Transportation in Animals and Plants Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 7
| Table of contents |

|
| Circulatory System |

|
| Blood |

|
| Blood Vessels |

|
| Heart |

|
| Excretion in Animals |

|
| Excretory System in Humans |

|
| Transport of Substances in Plants |

|
| Transport of Water and Minerals |

|
Every living thing, including animals and plants, needs food, water, and oxygen to stay alive. But how do these important substances move around in their bodies? And how do animals get rid of waste? The heart and blood vessels play a big role in this process, working together as the circulatory system. In this chapter, we will explore how substances are transported within animals and plants, helping them survive and stay healthy
Circulatory System
The circulatory system is like the body's transportation network. It carries important substances like oxygen, nutrients and water to every part of the body. It also helps remove waste products.
Main Parts of the Circulatory System:
- Heart: Pumps blood throughout the body.
- Blood: A liquid that transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste.
- Blood Vessels: Pathways for blood to flow to different parts of the body.
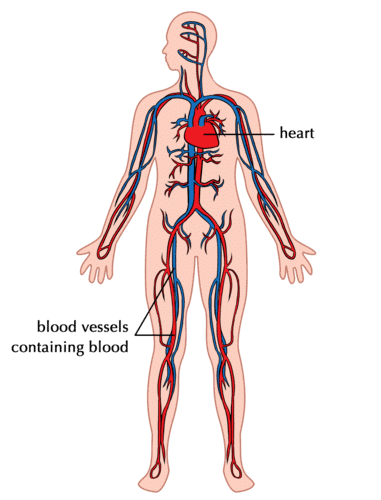 Circulatory System
Circulatory System
Let's discuss each of the main parts of Circulatory System in detail:
Blood
Blood is a fluid in the body that plays a key role in the circulatory system. It is responsible for transporting oxygen from lungs to the cells throughout the body. It also carries waste products, like carbon dioxide, away from the cells. This process allows waste products to be removed from the body.
Components of Blood are:
- Plasma
- Red Blood Cells
- White Blood Cells
- Platelets
Let's learn about each of them in detail:
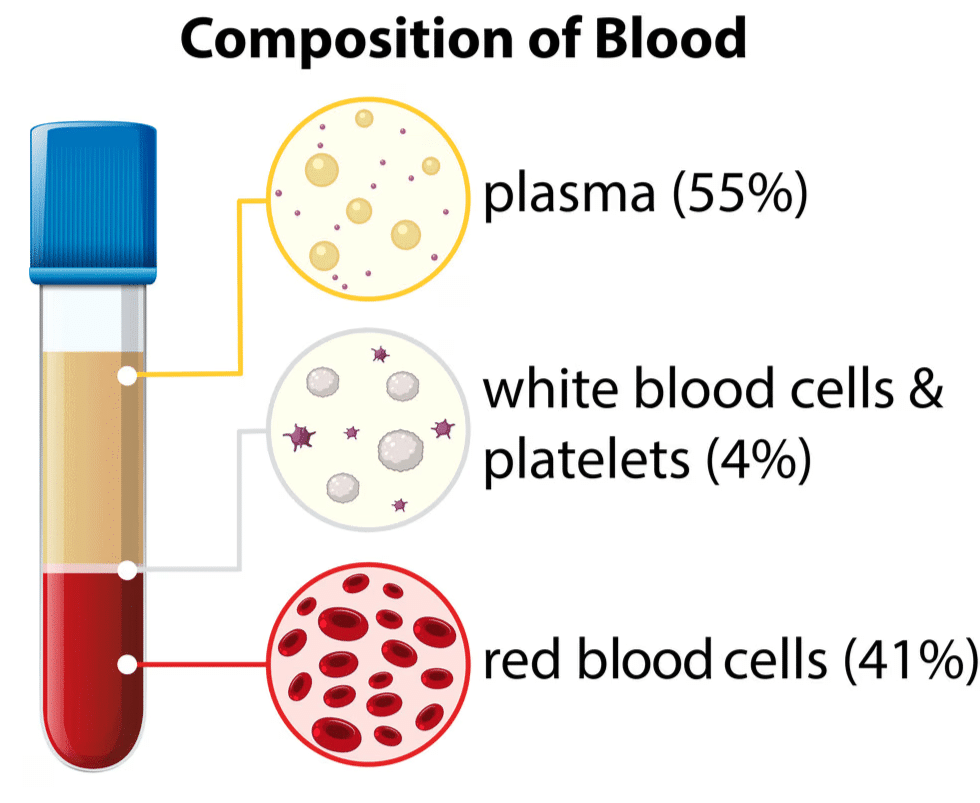 Components of Blood
Components of Blood
Plasma:
- The liquid part of blood.
