Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Physical Education for GCSE/IGCSE > The Consequences of a Sedentary Lifestyle & Obesity & Performance in Physical Activity/Sport
The Consequences of a Sedentary Lifestyle & Obesity & Performance in Physical Activity/Sport | Physical Education for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
The Impacts of a Sedentary Lifestyle
- Individuals who engage in minimal or no physical activity are considered to lead a sedentary lifestyle.
- A sedentary person is characterized by a lack of physical activity.
- Lifestyle refers to an individual’s daily routines and typical behaviors.
- For example, someone who spends their days moving between working at a desk, lounging on a couch, and resting in bed exemplifies a sedentary lifestyle.
- It can be challenging, especially for adults, to find opportunities to participate in physical activities or sports.
- According to a Sports England report for 2021/22, approximately 11.9 million adults in England were classified as inactive, engaging in less than 30 minutes of moderate physical activity per week.
- Living a sedentary lifestyle increases the likelihood of various physical and mental health problems.
- Some of the associated risks include:
- Weight gain or obesity
- Cardiovascular disease
- High blood pressure
- Type II diabetes
- Sleep disturbances
- Low self-esteem
- Fatigue or lack of energy
Obesity & Performance in Physical Activity/Sport
Understanding Obesity
- Obesity is a medical condition characterized by an excessive accumulation of body fat.
- It is identified by a body mass index (BMI) exceeding 30 or being more than 20% above the ideal weight-to-height ratio.
- Fat storage under the skin and around organs is normal for energy reserves, insulation, and organ protection.
- However, when fat accumulates excessively, as seen in obesity, it can significantly harm overall health.
Global Obesity Statistics
- According to the World Health Organization,in 2022, approximately 16% of the global population was obese, totaling around 890 million adults and 160 million children and adolescents.
Impact on Physical Activity and Sports
- Obesity adversely affects an individual’s capacity to engage in physical activities and sports.
- For example, obesity reduces endurance, strength, and speed, while also limiting flexibility and agility.
- This is primarily due to the extra body mass placing strain on bones and requiring greater effort to move the increased weight.
- Individuals with obesity often exhibit lower cardiovascular endurance, making intense or extended physical activities difficult.
Health Risks Associated with Obesity
People with obesity face a higher likelihood of various health issues compared to those with a healthy body mass.
Some examples include:
- Increased Cancer Risk: Certain cancers, such as colon cancer, are more prevalent due to poor dietary habits, particularly low-fiber diets lacking sufficient fruits and vegetables.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Excessive consumption of sugars and carbohydrates heightens the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. If untreated, it can cause damage to blood vessels, kidneys, eyes, gums, feet, and nerves.
- High Cholesterol: Consuming excessive fatty foods can lead to elevated cholesterol levels, causing blockages in blood vessels, particularly those near the heart.
- Heart Disease: These blockages increase the risk of heart disease or heart attacks.
Obesity and Heart Attack Diagram
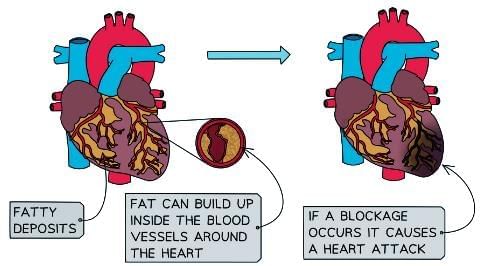
Mental and Social Health Impacts
Obesity affects not only physical health but also mental and social well-being.Examples include:
- Mental Health Challenges: Obesity can contribute to depression and reduced self-esteem, often linked to body image concerns and fear of judgment from others.
- Social Difficulties: Individuals with obesity may find it challenging to socialize or form new relationships.
- Mobility and Confidence Issues: A lack of confidence and mobility problems may prevent people with obesity from leaving their homes.
The document The Consequences of a Sedentary Lifestyle & Obesity & Performance in Physical Activity/Sport | Physical Education for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Physical Education for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
FAQs on The Consequences of a Sedentary Lifestyle & Obesity & Performance in Physical Activity/Sport - Physical Education for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is the relationship between obesity and physical performance in sports? |  |
Ans. Obesity can significantly impair physical performance in sports due to various factors such as reduced endurance, strength, and agility. Excess body weight can lead to decreased cardiovascular efficiency and increased strain on joints, which can hinder athletic performance and increase the risk of injuries.
| 2. How does a sedentary lifestyle contribute to obesity? |  |
Ans. A sedentary lifestyle, characterized by prolonged periods of inactivity, can lead to weight gain and obesity. Lack of physical activity reduces energy expenditure, and when combined with poor dietary choices, it results in a positive energy balance, leading to increased body fat over time.
| 3. What are the health consequences of obesity related to physical activity? |  |
Ans. Obesity is associated with numerous health consequences that can affect physical activity, including increased risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, joint problems, and respiratory issues. These health problems can limit an individual's ability to engage in physical activity and perform well in sports.
| 4. How can regular physical activity help in managing obesity? |  |
Ans. Regular physical activity helps manage obesity by increasing energy expenditure, improving metabolic health, and promoting weight loss. Engaging in a combination of aerobic exercises and strength training can enhance muscle mass, boost metabolism, and facilitate long-term weight management.
| 5. What strategies can individuals adopt to improve physical performance if they are obese? |  |
Ans. Individuals who are obese can improve physical performance by gradually incorporating regular physical activity into their routine, focusing on a balanced diet, setting realistic fitness goals, and seeking support from healthcare professionals or fitness trainers. Consistent efforts in these areas can lead to improved health and performance in physical activities and sports.
Related Searches















