Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Notes > Year 7 Chemistry (Cambridge) > The particle model
The particle model | Year 7 Chemistry (Cambridge) - Class 7 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Solids |

|
| Liquids |

|
| Gases |

|
| Changes of State |

|
Introduction
- Matter exists in three main states: solid, liquid, and gas.
- These states can change based on temperature and pressure.

Solids
- Description:
- Particles are tightly packed in a fixed, regular arrangement.
- Particles vibrate but do not move from their positions.
- Strong forces exist between particles.
- Example:
- Ice (solid water) maintains its shape and volume.
Liquids
- Description:
- Particles are close together but can move past each other.
- Particles have an irregular arrangement.
- Weak forces exist between particles.
- Example:
- Water flows and takes the shape of its container.
Gases
- Description:
- Particles are far apart and move freely.
- Particles have a random arrangement.
- Very weak forces exist between particles.
- Example:
- Steam (water vapor) spreads to fill any container.
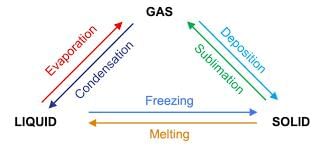
Changes of State
- Melting: Solid to liquid by heating (e.g., ice melting into water).
- Freezing: Liquid to solid by cooling (e.g., water freezing into ice).
- Boiling (Vaporization): Liquid to gas by heating (e.g., water boiling into steam).
- Condensation: Gas to liquid by cooling (e.g., steam condensing into water).
- Sublimation: Solid to gas without passing through liquid state (e.g., dry ice sublimating into carbon dioxide gas).
Demonstration
Visual Example:
- Show how solids retain shape, while liquids and gases take the shape of their containers.
- Demonstrate using ice cubes, water, and steam to illustrate each state.
Question for The particle modelTry yourself: Which state of matter has particles that are tightly packed in a fixed, regular arrangement with strong forces between them?View Solution
Conclusion
- Understanding states of matter helps explain how substances behave under different conditions.
- Temperature changes play a crucial role in altering states of matter.
The document The particle model | Year 7 Chemistry (Cambridge) - Class 7 is a part of the Class 7 Course Year 7 Chemistry (Cambridge).
All you need of Class 7 at this link: Class 7
|
7 videos|15 docs|8 tests
|
FAQs on The particle model - Year 7 Chemistry (Cambridge) - Class 7
| 1. What are the three states of matter? |  |
Ans. The three states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas.
| 2. How do particles behave in each state of matter? |  |
Ans. In a solid, particles are tightly packed and vibrate in place. In a liquid, particles are close together but can move around each other. In a gas, particles are spread out and move freely.
| 3. What happens to the arrangement and movement of particles as a substance changes from one state to another? |  |
Ans. As a substance changes from a solid to a liquid to a gas, the arrangement of particles becomes less orderly and the movement of particles becomes more chaotic.
| 4. How does temperature affect the state of matter of a substance? |  |
Ans. Increasing the temperature of a substance can cause it to change from a solid to a liquid to a gas, as the particles gain energy and move more freely.
| 5. Can a substance change directly from a solid to a gas without passing through the liquid state? |  |
Ans. Yes, a substance can change directly from a solid to a gas through a process called sublimation.
Related Searches