- Transports nutrients, hormones, and waste products.
Red Blood Cells (RBCs):
- Contain hemoglobin, an iron-based pigment that binds with oxygen.
- RBCs carry oxygen to the body and bring carbon dioxide back to the lungs for exhalation.
- Hemoglobin gives blood its red color.
White Blood Cells (WBCs):
- Protect the body by fighting infections caused by bacteria and viruses.
- Act as the body’s defense system.
Platelets:
- Tiny fragments that help in blood clotting.
- Prevent excessive bleeding when there is an injury.
- Low platelet count can cause excessive bleeding and be life-threatening.
Blood Vessels
Blood flows through narrow pipe-like structures in the body, known as blood vessels. These blood vessels transport food, oxygen and waste within the body.
- Different types of blood vessels transport important things like oxygen.
- When we breathe in, oxygen fills our lungs.
- This oxygen needs to be delivered to every part of the body.
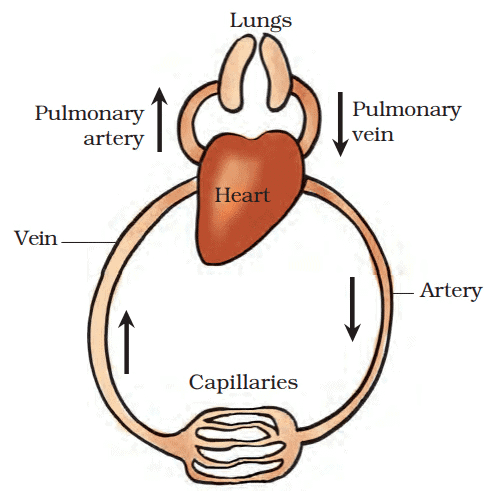
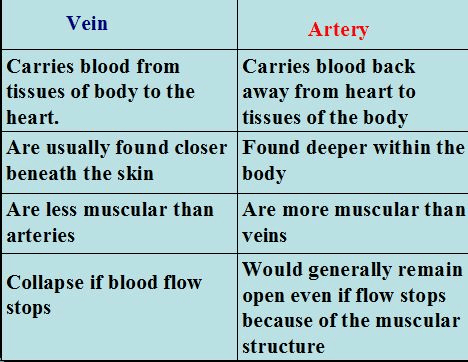
- Blood vessels called arteries carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
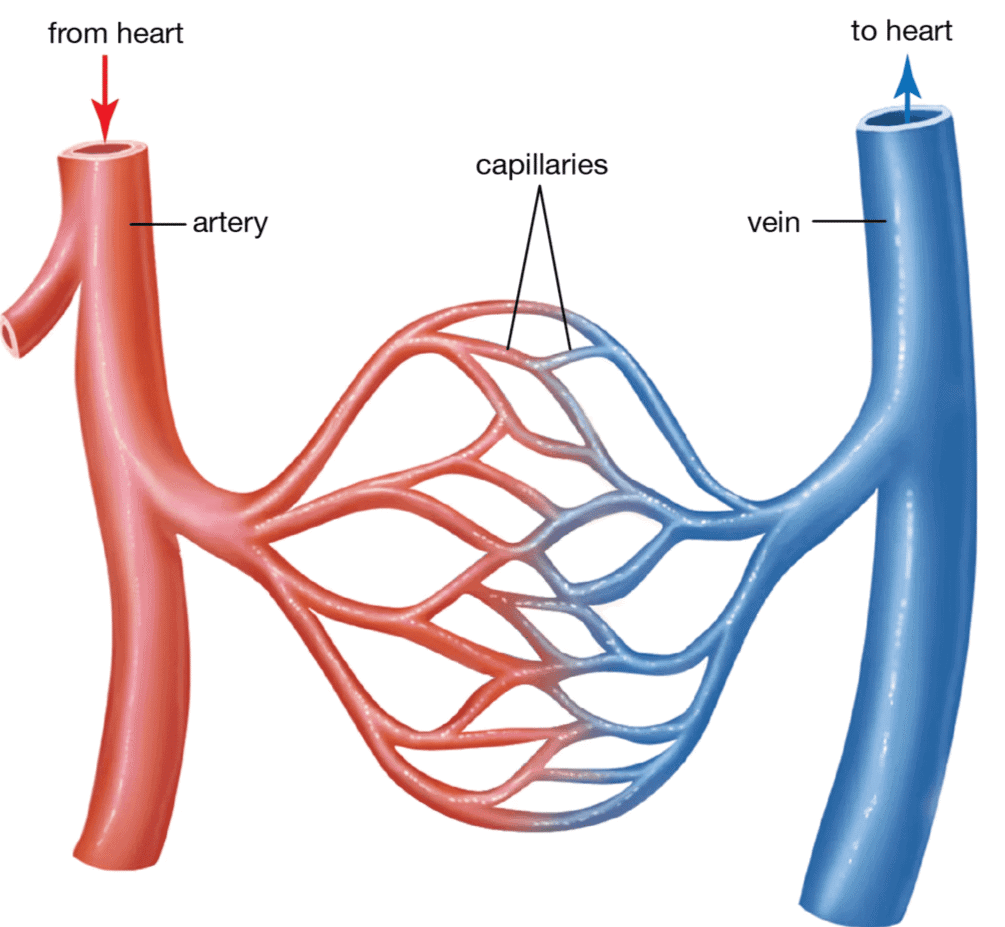 Blood Vessels
Blood Vessels
Types of Blood Vessels:
Types of Blood Vessels are:
- Arteries
- Veins
- Capillaries
Let's learn about each of them in detail:
1. Arteries:
- These blood vessels carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to the rest of the body.
- Arteries have thick and stretchy walls because the blood inside them moves very fast and under a lot of pressure.
Pulse: The pulse is the throbbing you feel when you place your fingers on certain parts of your body, like your wrist or neck.

- This throbbing happens because your heart is pumping blood through your arteries.
- The pulse is the result of that blood moving through the vessels.
Pulse Rate
