Transport in India- 2 | General Awareness - Bank Exams PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Water Transport |

|
| Inland Waterways in India |

|
| Shipping |

|
| Ports in India |

|
| Air Transport |

|
| Role of Airways in Regional Development |

|
| Challenges Faced by the Aviation Industry in India |

|
Water Transport
- Before Railways were developed, Inland Waterways were the main mode of transport.
- Waterways are the cheapest way to transport goods, especially heavy and bulky items with low specific costs.
- Water transport is fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly, with the potential to create many jobs.
- However, it has struggled against road and rail transport because it cannot match their speed.
- Currently, coastal and inland waterways account for 6% of India’s freight transport, while countries like Bangladesh ( 16%. and Thailand ( 12%. have a higher share of water-based transport, showing that India has room for improvement.
- The Central Government has exclusive control over shipping and navigation on inland waterways declared as ‘national waterways’ by Parliament. Other waterways are regulated by state governments or under the concurrent list

Inland Water Transport in India
- India has various options for Inland Water Transport (IWT), including rivers, canals, backwaters, creeks, and tidal inlets.
- There are over 5,000 km of navigable inland waterways in India that are being developed.
- IWT offers a competitive alternative with lower operating costs— 30% less than railways and 60% less than roads. It is also a sustainable mode for freight logistics and passenger transport.
- To harness IWT’s potential, the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) was established in 1986 to develop and regulate inland waterways.
- The government has identified important waterways as National Waterways to enhance the significance and efficiency of Inland Waterways.
- The National Waterways Act of 2016 expanded the number of National Waterways from five to 106.
- The major waterways identified in India, are as in the table below:
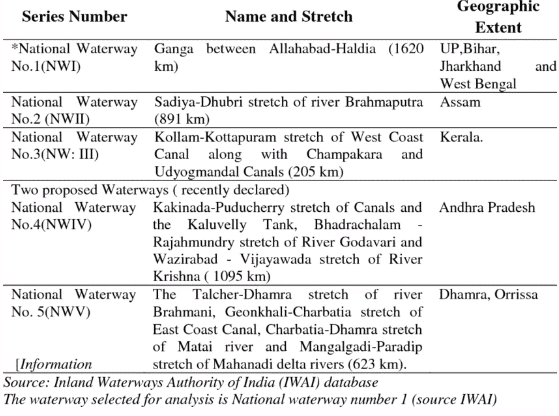
Inland Waterways in India
Current Initiatives:- Jal Marg Vikas Project (JMVP) for National Waterway-1 (NW-1).
- Arth Ganga and Arth Brahmaputra: Focus on holistic and sustainable development using NW-1 and NW-2 for freight and passenger transport.
- Inland Vessels Bill: Aims to regulate and promote inland water transport.
- Land Use Policy for Inland Waterways: Ensures optimal use of land adjacent to inland waterways.
- Dredging Policy for Inland Waterways: Facilitates regular dredging to maintain navigability.
- Promoting Private Participation: Encouraging private sector involvement in terminal operations and maintenance.
Growth in Cargo Transport:
- Total cargo transported through inland waterways reached 73.6 million tons per annum (MTPA) in 2019-20.
- Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 19% over the past five years.
Navigability in South India:
- Rivers in South India are often seasonal and less suitable for navigation.
- However, deltaic regions such as the Godavari, Krishna, Mahanadi, and the lower reaches of the Narmada and Tapi rivers are viable for waterways.
Navigable Canals:
- Buckingham Canal in Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu: A 413 km long canal facilitating water transport.
- Other navigable canals include the Son Canal, Odisha Canal, and Damodar Canal.
Advantages of Inland Waterways:
- Logistics Improvement:. coordinated inland waterways network can significantly enhance the logistics framework of the country.
- Road Decongestion: Waterways can alleviate congestion on roads and highways by transporting cargo via water.
- Land Acquisition Benefits: Waterways bypass the challenges of land acquisition, which often leads to delays and increased costs in projects.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Transporting goods via waterways is generally cheaper compared to other modes, lowering the point-to-point cost of goods.
- Fuel Efficiency:. study by RITES indicates the fuel efficiency of inland water transport, with one litre of fuel moving 215 tons through one kilometre on inland waterways, compared to 24 tons on road and 95 tons on rail.
Challenges in Inland Waterways Development:
- Channel Draft Variability: The draft of national waterways is not consistently 2 meters throughout the year, affecting navigability. Some rivers are seasonal and not navigable year-round.
- Dredging Requirements: Intensive capital and maintenance dredging is needed for identified waterways, which may face local resistance due to environmental concerns and potential displacement issues.
- Natural Obstacles: Waterfalls and sharp bends in rivers pose challenges for developing navigable waterways.
- Silting Issues: Silting reduces riverbed depth, complicating navigation. Desilting is a costly and challenging process.
- Water Diversion for Irrigation: Careful management of water diversion for irrigation is necessary to maintain adequate water levels in river channels.
Demand Growth: There needs to be an increase in demand for inland water transport to make it an economically viable transportation option. Measures Taken
Measures Taken
Indo-Myanmar Protocol: This protocol aims to establish multimodal connectivity between Kolkata and Mizoram via Myanmar. It offers a transit route that includes:
- Shipping from Kolkata to Sittwe Port:. distance of 539 kilometers.
- Inland Waterway Transport: From Sittwe to Paletwa (River Kaladan – 158 km), Paletwa to Indo-Myanmar border (Myanmar side – 110 km), and from the border to NH 54 at Lawngtlai (India – 100 km).
This route is faster and more efficient than the existing 'chicken neck' corridor through Siliguri.
Indo-Bangladesh Protocol: This protocol facilitates export and import trade between India and Bangladesh using National Waterways (NW-1 and NW-2). It enables riverine trade through Bangladesh, particularly benefiting Assam, as domestic movements on NW-2 between Assam and Haldia/Kolkata pass through a significant stretch in Bangladesh.
Linkage with Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFCs) and Sagarmala Project: The waterways are proposed to be linked with the eastern and western DFCs and the Sagarmala Project. This linkage aims to promote port-led development and facilitate the swapping/ shifting of commodities and cargo between waterways, DFCs, and road transport.
