Bank Exams Exam > Bank Exams Notes > NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation > The Individual Processes: Perception
The Individual Processes: Perception | NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation - Bank Exams PDF Download
Definition of Perception
Perception is how our brain organizes, identifies, and interprets sensory information to understand the world around us.
Nervous System and Physical Stimulation
- All perception involves signals in our nervous system, which result from the physical stimulation of our sense organs.
- For example, vision is triggered by light hitting our eyes, smell is influenced by odor molecules, and hearing is linked to pressure waves.
Active Role of Perception
- Perception isn't just passive reception of signals; it can be influenced by learning, memory, and expectations.
"Top-Down" and "Bottom-Up" Processing
- "Bottom-up" processing involves basic information that builds higher-level understanding, like recognizing shapes.
- "Top-down" processing is influenced by our concepts and expectations, shaping how we perceive things based on our knowledge.
Complexity of Nervous System
- Perception relies on the intricate functions of our nervous system.
- Despite this complexity, the process feels mostly effortless because much of it happens without conscious awareness.
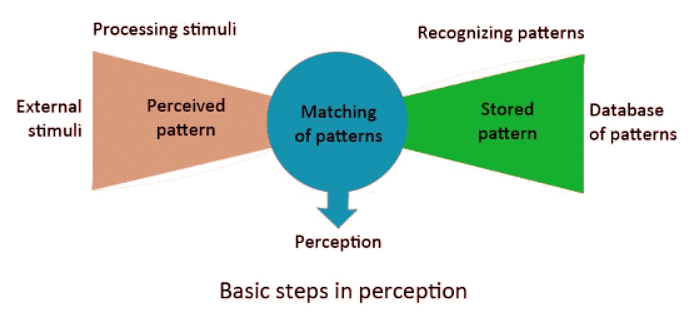
Perception is a three phase process of selecting, organizing and interpreting information. 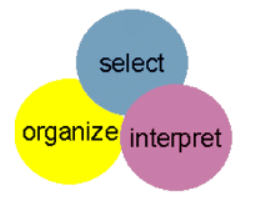
Question for The Individual Processes: PerceptionTry yourself: What is the process of perception?View Solution
Cognitive Bias
- What is Cognitive Bias:
- Cognitive bias is a tendency for our judgment to go off track in certain situations, leading to distorted perceptions, inaccurate judgments, or irrational interpretations.
- Pattern of Deviation:
- It's a consistent deviation from what's considered normal or expected judgment.
- This can be compared with judgments from people outside the situation or based on independently verifiable facts.
- Evolution of Cognitive Biases:
- Researchers have identified various cognitive biases over the past six decades in fields like cognitive science, social psychology, and behavioral economics.
- Adaptive and Heuristic Biases:
- Some biases may be helpful, leading to more effective actions or quicker decisions when speed is crucial (heuristics).
- Mechanisms and Information Processing:
- Other biases might arise from a lack of mental mechanisms or limited capacity for processing information (bounded rationality).
- Diverse Causes:
- Cognitive biases can stem from different causes, ranging from adaptive strategies to cognitive limitations.
The following is a list of the more commonly studied cognitive biases:
- Framing by using a too-narrow approach and description of the situation or issue.
- Hindsight bias, sometimes called the "I-knew-it-all-along" effect, is the inclination to see past events as being predictable.
- Fundamental attribution error is the tendency for people to over-emphasize personality-based explanations for behaviors observed in others while under-emphasizing the role and power of situational influences on the same behavior.
- Confirmation bias is the tendency to search for or interpret information in a way that confirms one's preconceptions; this is related to the concept of cognitive dissonance.
- Self-serving bias is the tendency to claim more responsibility for successes than failures. It may also manifest itself as a tendency for people to evaluate ambiguous information in a way beneficial to their interests.
- Belief bias is when one's evaluation of the logical strength of an argument is biased by their belief in the truth or falsity of the conclusion.
Question for The Individual Processes: PerceptionTry yourself: What is the tendency for people to over-emphasize personality-based explanations for behaviors observed in others while under-emphasizing the role and power of situational influences on the same behavior?View Solution
The document The Individual Processes: Perception | NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation - Bank Exams is a part of the Bank Exams Course NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation.
All you need of Bank Exams at this link: Bank Exams
|
846 videos|1297 docs|420 tests
|
FAQs on The Individual Processes: Perception - NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation - Bank Exams
| 1. What is cognitive bias and how does it relate to individual perception? |  |
Ans. Cognitive bias refers to the systematic errors in thinking that individuals tend to make when processing information or making decisions. It influences our perception by distorting our interpretation of reality based on our preconceived notions, beliefs, or experiences.
| 2. Can cognitive biases be beneficial in any way? |  |
Ans. While cognitive biases are generally considered to be errors in thinking, some biases can have adaptive benefits. For example, the confirmation bias, where individuals seek out information that confirms their existing beliefs, can help maintain consistency and efficiency in decision-making. However, it can also lead to errors when it comes to evaluating new or contradictory information.
| 3. How can cognitive biases impact decision-making? |  |
Ans. Cognitive biases can significantly impact decision-making by introducing errors and distortions. They can influence how we gather, process, and interpret information, leading to biased judgments and suboptimal choices. For example, the availability bias can make individuals overestimate the likelihood of events that are more easily recalled or readily available in their memory.
| 4. Are cognitive biases inherent to all individuals? |  |
Ans. Yes, cognitive biases are inherent to all individuals as they are a result of how our brains process information. However, the extent to which individuals are influenced by biases can vary. Factors such as education, awareness, and critical thinking skills can help individuals mitigate the impact of biases on their decision-making.
| 5. Can cognitive biases be overcome or minimized? |  |
Ans. While cognitive biases cannot be completely eliminated, individuals can employ strategies to minimize their impact. Awareness of common biases, critical thinking, seeking diverse perspectives, and considering multiple sources of information can help individuals make more rational and informed decisions. Additionally, involving others in decision-making processes can provide different viewpoints and reduce the influence of biases.
Related Searches
