- The pulse rate is the number of times you feel the pulse in one minute.
- It tells you how fast your heart is beating.
- For most people who are resting, the pulse rate is usually between 72 and 80 beats per minute.
- Your pulse rate can change depending on your activity level, emotions, or overall health.
2. Veins:
- Veins carry blood that is low in oxygen and full of waste products back to the heart.
- Blood moves through the body and collects waste materials like carbon dioxide from the cells.
- This used blood needs to return to the heart to be sent to the lungs. In the lungs, carbon dioxide is removed when we breathe out.
- Veins are the blood vessels that carry this blood back to the heart.
- Pulmonary artery carries blood from the heart. It carries carbon dioxide-rich blood to the lungs.
- Pulmonary vein carries oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the heart.
3. Capillaries:
- Capillaries are extremely thin blood vessels that form a network between the arteries and veins.
- When arteries reach the tissues, they divide into these tiny capillaries.
- The capillaries come together to create veins. These veins then carry blood back to the heart.
Heart
The heart is a vital organ that acts like a pump for the body.
- Its primary job is to ensure continuous blood circulation through the blood vessels.
- This process allows oxygen and nutrients to reach every part of the body while removing waste products like carbon dioxide.
Location and Size of the Heart
- Location: The heart is located in the chest, slightly to the left side.
- Size: It is roughly the size of your fist, making it compact yet powerful enough to perform its essential function.
Structure of the Heart
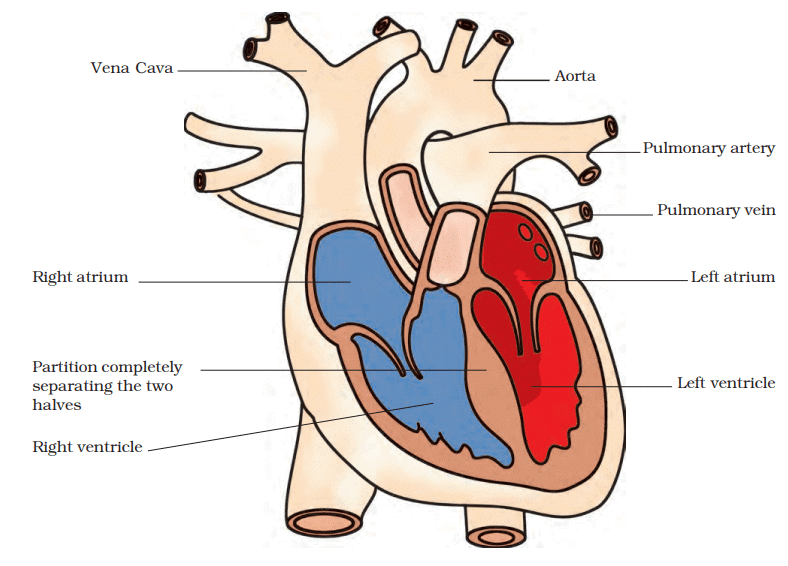
1. Four Chambers:
- The heart has four chambers to prevent the mixing of oxygen-rich blood with carbon dioxide-rich blood.
