Tissues Class 9 Worksheet Science Chapter 6
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Fill in the blanks |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
| Crossword Puzzle |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1. Which of the following is a type of connective tissue that transports substances in the body?
(a) Bone
(b) Blood
(c) Cartilage
(d) Tendon
(b) Blood
Solution: Blood is a connective tissue that transports gases, nutrients, hormones, and waste materials throughout the body.
Q2. What is the main function of ligaments in the body?
(a) Connect muscles to bones
(b) Provide flexibility to bones
(c) Connect bones to other bones
(d) Store minerals like calcium and phosphorus
(c) Connect bones to other bones
Solution: Ligaments are a type of connective tissue that is highly elastic and helps in connecting one bone to another, providing strength and stability to joints.
Q3. Which of the following tissues is responsible for the transport of water and minerals in plants?
(a) Phloem
(b) Parenchyma
(c) Collenchyma
(d) Xylem
(d) Xylem
Solution: Xylem consists of tubular structures like tracheids and vessels, which transport water and minerals from the roots to other parts of the plant.
Q4. Which of the following tissues provides protection to organs and forms a barrier in the body?
(a) Muscular tissue
(b) Nervous tissue
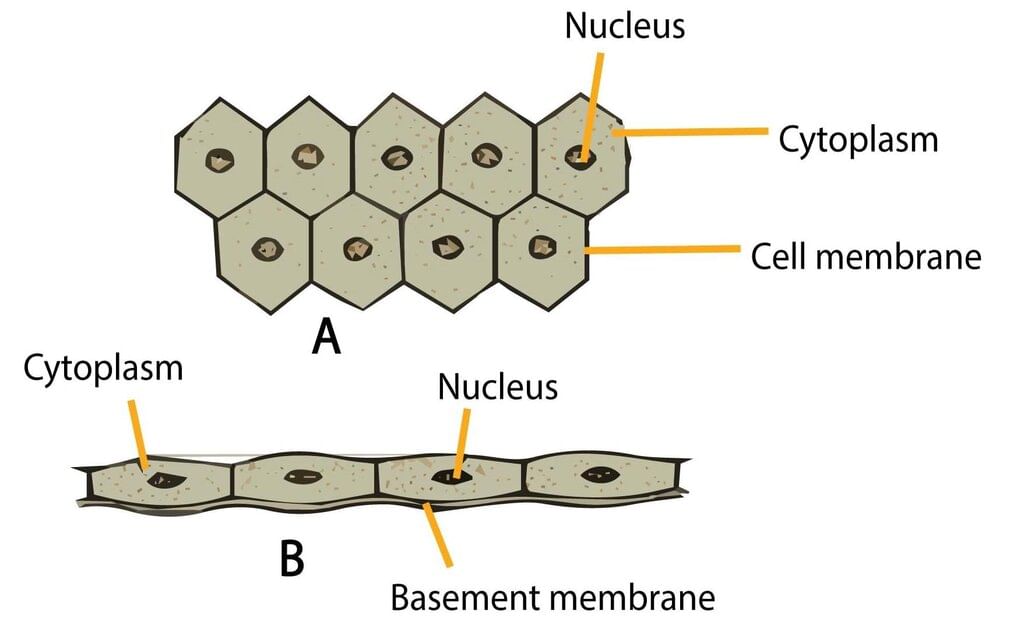
(c) Epithelial tissue
(d) Connective tissue
(c) Epithelial tissue
Solution: Epithelial tissue covers organs and cavities in the body, forming a continuous sheet that acts as a protective barrier and regulates material exchange.
Q5. Which of the following tissues makes the plant hard and stiff, and is found in the husk of a coconut?
(a) Parenchyma
(b) Collenchyma
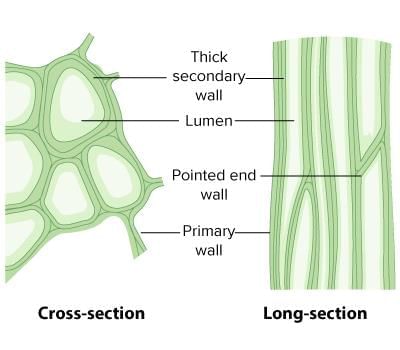
(c) Sclerenchyma
(d) Phloem
(c) Sclerenchyma
Solution: Sclerenchyma is a type of permanent tissue that provides strength and stiffness to plant parts. Its cells are dead with thick lignified walls, and it is found in stems, around vascular bundles, and in hard coverings like the husk of a coconut.
