The Mughals Dynasty | General Awareness - Bank Exams PDF Download
Introduction
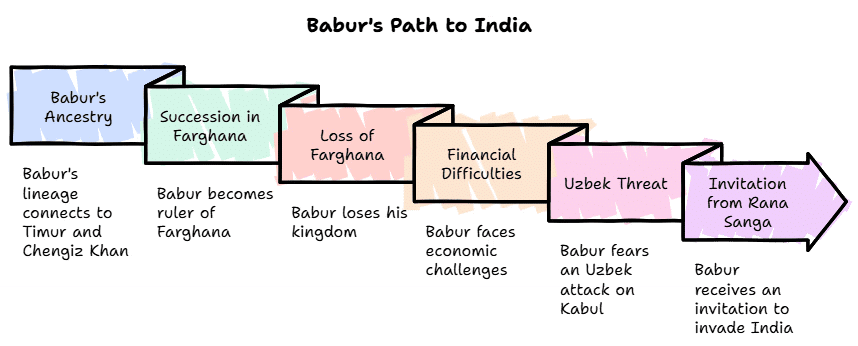
- The Mughals were descendants of two great lineages of rulers.
- Babur: founder of the Mughal Empire in India was related to Timur from his father’s side and to Chengiz Khan through his mother.
- Babur succeeded his father as the ruler of Farghana (Uzbekistan), but soon lost his kingdom.
- Financial difficulties, apprehension of Uzbek attack on Kabul and invitation of Rana Sanga to invade India forced Babur to look towards India.
Babur (1526 – 1530)
- Babur, the founder of the Mughal empire in India, traced his ancestry to the Timurid dynasty.
- Embassies from Daulat khan and Rana Sanga inviting Babur to displace Ibrahim Lodhi led to the First Battle of Panipat in 1526, and he defeated Ibrahim Lodi.
- He used an ottoman (Rumi) device in this war.
- He also heavily used Gunpowder in this war, though it was known in India in earlier times.
- He defeated Sangram Singh (Rana Sanga) of Mewar in the Battle of Khanwa in 1527, resulting in strengthening his position in the Gangetic plains.

- He defeated another Rajput ruler, Medini Rai (of Chanderi) in the Battle of Chanderi in 1528.
- He defeated the Afghan chiefs under Mahmud Lodi (brother of Ibrahim Lodi) in the Battle of Ghagra in 1529.
- He declared was as Jihad and assumed the title Gazzi after his victory.
- Died in 1530. Buried at Aram Bagh in Agra; later his body was taken to Aram Bagh, Kabul.
Literature
- Babur composed Tuzuk-i-Baburi, a Masnavi, and the Turkish translation of a well-known Sufi work.
- Tuzuk-i-Baburi was translated into Persian as Baburnama by Abdur Rahim Khankhana
Architecture
- Babur also established a tradition of Gardening by laying out a number of formal gardens with running water.
- He built two mosques, one at Kabulibagh, Panipat, and another in Sambhal, Rohilkhand
Humayun (1530 – 1556)
- Humayun became the Mughal Emperor on 29 December 1530 at the age of 23.
- He did a blunder by dividing his empire among his three brothers- Kamran, Hindal & Askari.
- In the Battle of Chausa, 1539, Humayun was defeated for the first time by Shershah Suri but he escaped.
- In the next year (1540) Shershah completely defeated Humayun in the Battle of Kanauj (or Biligrama) and founded the Sur dynasty.
- After the lapse of 15 years, Humayun re-captured the Empire by defeating the last Sur ruler Sikandar Shah Suri in the Battle of Sirhind, 1555. Bairam Khan, his most faithful officer, helped him in this.
 Humayun
Humayun - The period from 1540 to 1555 is known as the period of the temporary eclipse of the Mughal.
- Humayun died by an accidental fall from the staircase of his Library 'Shermandal' at the Puranakwila in Delhi on 24 January 1556.
- Humayun was an accomplished mathematician and astronomer. He earned the title Insan-i-Kamil (Perfect Man), among the Mughals.
Literature
- Humayun's biography Humayun Namah was written by Humayun's half-sister Gulbadan Begum. The language used to write this biography was a mixture of Turkish and Persian.
