Solved Examples: Time & Distance | General Aptitude for GATE - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
The Basics of Time, Speed & Distance
Time:
Time is a measure of duration or the interval between two events. It can be quantified in seconds, minutes, hours, days, etc. In the context of time, some key points include:
- Units of Time: Common units include seconds (s), minutes (min), hours (hr), days (d), weeks, months, and years.
- Notation: Time can be expressed in different formats, such as 24-hour notation (e.g., 14:30) or 12-hour AM/PM notation (e.g., 2:30 PM).
Speed:
Speed refers to the rate at which an object covers a distance in a given amount of time. It is a measure of how fast or slow an object moves relative to a reference point. Key aspects of speed include:
- Formula: The formula for speed is Speed=TimeDistance.
- Units: Speed is typically measured in units like meters per second (m/s), kilometers per hour (km/h), miles per hour (mph), etc.
- Types of Speed: Average speed refers to the total distance traveled divided by the total time taken. Instantaneous speed is the speed at any particular instant.
Distance:
Distance is the measure of how far an object has moved or the length of the path traveled between two points. Important considerations for distance include:
- Units: Common units of distance include meters (m), kilometers (km), miles (mi), feet (ft), etc.
- Calculations: The distance between two points can be calculated using geometric formulas (e.g., Pythagorean theorem for straight-line distance) or using specific route distances in real-world scenarios.
Relationship between Time, Speed and Distance
The relationship between time, speed, and distance can be described by the formula:
- Distance = Speed × Time
This formula shows that the distance traveled is directly proportional to the speed and the time taken. Understanding this relationship is crucial for solving problems involving time, speed, and distance, such as calculating travel times, average speeds, or distances covered in various scenarios.
Applications
These concepts find applications in numerous fields:
- Transportation: Planning travel routes, estimating travel times, and designing efficient transportation systems.
- Sports: Measuring athletic performance and analyzing speed in various sports activities.
- Physics: Understanding motion, acceleration, and velocity of objects.
Engineering: Designing vehicles, optimizing traffic flow, and planning logistics.
Example: Rishi Kapoor can swim a certain course against the river flow in 84 minutes; he can swim the same course with the river flow in 9 minutes less than he can swim in still water. How long would he take to swim the course with the river flow?
Solution:
- Speed of Rishi Kapoor in still water, = 93 minutes/course (from 84).
- Speed of the river flow, minutes/course (from 84).
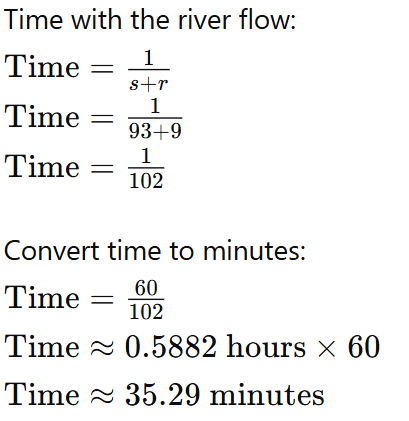
- Therefore, Rishi Kapoor would take approximately minutes to swim the course with the river flow.
Time and Distance - Examples
1. The fundamental relationship between Distance (s), time (t) and speed (v) is given by: s = v x t.
If x1 & x2 are the distances covered at velocities v1 & v2 respectively then the average velocity over the
entire distance (x1 + x2) is given by
6. For the same distance, the time is inversely proportion to the speed of the
object. These types of problems can be solved as the problems of
percentage.
Ex.1 If I decrease my speed by 20% of original speed, I reach office 7 minute late. What is my usual time and new time of reaching office?
Sol. Since speed is decreased by 20% i.e. of the original. New speed will become
of the original
speed. For the same distance, the time will become of original time. Therefore new time increase by
of the original. This is given equal to 7 minutes.
So Usual time = 7 × 4 = 28 minutes and New time = 28 + 7 = 35 minutes.
7. When time is constant the ratio of speeds of the object is equal to the ratio of the distance covered by
them i.e.
Ex.2 A train leaves Calcutta for Mumbai, a distance of 1600 kms at the same time a train leaves Mumbai to Calcutta. The trains meet at Nagpur which is at a distance of 700 kms from Mumbai. What is the ratio of the speeds of the trains?
Sol.