- The upper two chambers are called atria (singular: atrium).
- The lower two chambers are called ventricles.
2. Function of the Wall:
- A wall, or septum, separates the left and right sides of the heart.
- This wall ensures that oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and carbon dioxide-rich blood from the body do not mix.
Direction of Blood Flow
Blood flow in the heart is unidirectional, meaning it follows a specific path:
- From the Heart to the Lungs: Oxygen-poor blood is pumped from the heart to the lungs where it picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide.
- Back to the Heart: Oxygen-rich blood returns to the heart from the lungs.
- Pumped to the Body: The heart then pumps this oxygenated blood to the rest of the body through arteries.
Heartbeat
A heartbeat is the sound and rhythm made by your heart as it pumps blood through your body.
- Heart Muscles: The walls of the heart are made up of strong muscles that contract and relax rhythmically to produce heartbeats.
- How to Recognize a Heartbeat: You can feel the heartbeat by placing your palm on the left side of your chest.
- Stethoscope: A device used to amplify the sound of a heartbeat. It has a chest piece with a sensitive diaphragm.
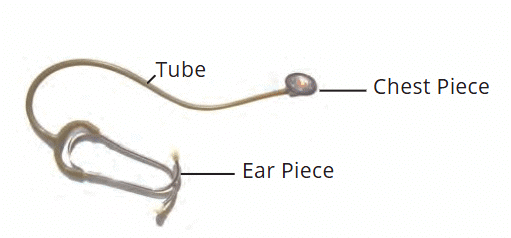 Stethoscope
Stethoscope
- Importance of Heartbeat: Regular beating of the heart ensures continuous blood circulation, delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body while removing waste.
Do Sponges and Hydra Have Blood?
- No Circulatory System: Sponges and Hydra do not have a circulatory system or blood like humans.
- How They Survive:
- They live in water, which:
- Brings food and oxygen directly into their bodies.
- Removes waste and carbon dioxide as water flows out.
- Why They Don’t Need Blood: The movement of water fulfills their transport needs, making a circulatory system unnecessary.
Excretion in Animals
The cells in the body perform various activities. Waste products such as urea, uric acid and excess water are formed and have to be removed from the body. The process of the removal of waste produced in the cells in living organisms is called excretion. The organs that help in the process of excretion constitute the excretory system.
Excretory Products in Animals
- Aquatic animals like fishes excrete ammonia, which dissolves directly in water.
- Some terrestrial animals such as birds, lizards, and snakes excrete a semi-solid, white compound known as uric acid.
- Humans primarily excrete urea as their major excretory product.
Excretory System in Humans
The excretory system is vital for maintaining health by removing waste products and excess substances from the blood.
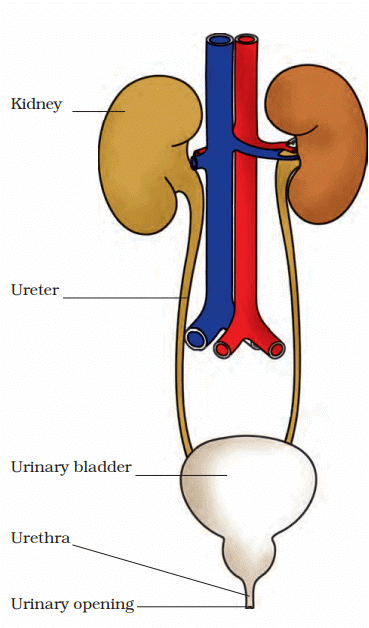
How Blood is Filtered?
Role of Kidneys:
- Blood is filtered in the kidneys through tiny blood vessels called capillaries.
- Harmful substances such as urea, extra salts, and toxins are removed.
- Useful substances like water and nutrients are reabsorbed into the blood.