Architecture
- The Purnakwila was constructed by Humayun but its construction was completed by Shershah.
- Humayun's tomb is situated in Delhi (the first building in India to have double domes) which was built by Haji Begum
- Humayun tomb is known as the predecessor of Tajmahal because Taj was modeled after this, also known as a dormitory of the house of Timur. Mirak Mirza Ghias was its architect.
- In 1533 Humayun built the city of Dinpanah (world refuge) in Delhi as his second capital.
SHER SHAH SURI (1540-45)
- Founder of Sur dynasty and second Afghan Empire (after Lodhi).
- Sher Shah’s rule lasted for five years.
 Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri
Administration
- Construction of Historic Structures: Purana Qila (Old Fort) and the Sasaram Mausoleum were erected during this era.
- Literary Contribution: Malik Muhammad Jayasi authored the renowned Hindi work "Padmavat" during his reign.
- Continuation of Administrative System: Sher Shah maintained and expanded the central administration established during the Sultanate period.
- Key Officials:
- Diwan-i-Wizarat/Wazir: Responsible for Revenue and Finance.
- Diwan-i-Ariz: Head of the Army.
- Diwan-i-Rasalat: Overseer of Foreign Affairs.
- Diwan-i-Insha: Minister for Communications.
- Barid: Intelligence Officer.
- Administrative Divisions: The empire was divided into "sarkars," each headed by a Chief Shiqdar (law and order) and Chief Munsif (judge).
- Local Administration: Sarkars were further subdivided into parganas, each administered by a Shiqdar (military officer), Amin (land revenue), Fotedar (treasurer), and Karkuns (accountants).
- Village-Level Governance: Mauza (village) served as the lowest level of administration.
- Iqtas: Various administrative units known as iqtas were established.
- Land Revenue System: Sher Shah implemented a well-organized land revenue system with officials known as Amils and Qanungo responsible for revenue records.
- Land Survey and Assessment: A meticulous land survey was conducted, and land was classified into good, middle, and bad categories. The state's share was one-third of the average produce, paid in cash or crops.
- Introduction of New Currency: Sher Shah introduced new silver coins called "Rupiya," in circulation until 1835.
- Infrastructure Development: He constructed the Shahi (Royal) road from the Indus Valley to the Sonar Valley in Bengal, later renamed the Grand Trunk (GT) road by the British, connecting Calcutta and Peshawar.
- Sarais and Market Towns: Sher Shah built Sarais (lodging) that also functioned as post offices, many of which evolved into market towns.
- Administrative Control: Each Sarai was overseen by a Shahana (custodian).
- Military Practices: Sher Shah adopted the horse branding practice from Alauddin Khalji and maintained a personal royal force known as Khasa Kail.
Akbar (1556 – 1605)
 Akbar
Akbar
- Akbar was crowned at Kalanaur at the age of 13 years in 1556.
- He was coronated when he was just 14 years old.
- Bairam Khan represented him in the Second Battle of Panipat in 1556 against Hemu Vikramaditya. Hemu was defeated.
- Between 1566 – 1560, Akbar ruled under Bairam Khan’s regency.
- Akbar’s armies had conquered Kashmir, Sindh, Orrisa, Central India, and also conquered Gujarat (1572- 1573) and Bengal (1574-1576).
- Akbar's last campaign was against Asirgarh, resulting in the annexation of Khandesi (1601).
- Married Raja Bharmal’s daughter in 1562 which paved the way for friendship between Rajputs and Mughals (except Mewar).
- Won Gujarat in 1572. It was in order to celebrate his victory that Akbar got the Buland Darwaza constructed at Fatehpur Sikri.
- Fought Battle of Haldighati with Maharana Pratap in which Maharana was defeated.
- Built Ibadatkhana (Hall of prayer) at Fatehpur Sikri.
- Formulated an order called Din-i-Ilahi or Tauhind-i-Ilahi in 1582. Birbal, Abul Fazal and Faizi joined the order.
- His land Revenue system was known as Todar Mal Bandobast or Zabti System.
- Also introduced the Mansabdary System to organize the nobility as well as the army.
