Types of Graphs in Graph Theory | Engineering Mathematics - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Types of Graphs
Though, there are a lot of different types of graphs depending upon the number of vertices, number of edges, interconnectivity, and their overall structure, some of such common types of graphs are as follows:
1. Null Graph
- A null graph is a graph in which there are no edges between its vertices. A null graph is also called empty graph.
Example:
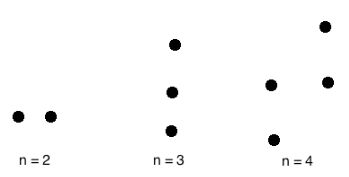
A null graph with n vertices is denoted by Nn.
2. Trivial Graph
- A trivial graph is the graph which has only one vertex.
Example:
In the above graph, there is only one vertex 'v' without any edge. Therefore, it is a trivial graph.
3. Simple Graph
- A simple graph is the undirected graph with no parallel edges and no loops.
- A simple graph which has n vertices, the degree of every vertex is at most n -1.
Example:
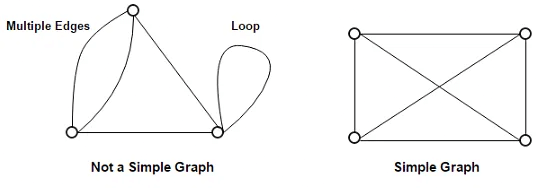
In the above example, First graph is not a simple graph because it has two edges between the vertices A and B and it also has a loop.
Second graph is a simple graph because it does not contain any loop and parallel edges.
4. Undirected Graph
- An undirected graph is a graph whose edges are not directed.
Example:
In the above graph since there is no directed edges, therefore it is an undirected graph.
5. Directed Graph
- A directed graph is a graph in which the edges are directed by arrows.
- Directed graph is also known as digraphs.
Example:
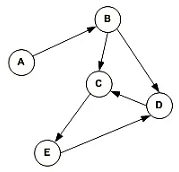
In the above graph, each edge is directed by the arrow. A directed edge has an arrow from A to B, means A is related to B, but B is not related to A.
6. Complete Graph
- A graph in which every pair of vertices is joined by exactly one edge is called complete graph. It contains all possible edges.
- A complete graph with n vertices contains exactly nC2 edges and is represented by Kn.
Example:
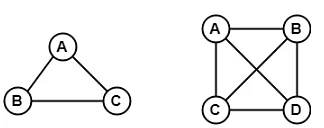
In the above example, since each vertex in the graph is connected with all the remaining vertices through exactly one edge therefore, both graphs are complete graph.
7. Connected Graph
- A connected graph is a graph in which we can visit from any one vertex to any other vertex. In a connected graph, at least one edge or path exists between every pair of vertices.
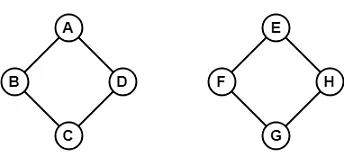
Example:
In the above example, we can traverse from any one vertex to any other vertex. It means there exists at least one path between every pair of vertices therefore, it a connected graph.
8. Disconnected Graph
- A disconnected graph is a graph in which any path does not exist between every pair of vertices.
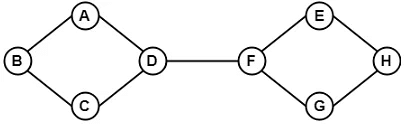
Example:
The above graph consists of two independent components which are disconnected. Since it is not possible to visit from the vertices of one component to the vertices of other components therefore, it is a disconnected graph.
9. Regular Graph
- A Regular graph is a graph in which degree of all the vertices is same.
- If the degree of all the vertices is k, then it is called k-regular graph.
Example:
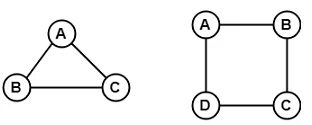
In the above example, all the vertices have degree 2. Therefore they are called 2- Regular graph.
10. Cyclic Graph
- A graph with 'n' vertices (where, n>=3) and 'n' edges forming a cycle of 'n' with all its edges is known as cycle graph.
- A graph containing at least one cycle in it is known as a cyclic graph.
- In the cycle graph, degree of each vertex is 2.
- The cycle graph which has n vertices is denoted by Cn.
Example 1:
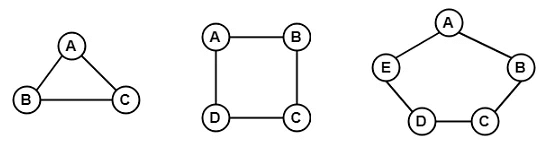
In the above example, all the vertices have degree 2. Therefore they all are cyclic graphs.