Formation and Flow of Urine
- Formation in Kidneys: The harmful substances filtered from the blood combine with water to form urine.
- Transport Through Ureters: Urine travels from the kidneys to the urinary bladder via narrow tubes called ureters.
- Temporary Storage in Urinary Bladder: The bladder stores urine temporarily and stretches as it fills. This stretch signals the need to urinate.
- Elimination via Urethra: When the bladder is full, urine is expelled through the urethra, a muscular tube connecting the bladder to the outside.
Urine Composition and Output
- An adult passes about 1 to 1.8 liters of urine every 24 hours.
- 95% water, 2.5% urea, and 2.5% other waste products.
Note: The functioning of the kidneys stops when there is an infection. This is known as kidney failure.
As a result, waste products remain in the blood. When blood is not filtered, survival becomes difficult, so it is filtered through an artificial kidney. The process is called Dialysis. The artificial kidney is called a dialysis machine.
Sweating and it's purpose
- Sweat consists of water and salts. In summer, white patches can form on clothes, notably in areas like underarms, due to salts present in sweat.
- Sweat serves another purpose. Similar to how water evaporating from the pores of an earthen pot (matka) cools the pot, sweat evaporating from our skin helps in cooling our bodies.
Transport of Substances in Plants
Plants make their own food by taking in carbon dioxide from the air, minerals and water from the soil. They release oxygen and water vapour and the process is termed Photosynthesis. Plants get energy from the food to perform vital activities. Food and water are transported to various cells in the body.
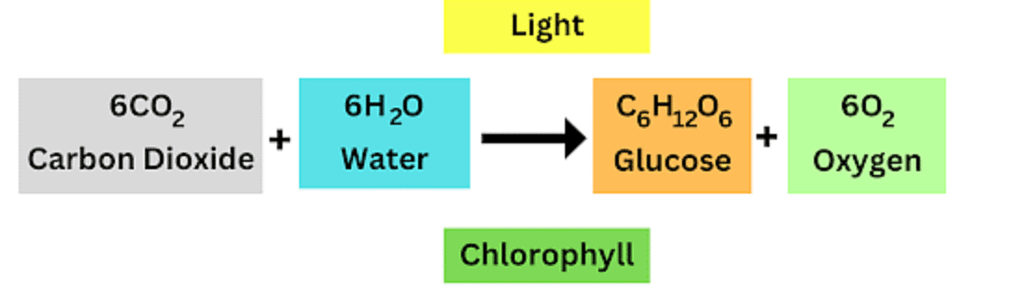 Photosynthesis equation
Photosynthesis equation
Transport of Water and Minerals
Water Absorption by Roots
- Plants absorb water and minerals through root hairs, tiny structures that increase the root's surface area.
- Root hairs directly contact water between soil particles for better absorption of nutrients.
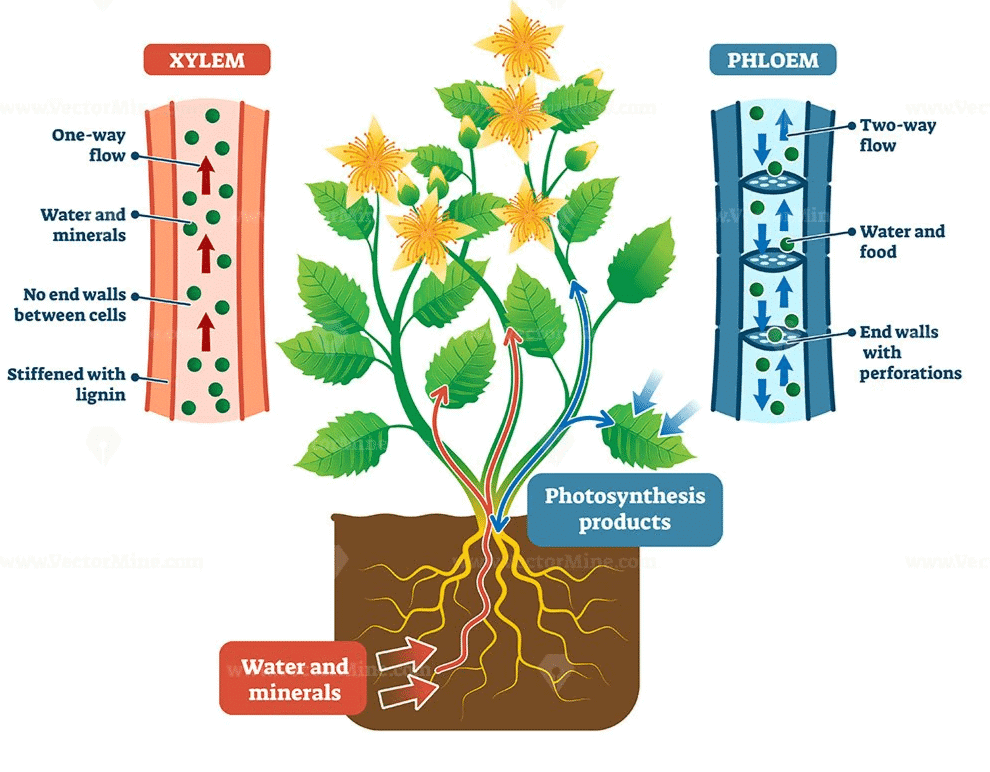 Xylem and PhloemRole of Xylem
Xylem and PhloemRole of Xylem
- Xylem: Specialized vascular tissue that transports water and minerals from roots to other parts of the plant.