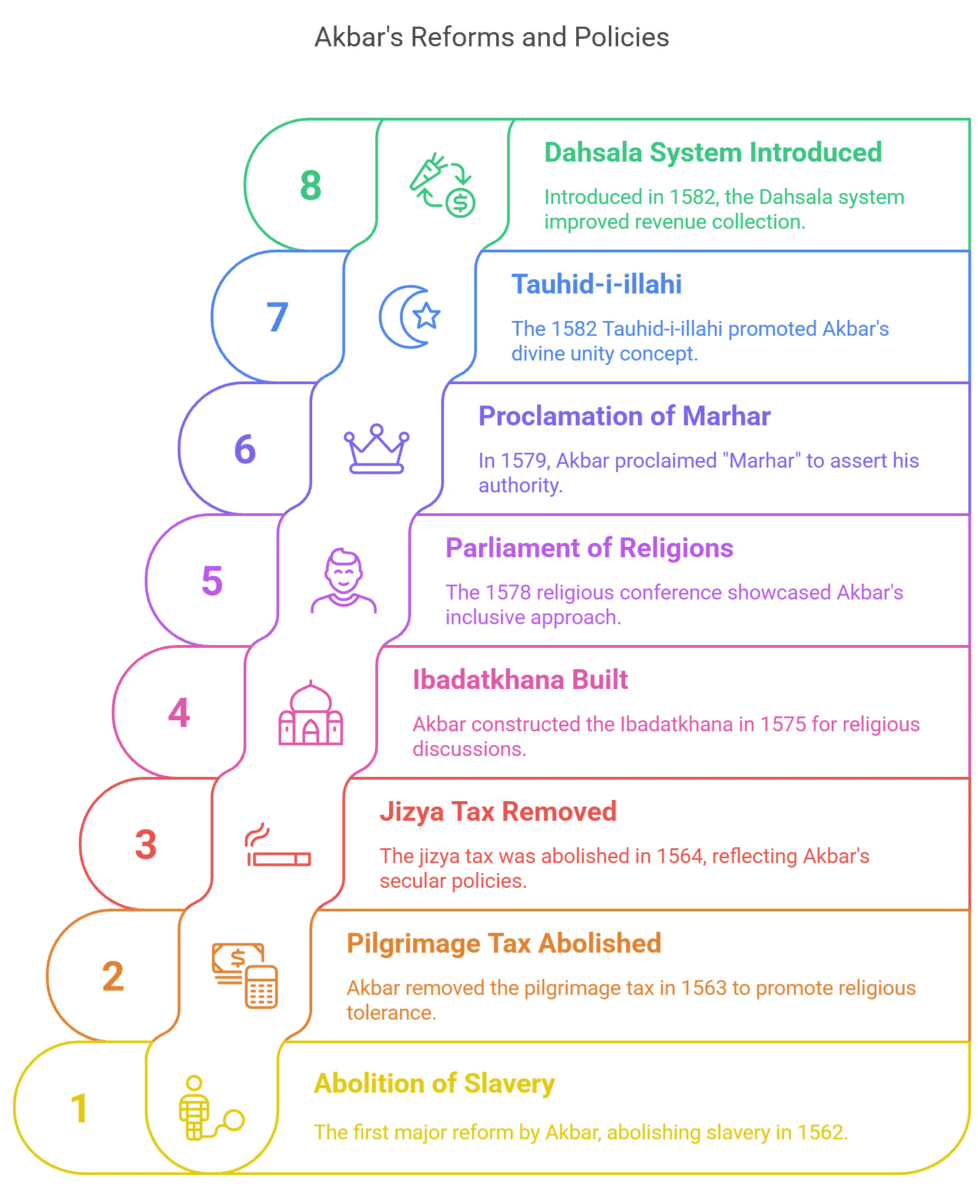
Main Event During the Reign of Akbar
- Abolition of slavery - 1562
- Abolition of Pilgrimage Tax - 1563
- Abolition of Jizya Tax- 1564
- Ibadatkhana was built in Fatehpur Sikri - 1575
- Parliament of Religions in Ibadatkhana - 1578
- Proclamation of "Marhar" - 1579
- Proclamation of Tauhid-i-illahi - 1582
- Entire empire divided into 12 provinces [After victory of south it became 15] - 1575 to 1576
- 'Dahsala System' introduced by Todarmal - 1582
- 'Mansabdari System' introduced - 1573 to 1574
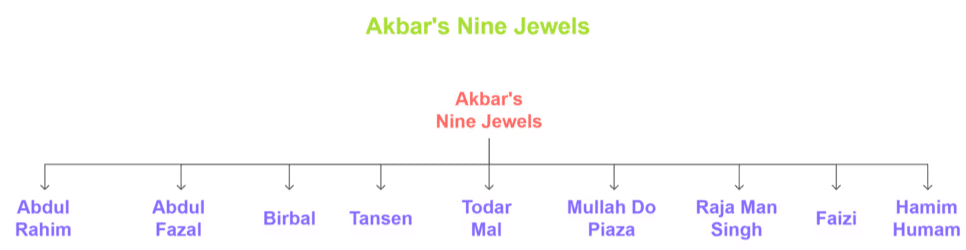
Nine-jewels or Navratna of Akbar
- Abdul Rahim - Hindi Scholar
- Abdul Fazal - Chief Advisor
- Birbal - Wittiness
- Tansen - Singer
- Todar Mal - Finance Minister
- Mullah Do Piaza - Advisor
- Raja Man Singh - General [Senapati]
- Faizi - Poet
- Hamim Humam – Physician
Jahangir (1605 – 1627)
 Jahangir
Jahangir
- He executed the fifth Sikh guru, Guru Arjun Dev, who had helped the revolting Prince Khusrau.
- His greatest failure was the loss of Kandahar to Persia in 1622.
- The most important event in Jhangir’s life was his marriage to Mehr-un-Nisa, the widow of Sher Afghani in 1611. The title of Nur-Jahan was conferred on her.
- Had a Chain of Justice outside his palace in Agra (called Zanjir-i-Adil).
- Captain Hawkins (1608-11) and Sir Thomas Roe (1615-1619) visited his court.
- Tobacco growing started during his reign. It was brought by the Portuguese.
- Painting reached its zenith during his reign.
Shah - Jahan (1628 – 1658)
- This reign is named as ‘Golden Age’ of the Mughal Empire.
- 2 Frenchmen, Bernier and Tavernier, and an Italian adventurer Manucci visited India during his reign.