S1: Speed of the train leaving from Calcutta to Mumbai.
S2: Speed of the train leaving from Mumbai to Calcutta.
Given:
- Distance from Mumbai to Nagpur km.
- Distance from Calcutta to Nagpur (since the total distance between Calcutta and Mumbai is 1600 km).
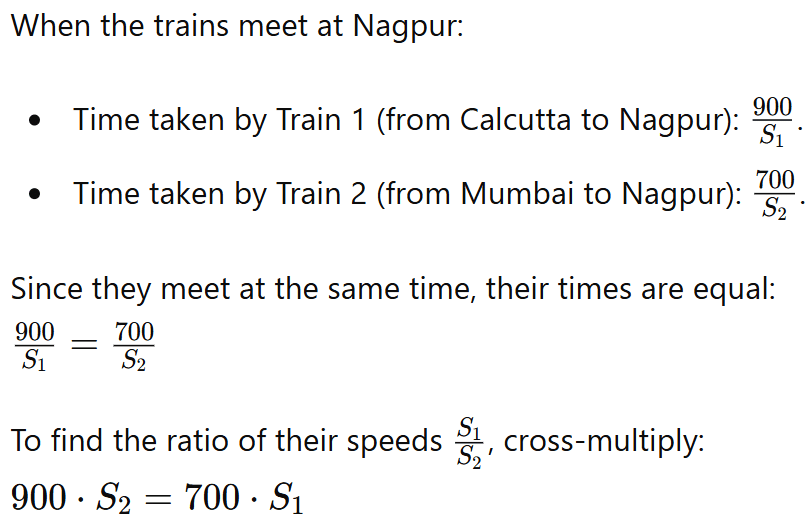

Ex.3 A train 110 m long travels at 60 kmph. How long does it take?
(a) To pass a telegraph post by the side of the track?
(b) To pass a man running at 6 kmph in the same direction as the train?
(c) To pass a man running at 6 kmph in the opposite direction?
(d) To pass a station platform 240 m long?
(e) To pass another train 170 m long, running at 40 kmph in the same direction?
(f) To pass another train 170 m long, running at 60 kmph in the opposite direction?
Sol. (a) Speed of train =
∴ Time taken to cross the telegraph post =
(b) Speed of man =
∴ Time taken to pass the man = Length of the train/ Relative velocity seconds.
(c) Time = Length of the train/ Relative velocity =
(d) Time = (Length of the train + Length of platform) / Relative velocity
21 seconds.
(e) Speed of the second train =
∴ Time = Sum of the length of the two trains/ Relative velocity
(f) Time = Sum of the length of the two trains/Relative velocity
Boats & Streams
Let Speed of boat in still water = b km/hr
Speed of stream = w km/hr
Speed of boat with stream (Down Stream), D = b + w
Speed of boat against stream (Up stream), U = b - w
Speed of boat in still water,
Speed of stream,
Ex.4 A man can row 4.5 km/hr in still water. It takes him twice as long to row upstream as to row downstream. What is the rate of the current?
Sol. Speed of boat in still water (b) = 4.5 km/hr.
It is given upstream time is twice to that of down stream.
⇒ Downstream speed is twice to that of upstream.
So b + u = 2(b - u)
Circular Motion
Circular Motion with two people
Ex.5 Sachin and Saurav, as a warm-up exercise, are jogging on a circular track. Saurav is a better athlete and jogs at 18km/hr while Sachin jogs at 9 km/hr. The circumference of the track is 500m (i.e. ½ km). They start from the same point at the same time and in the same direction. When will they be together again for the first time?
Sol. Method 1: Since Saurav is faster than Sachin, he will take a lead and
as they keep running, the gap between them will keep widening. Unlike
on a straight track, they would meet again even if Saurav is faster than
Sachin.
The same problem could be rephrased as “In what time would Saurav
take a lead of 500 m over Sachin”?
Every second Saurav is taking a lead of
over Sachin in Therefore, they would meet for the first time after 200
sec.
In general, the first meeting if both are moving in the same direction and
after both have started simultaneously occurs after
Method 2: For every round that Sachin makes, Saurav would have made 2 rounds because the ratio of
their speeds is 1 : 2. Hence, when Sachin has made 1 full round, Saurav would have taken a lead of 1
round. Therefore, they would meet after
Ex.6 Suppose in the earlier problem when would the two meet for the first time if they are moving in the opposite directions?