The inland waterway project is envisioned as part of a broader ambition to connect several major infrastructure projects.
Actions Needed:
- Micro-Level Studies: Conduct detailed micro-level studies for each riverine system to assess viability and identify specific challenges before implementation.
- Coordinated Strategy: Develop a coordinated strategy that complements the national waterways network with other non-declared waterways and integrates them with road and rail networks.
- Address Local Concerns: Consider local needs, competing uses, and potential resistance while working closely with local governments to ensure smooth implementation.
- Stakeholder Coordination: Foster collaboration among various stakeholders, including government agencies at all levels, to streamline decision-making and project execution.
- Pilot Projects: Implement pilot projects to test the viability of proposed waterways and gather insights for broader application.
- Capacity Building: Enhance the capacity of local administration and stakeholders involved in the management and development of waterways.
- Continuous Monitoring: Establish a mechanism for continuous monitoring and evaluation of implemented projects to ensure they meet the desired objectives and can be scaled up effectively.
Shipping
- Historical Context: India has a rich history of maritime trade dating back to ancient times, with Indian boats and ships sailing in the Indian Ocean for over 4,000 years, trading with the Middle East.
- Current Role: Today, shipping is a crucial component of India's transport sector, with nearly 90% of the country's trade volume (77% by value) being moved by sea. This makes shipping a backbone of trade and economic growth.
- Merchant Fleet: India now boasts the largest merchant shipping fleet among developing countries.
Coastal Shipping:
- Overview: Coastal shipping involves the movement of goods and passengers between ports within a country. India, with its long coastline and resilient domestic economy, has the potential to develop a substantial coastal shipping industry.
- Current Scenario: Domestic movement of goods in India is primarily through road, followed by railways, with coastal shipping accounting for a meager share. Currently, coastal shipping in India mainly handles Petroleum, Oil and Lubricants (POL), coal, and iron ore, which constitute approximately 80% of the total coastal movement.
- Potential Benefits: Coastal shipping can significantly reduce logistics costs and enhance economic development, as evidenced by experiences in developed regions like the European Union. For instance, the cost of coastal movement of cargoes in the EU was about 20% and 40% that of road and rail movement, respectively. India can capitalize on its long coastline to develop this sector further.
Challenges: The shipping industry in India faces several challenges, including:
- Institutional Challenges: Bureaucratic rigidity, overlapping governmental powers, and lack of a single-window clearance system hinder progress.
- Infrastructural Challenges: Urgent capacity increases are needed for major and minor ports, and Indian cargo cycle times need to be competitive globally. Additionally, road network development, electricity, and overall infrastructural improvement are essential.
- Financial Challenges: High taxes such as Customs Duty on Bunkers, Landing Fees, and Income Tax without significant exemptions burden the shipping industry.
- Vessel Size: The trend of larger vessels due to rising demand poses challenges, as many ports in India struggle to accommodate these ships.
Recent Measures: The Indian government has taken steps to support the shipping industry, such as:
- Approving a scheme to provide Rs 1,624 crore over five years as a subsidy to Indian shipping companies participating in global tenders for government cargo.
- Implementing the Sagarmala Project, which aims to leverage the country’s coastline and inland waterways for industrial development. This project includes modernizing port infrastructure, improving port connectivity, and creating coastal economic zones to promote port-led industrialization.
- Potential Impact of Sagarmala: The Sagarmala Project could boost India’s merchandise exports to $110 billion by 2025 and create an estimated 10 million new jobs.
Importance of Sagarmala: Given India's strategic location along key international trade routes in the Indian Ocean and its extensive coastline of over 7,000 km, projects like Sagarmala are crucial for enhancing port capacity and modern facilities. This will reduce shipping times, lower transport costs, and increase India's share in global trade. Transport costs in India currently account for 18% of GDP, compared to less than 10% in China, highlighting the need for efficient logistics solutions.
Ports in India
Major Ports: There are 13 major ports in India, which are under the supervision of the Central Government. These ports handle about 90% of India's foreign trade. The major ports on the west coast include:- Mumbai
- Jawaharlal Nehru Port
- Kandla
- Marmagao
- Mangalore
- Kochi
The major ports on the east coast are:
- Kolkata/Haldia
- Paradwip
- Vishakapatnam
- Chennai
- Ennore
- Tuticorin
Minor Ports: There are around 200 medium and small ports in India, which are managed by the concerned state governments. These ports play a crucial role in handling the remaining portion of foreign trade and domestic cargo.
Port Development: The Indian government is focusing on enhancing port infrastructure and capacity to handle larger vessels and increase efficiency. Initiatives include the Sagarmala Project, which aims to modernize port facilities, improve connectivity, and promote coastal economic zones.
Air Transport
- Air Transport is the quickest way to get from one place to another, making the world feel much smaller and closer together.
- This type of transport is crucial when speed and time are really important.
- For a big country like India, with its long distances and varied landscapes and weather, air transport is very necessary.
- Air travel in India started in a small way in 1911, when mail was flown over a short distance of 10 kilometers between Allahabad and Naini.
- In 1933, the Indian National Airways began air services between Karachi and Lahore.
- When India became independent, there were four main air transport companies: Tata Sons Limited/Air India, Indian National Airways, Air Services of India, and Deccan Airways.

