since 5 o'clock.
- He has been fishing for two hours.
- They have been playing for several hours.
|
20 videos|143 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Tense - 1 - English Grammar Basic - Class 10
| 1. What are the three types of tenses? |  |
| 2. Can you provide examples of sentences in the present tense? |  |
| 3. How is the present tense used in English grammar? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between simple present tense and present continuous tense? |  |
| 5. How can I improve my understanding and usage of the present tense in English? |  |
