Fill in the blanks
(i) ________________ tissue is found between the skin and muscles, around blood vessels and nerves and in the bone marrow.
Areolar connective
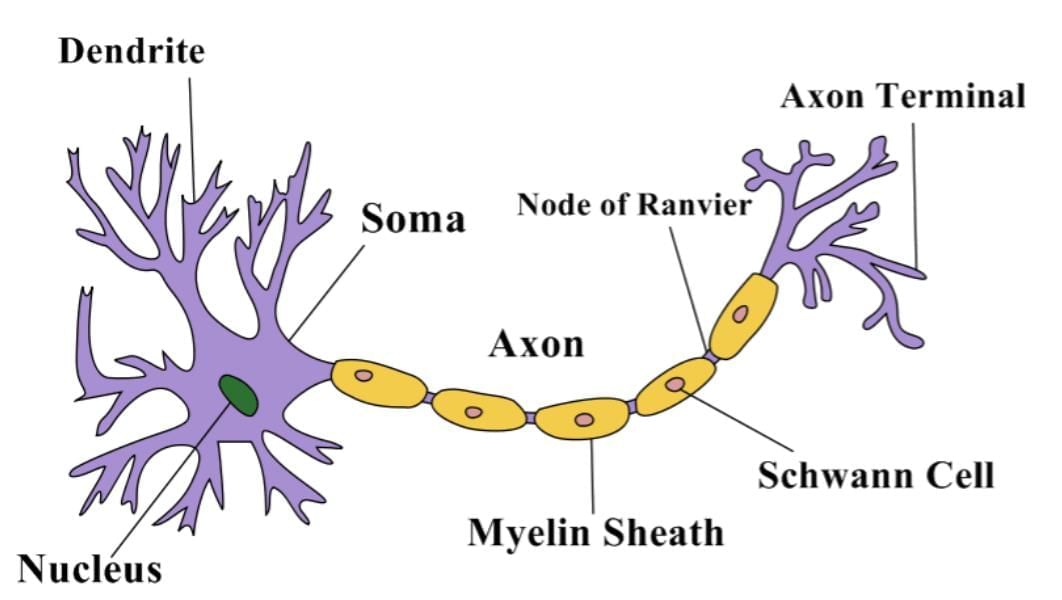
(ii) The signal that passes along the nerve fibre is called a _______________.
nerve impulse
(iii) Xylem and phloem together form a __________ in plants.
vascular bundle
(iv) __________ is the most common simple permanent tissue, consisting of unspecialized cells with thin cell walls.
Parenchyma
(v) The flexibility in plants is due to permanent tissue named ____________.
collenchyma
Short Answer Questions
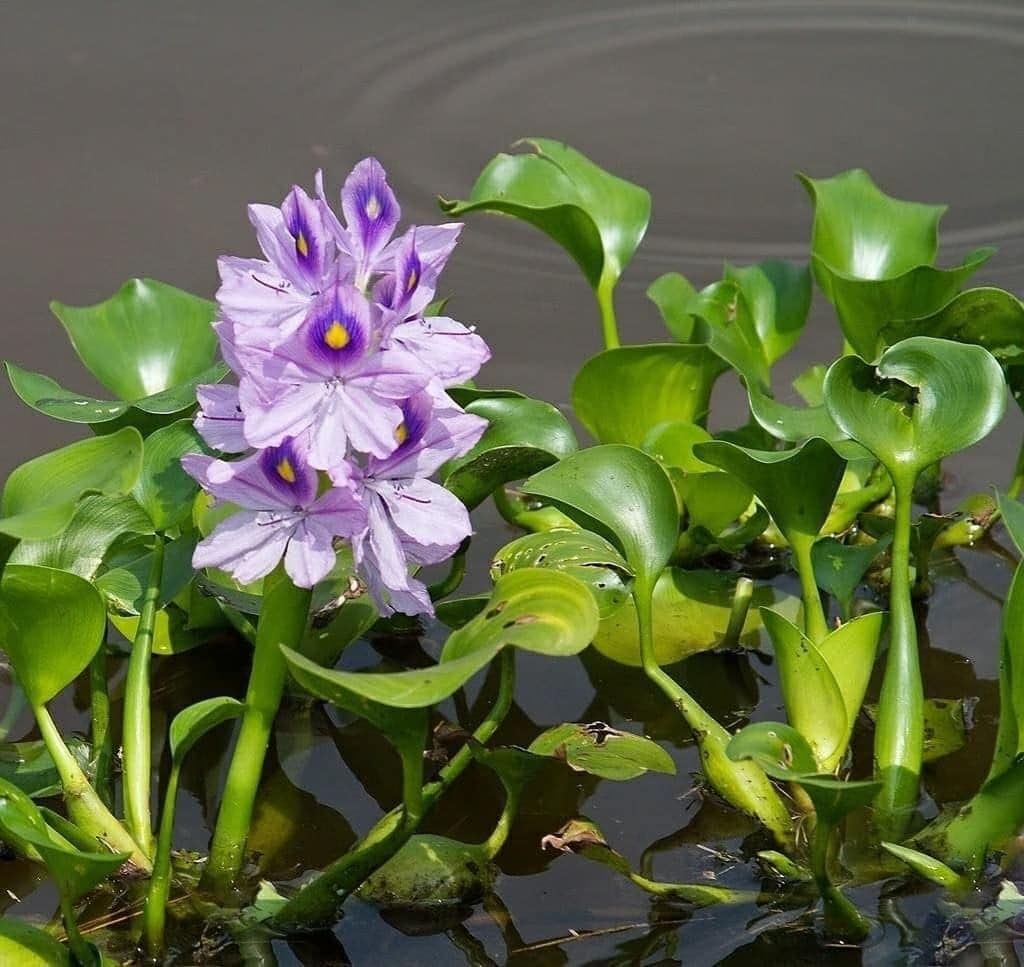
Q1. Water hyacinth floats on the water surface. Explain.
Water hyacinth floats on the surface of water due to presence of aerenchyma. It is modified form of parenchyma, which contains large air cavities. It provides buoyancy which helps water hyacinth in floating.
Q2. What are the different types of connective tissue?
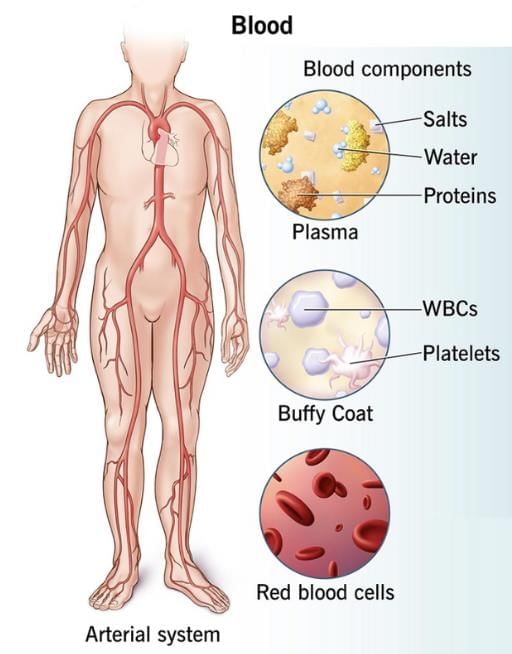
Blood – It has a fluid matrix (plasma) and transports gases, food, hormones, and waste materials.
Bone – A strong, non-flexible tissue that supports the body, anchors muscles, and protects organs.
Ligament – Connects bones to bones; it is elastic and strong with very little matrix.
Tendon – Connects muscles to bones; it is strong and fibrous but has limited flexibility.
Cartilage – Has a solid matrix of proteins and sugars; provides smoothness at joints and is found in the nose, ear, trachea, and larynx.
Areolar tissue – Found between skin and muscles and around organs; fills spaces and helps in repair.
Adipose tissue – Stores fat under the skin and around internal organs; also acts as an insulator.
Q3. Define the process of differentiation.
In a multicellular organism, cells become specialized to perform different functions. They take up a specific role and lose the ability to divide. As a result, they form a permanent tissue. This process of taking up a permanent shape, size, and a function is called differentiation. Differentiation leads to the development of various types of permanent tissues.