Airport Authority of India (AAI):
- The Airport Authority of India (AAI) is in charge of making sure air traffic in India is safe and efficient. They also handle aeronautical communication to help control air traffic across the whole Indian airspace.
- The AAI manages Indian airspace, including areas beyond the country’s borders, following guidelines from the International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO).
- The AAI’s International Airports division develops and operates international airports in India. They are working on building new terminal complexes and upgrading runways and terminal buildings at various international airports.
- However, improving airport infrastructure requires a lot of money, and the government cannot fund it all by itself.
- To address this, the government is encouraging private investors, both domestic and foreign, as well as Non-Resident Indians (NRIs), to participate in the improvement process.
India Aviation Industry:
- In 2017, India had the third-largest civil aviation market in the world.
- By2030, India is expected to surpass China and the United States in civil aviation, according to the International Air Transport Association (IATA).
- Despite this growth, a lot of India’s aviation potential is still untapped.
- Major airlines in India, in order of market share, include IndiGo, Air India, SpiceJet, and GoAir.
- The Ministry of Civil Aviation oversees civilian aviation in India, with regulatory oversight provided by the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA).
Role of Airways in Regional Development
- Aviation Sector as a Growth Catalyst: The aviation sector serves as a central hub for various activities. Airports act as growth poles, stimulating regional development through spillover and trickle-down effects.
- Boost to Tourism: Airways significantly enhance the tourism sector, which in turn drives the development of supporting infrastructure such as roads, railways, hotels, and markets.
- Local Skill Enhancement and Information Diffusion: The influx of tourists facilitates the exchange of views and information between tourists and locals, leading to the enhancement of local skills and the creation of new employment opportunities.
- Patronage for Local Art: Increased air connectivity boosts patronage for local art, contributing to the regional economy.
- Highlighting Local Issues: Improved connectivity with remote areas helps highlight local issues, attracting government attention for redressal. This prevents extreme regionalism and isolation.
Challenges Faced by the Aviation Industry in India
Shortage of Trained Employees: There is a significant lack of trained and skilled personnel in the aviation sector, leading to intense competition for employees and driving wages to unsustainable levels.
Regional Connectivity: Despite the presence of numerous airlines, regional connectivity remains a challenge due to the insufficient number of airports and the necessary supporting infrastructure.
Rising Fuel Prices: Jet fuel costs constituted about 45% to 50% of total operational costs in 2018, posing significant operational challenges for airlines.
Declining Yields: Pricing and yield are crucial for airline operations. Commercial liberalization has intensified competition, leading to a reduction in real yields for airline companies.
Gaps in Infrastructure: Airport infrastructure and Air Traffic Control (ATC) systems are inadequate to support development. While efforts are being made to redesign the infrastructure, noticeable improvements will take time.
Technical Challenges: The Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) industry in India is underdeveloped, affecting the cost-effective maintenance of aircraft. Additionally, the lack of a domestic aircraft manufacturing base results in increased imports, making operations more capital-intensive.
|
365 videos|701 docs|149 tests
|
FAQs on Transport in India- 2 - General Awareness - Bank Exams
| 1. What are the different modes of transport in India? |  |
| 2. Which is the largest mode of transport in India? |  |
| 3. How extensive is the railway network in India? |  |
| 4. Are waterways extensively used for transportation in India? |  |
| 5. How is air travel in India? |  |
