Sol. If the two are moving in the opposite directions, then
Relative speed = 2.5 + 5 = 7.5 m/s.
[Hence, time for the first meeting = Circumference / Relative speed
Ex.7 If the speeds of Saurav and Sachin were 8 km/hr and 5 km/hr, then after what time will the two meet for the first time at the starting point if they start simultaneously?
Sol.
Given:
- Saurav's speed 8 km/hr
- Sachin's speed 5 km/hr
They start simultaneously from the same point and we need to find out after what time they meet again at the starting point.
The relative speed between Saurav and Sachin when moving in opposite directions is
= 8+5 = 13km/hr.
They meet after covering the total distance of the track once, which is the sum of distances they cover individually before meeting.

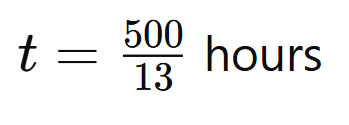
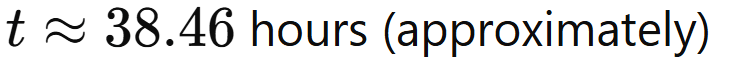
Therefore, Saurav and Sachin will meet at the starting point again after approximately hours.
Ex.8 Let us now discuss the cases of circular motion with three people: Laxman joins Saurav and Sachin, and all of them run in the same direction from the same point simultaneously in a track of length 500 m. Laxman moves at 3 km/hr, Sachin at 5 km/hr and Saurav at 8 km/hr. When will all of them be together again?
a. for the first time?
b. for the first time at the starting point?
Sol. (a) Break the problem into two separate cases.
In the first case, Saurav moves at the relative speed of (8 - 5) = 3 km/hr with respect to Sachin.
At a relative speed of 3 km/hr, he would meet Sachin after every = 600 sec = 10 min.
In the second case, Saurav moves at the speed of (8 - 3) km/hr = 5 km/hr with respect to Laxman.
At a relative speed of 5 km/hr, he would meet Laxman after every = 360 sec = 6 min.
∴ If all the three have to meet, they would meet after every [LCM (10, 6)] min = 30 min or ½ hour.
Hence, they would all meet for the first time after 30 min.
(b) If we need to find the time after which all of them would be at the starting point simultaneously for the
first time, we shall use the same method as in the case involving two people.
At a speed of 8 km/hr, Saurav takes 225 sec. to complete one circle.
At a speed of 5 km/hr, Sachin takes 360 sec. to complete one circle.
At a speed of 3 km/hr, Laxman would take 600 sec. to complete one circle.
Hence, they would meet for the first time at the starting point after
LCM (225, 360, 600) sec. = 1800 sec.
Ex.9 A thief is spotted by a policeman from a distance of 200 m. When the policeman starts a chase, the thief starts running. Speed of thief is 10 Kmph and that of policeman is 12 kmph. After how many hours will the policeman catch the thief?
Sol. 
Ex.10 A man steals a car at 1 : 30 pm & drives at 40 kmph. At 2 pm the owner starts chasing his car at 50 kmph. At what time does he catch the man?
Sol.
Time difference when owner starts chasing = 2:00 pm - 1:30 pm = 0.5 hours.
Distance covered by thief in 0.5 hours: Distance = Speed × Time = 40 km/h × 0.5 hours = 20 km.
Speed of owner = 50 km/h.
Time taken for owner to cover 20 km: Time = Distance / Speed = 20 km / 50 km/h = 0.4 hours.
Convert 0.4 hours to minutes: 0.4 hours × 60 minutes/hour = 24 minutes.
Therefore, the owner catches the thief at 2:00 pm + 24 minutes = 2:24 pm.
|
193 videos|169 docs|152 tests
|
FAQs on Solved Examples: Time & Distance - General Aptitude for GATE - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. How are time, speed, and distance related to each other when solving problems? |  |
| 2. How can I calculate the speed of an object if the distance traveled and time taken are known? |  |
| 3. How do I find the time taken to cover a certain distance if the speed is known? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the concept of relative speed in the context of time, speed, and distance problems? |  |
| 5. How can I use the concept of time, speed, and distance to solve real-life problems, such as calculating travel time or average speed? |  |

