 Shah Jahan
Shah Jahan - Built Taj Mahal, Moti Masjid at Agra. Jama Masjid and Red Fort at Delhi, etc.
- There was a brutal war of succession among his four sons (Dara, Shuja, Aurangzeb, and Murad) during the last days of his reign.
- Shahjahan liked Dara, but Aurangzeb came out victorious. Thus, he had to spend the last 8 years of his life in prison.
Aurangzeb Alamgir (1658 – 1707)
- In his rule, various rebellions took place – Jat peasantry at Mathura, Satnami peasantry in Punjab, and Bundelas at Bundelkhand.
- He caused a serious rift in the Mughal – Rajput alliance by his policy of annexation of Marwar in 1678 after the death of Raja Jaswant Singh.
- In 1675, he ordered the arrest and execution of the ninth Sikh guru, Guru Tegh Bahadur.
 Aurangzeb Alamgir
Aurangzeb Alamgir - The Mughal conquests reached the territory climax during his reign, as Bijapur (1686) and Golconda (1687) were annexed to the Mughal Empire. The Mughal empire stretched from Kashmir in the north to Jinji in the south, from the Hindukush in the west to Chittagong in the east.
- He was called a ‘ Darvesh’ or a ‘Zinda Pir’. He also forbade sati.
- The empire lost power after Aurangzeb’s rule. His successors were weak and incapable rulers.
Note
- Ambitious nobles became direct contenders of power after Aurangzeb. The Sayyid brothers (also known as King-Makers) put three principles on the throne.
- One of the generals of Nadir Shah, Ahmad Shah Abdali invaded India repeatedly between 1748 – 1767. He defeated the Marathas in the Third Battle of Panipat in 1761. In this battle, Marathas were led by Sadashiv Rao Bhau, while the Peshwa at that time was Balaji Bajirao.