- Forms a continuous network of channels connecting roots, stems, branches, and leaves.
Transport Across the Plant
- Water and minerals move throughout the plant via xylem.
- Phloem: Another vascular tissue responsible for transporting food produced in leaves to all parts of the plant.
Importance of Xylem and Phloem
- Both xylem and phloem work together to provide water, nutrients, and food, ensuring the plant stays healthy and grows efficiently.
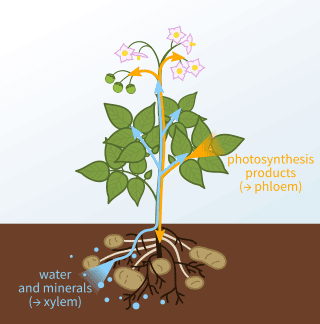
Transpiration
- Transpiration is the process where plants release water vapor into the air through small openings on their leaves called stomata.
- It helps plants cool down and remove excess water, similar to sweating in humans.
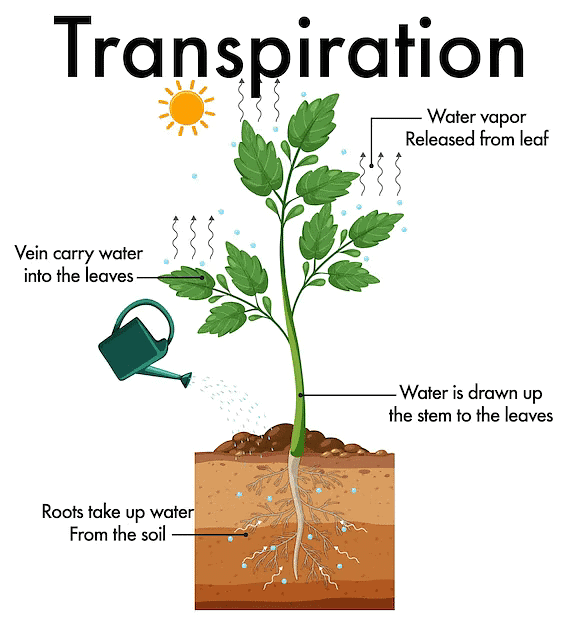
Role in Water and Nutrient Transport
- The loss of water from leaves creates a suction force, known as transpiration pull, which:
- Draws water and minerals from the roots to other parts of the plant.
- Allows water to reach even the tallest trees.
How Transpiration Happens
- Water absorbed by roots moves up to the leaves.
- Only a small amount of water is used to make food; the rest is released as water vapor through stomata.
Effects of Transpiration
Cooling Effect:
- Adds moisture to the atmosphere, cooling the surrounding environment.
Suction Force:
- Helps the plant absorb more water and minerals from the soil, ensuring proper hydration and nutrition.
We learned how animals use their circulatory system to move blood, nutrients, and wastes. Plants use xylem and phloem to transport water, nutrients, and food. These systems are vital for the survival and function of all living organisms.
|
112 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Transportation in Animals and Plants Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 7
| 1. What are the main components of the circulatory system in humans? |  |
| 2. How does excretion occur in animals? |  |
| 3. What role does the heart play in the circulatory system? |  |
| 4. How do plants transport water and minerals? |  |
| 5. What is the structure and function of blood vessels? |  |
