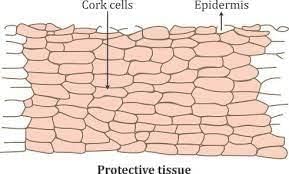
Q4. How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
In plants the secondary meristem cuts off many external layers of cells that are dead and arranged in a compact manner. Such layers together make cork. They have deposition of suberin which is very hard and impermeable hence protects plants from unfavorable conditions and microbial attack etc.
Q5. What are complex permanent tissues? Name their types and describe their functions.
Ans: Complex permanent tissues are made up of more than one type of cell that work together to perform a specific function. The two main types are xylem and phloem.
Xylem transports water and minerals vertically and is made of tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma, and xylem fibres.
Phloem transports food from leaves to other parts of the plant and is made of sieve cells, sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres, and phloem parenchyma.
Q6. If a potted plant is covered with a glass jar, water vapour appears on the wall of the glass jar. Explain why?
Plant always loose water from the surface of leaves. This process is known as transpiration. Water reaches leaves by xylem vessels, where evaporation takes place by stomata.
Q7. What is the utility of tissues in multicellular organisms?
There is a clear cut division of labour in multicellular organisms i.e. different parts of the body of a multicellular organism perform specific functions. For example, brain controls all other parts of body, heart pumps blood to all parts of body, kidneys remove waste materials from body, sense organs collect information from external sources for sensory perception etc. All these functions would never be possible without formation of tissues in multicellular organisms.
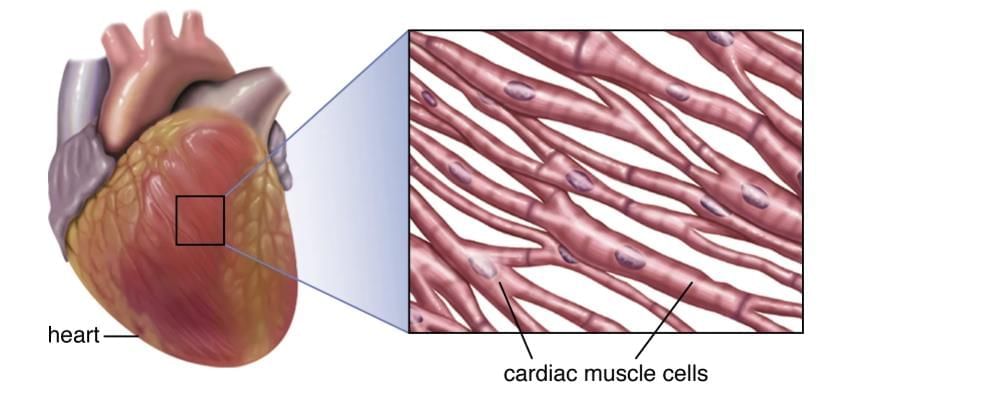
Q8. Give three features of cardiac muscles.
(1) Cardiac muscles are involuntary i.e. they don’t work under our will.
(2) Its cells are cylindrical, branched, striated and uninucleate.
(3) It shows rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout the person’s life.
Q9: What is glandular epithelium, and how is it formed?
Glandular epithelium is a type of epithelial tissue specialised to secrete substances. It is formed when a portion of the epithelial tissue folds inward to create a multicellular gland.
Q10. Draw a labelled diagram of a Neuron.