- A later Mughal emperor, Shah Alam II joined hands with Mir Qasim of Bengal and Shuja-ud-Daula of Awadh in the Battle of Buxar against the British in 1764. They were defeated by the British.
Later Mughals and Decline of Mughals
A war of succession broke out among the sons when father Aurangzeb died in 1701. Muazzam emerged victorious after defeating Muhammad Azam Shah in the Battle of Jajau.
Bahadur Shah (1707-1712):
- War of succession after Aurengzeb's death.
- Muazzam defeats and kills brothers, becomes Bahadur Shah.
- Reverses Aurengzeb's policies, adopts tolerant attitude towards Hindus.
- Releases Maratha prince Shahu, makes peace with Rajputs, Jats, and Bundelas.
- Offers high mansab to Guru Govind Singh, faces Sikh revolt under Banda Bahadur.
- Termed 'Shah-i-Bekhabar' for lavish grants, sons leave his body unburied.
Jahandar Shah (1712-1713):
- Comes to power with Zulfiquar Khan's support.
- Indulges in pleasure, administration controlled by Zulfiquar Khan.
- Abolishes Jizya tax, introduces oppressive Izara system.
- Grants Chauth and Sardeshmukhi rights to Marathas.
Farrukhsiyar (1713-1719):
- Supported by Sayyid Brothers, Abdullah Khan, and Hasan Ali.
- Sayyid Brothers take control of administration.
- Introduces religious tolerance, abolishes Pilgrimage tax.
- British receive Royal Farman in 1717, misused provisions.
- Sayyid Brothers dethrone Farrukhsiyar with Peshwa Balaji Vishwanath's help.
Muhammad Shah (1719-1748):
- Nobles led by Asaf Jah kill Sayyid Brothers.
- Muhammad Shah weak and indulgent, called 'Rangeela.'
- Irreversible decline of Mughal empire begins.
- Semi-independent states emerge: Bengal, Awadh, Hyderabad.
- Nadir Shah's massacre in Delhi (1739), decline accelerates.
Ahmed Shah (1748-1754):
- Abdali invades Mughal territories in 1749 and 1752.
- Mughal emperor surrenders Multan and Punjab to Abdali.
Alamgir II (1754-1759):
- Marathas invade Delhi, occupy Lahore and Punjab.
- Battle of Plassey fought during his reign.
Shah Alam II (1760-1806):
- Supported by Maratha Sardar Sada Shiv Rao Bhau.
- Witnessed Third Battle of Panipath (1761) and Battle of Buxar (1764).
- Exiled by Abdali, reinstated by Marathas in 1771.
- Blinded by Rohilla leader Zabita Khan, restored by Mahad Ji Scindia in 1788.
Akbar II (1806-1837):
- Titles 'Raja' to social reformer Rammohan Roy.
- English East India Company stops minting coins in Mughal emperor's name in 1835.
Bahadur Shah II (1837-1857):
- Reign during the Revolt of 1857.
- Mughal rule legally ends on November 01, 1858, with Queen Victoria's declaration.
Reasons for Decline of the Mughals

- Lack of stability after Aurangzeb.
- Most of the emperors became puppets in the hands of powerful Nobles who often ran administration on their behalf.
- Weal military and political administration as exposed by Nadir Shah and Ahmad Abdali’s invasion
- Emergence of autonomous states and hence weakening of central power.
- Orthodox policy of Aurangzeb: His attitude towards Marathas, Rajputs and Jats made them his enemy. His religious policies too alienated the Hindus.
|
365 videos|701 docs|149 tests
|
FAQs on The Mughals Dynasty - General Awareness - Bank Exams
| 1. Who was the founder of the Mughal Empire and what were his significant achievements? |  |
| 2. What were the key contributions of Akbar during his reign? |  |
| 3. How did Sher Shah Suri impact the Mughal Empire during his rule? |  |
| 4. What were the main reasons for the decline of the Mughal Empire? |  |
| 5. How did the reign of Aurangzeb differ from that of his predecessors? |  |

