Crossword Puzzle
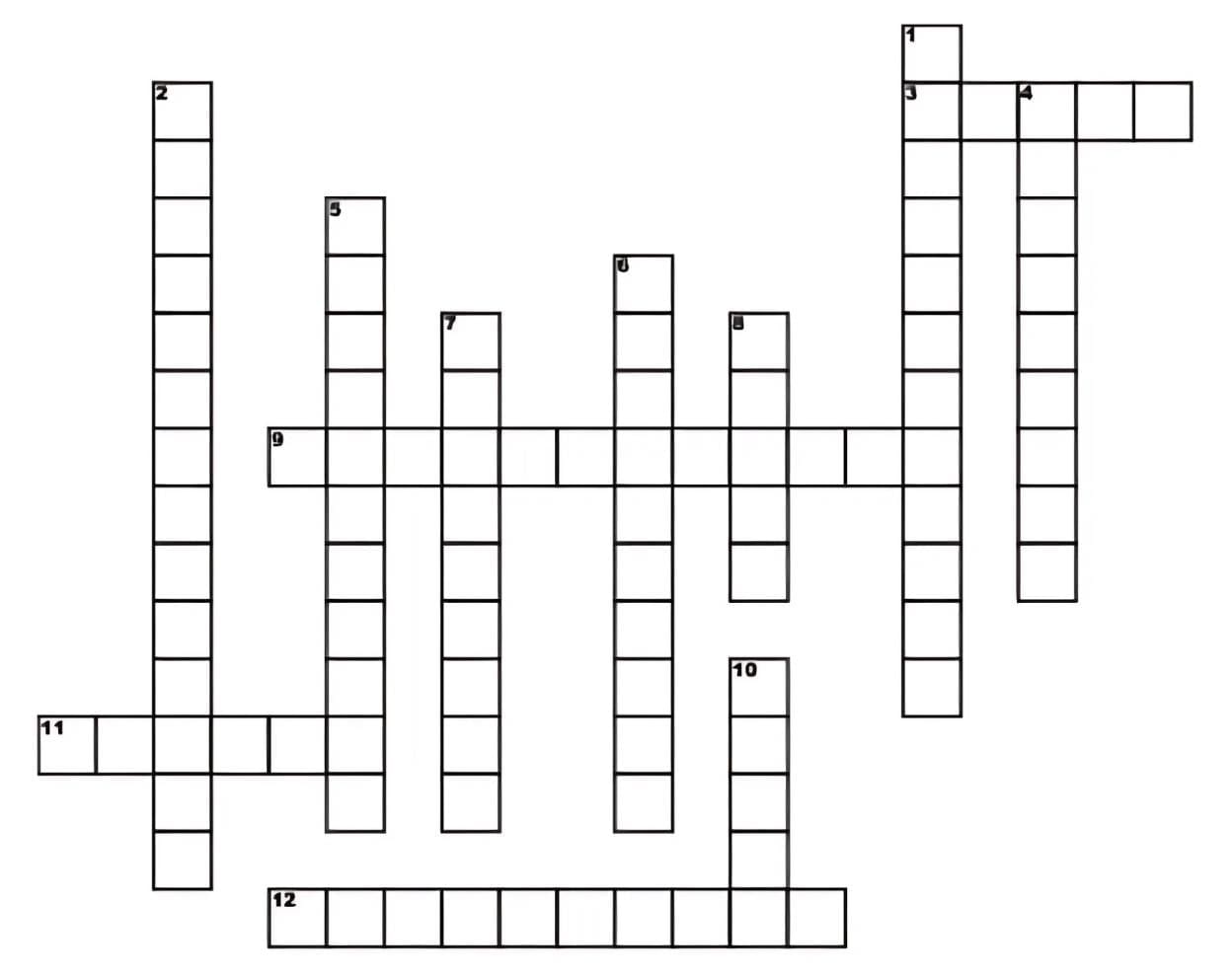
Across Clues
3. A component of the waxy outer coating of aquatic plant leaves.
9. Tissue responsible only for growth.
11. Conducts dissolved food materials produced by photosynthesis.
12. Most abundant of the cell types found in the major parts of higher plants.
Down Clues
1. Thick, tough secondary walls impregnated with lignin
2. Certain cells are associated with the sieve tube
4. Tubes with pits rather than openings at the ends
5. Provide flexible support for growing and mature plant organs. An extra primary wall in the corners
6. Parenchyma tissue with connected air spaces
7. Outermost layer of cells
8. Pairs of cells that border stomata
10. Chief conducting tissue of water and minerals
Answer
Across
3. Cutin
9. Meristem
11. Phloem
12. ParenchymaDown
1. Sclerenchyma
2. Companion
4. Tracheids
5. Collenchyma
6. Aerenchyma
7. Epidermis
8. Guard cells
10. Xylem
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Tissues Class 9 Worksheet Science Chapter 6
| 1. What are the main types of plant tissues? |  |
| 2. How do animal tissues differ from plant tissues? |  |
| 3. What is the function of xylem in plants? |  |
| 4. What role do epithelial tissues play in animals? |  |
| 5. Why is understanding plant and animal tissues important in biology? |  |