Example 2:
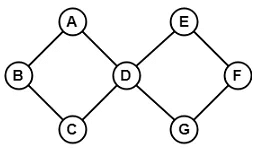
Since, the above graph contains two cycles in it therefore, it is a cyclic graph.
11. Acyclic Graph
- A graph which does not contain any cycle in it is called as an acyclic graph.
Example:
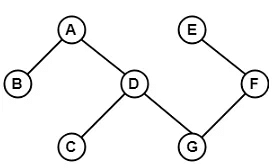
Since, the above graph does not contain any cycle in it therefore, it is an acyclic graph.
 |
Download the notes
Types of Graphs in Graph Theory
|
Download as PDF |
12. Bipartite Graph
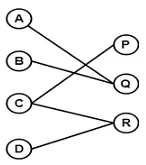
- A bipartite graph is a graph in which the vertex set can be partitioned into two sets such that edges only go between sets, not within them.
- A graph G (V, E) is called bipartite graph if its vertex-set V(G) can be decomposed into two non-empty disjoint subsets V1(G) and V2(G) in such a way that each edge e ∈ E(G) has its one last joint in V1(G) and other last point in V2(G).
- The partition V = V1 ∪ V2 is known as bipartition of G.
Example 1:
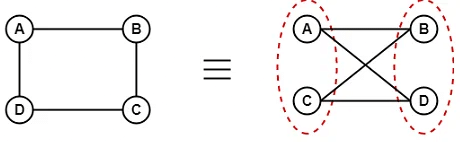
Example 2:
13. Complete Bipartite Graph
- A complete bipartite graph is a bipartite graph in which each vertex in the first set is joined to each vertex in the second set by exactly one edge.
- A complete bipartite graph is a bipartite graph which is complete.
- Complete Bipartite graph = Bipartite graph + Complete graph
Example:
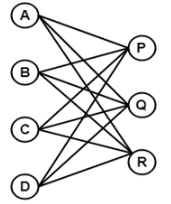
The above graph is known as K4,3.
14. Star Graph
- A star graph is a complete bipartite graph in which n-1 vertices have degree 1 and a single vertex have degree (n -1). This exactly looks like a star where (n - 1) vertices are connected to a single central vertex.
- A star graph with n vertices is denoted by Sn.
Example:
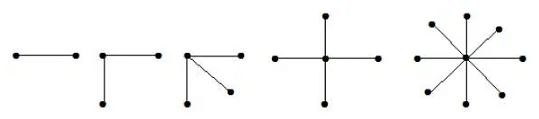
In the above example, out of n vertices, all the (n-1) vertices are connected to a single vertex. Hence, it is a star graph.
15. Weighted Graph
- A weighted graph is a graph whose edges have been labeled with some weights or numbers.
- The length of a path in a weighted graph is the sum of the weights of all the edges in the path.
Example:
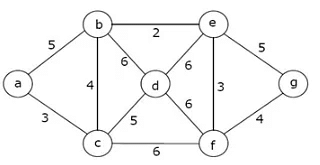
In the above graph, if path is a -> b -> c -> d -> e -> g then the length of the path is 5 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 5 = 25.
16. Multi-graph
- A graph in which there are multiple edges between any pair of vertices or there are edges from a vertex to itself (loop) is called a multi - graph.
Example:
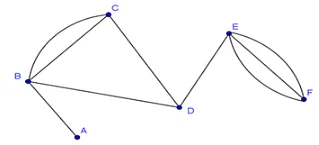
In the above graph, vertex-set B and C are connected with two edges. Similarly, vertex sets E and F are connected with 3 edges. Therefore, it is a multi graph.
17. Planar Graph
- A planar graph is a graph that we can draw in a plane in such a way that no two edges of it cross each other except at a vertex to which they are incident.
Example:
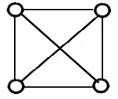
The above graph may not seem to be planar because it has edges crossing each other. But we can redraw the above graph.
The three plane drawings of the above graph are:
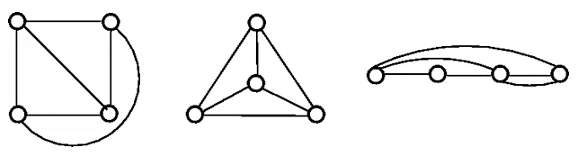 The above three graphs do not consist of two edges crossing each other and therefore, all the above graphs are planar.
The above three graphs do not consist of two edges crossing each other and therefore, all the above graphs are planar.
18. Non - Planar Graph
- A graph that is not a planar graph is called a non-planar graph. In other words, a graph that cannot be drawn without at least on pair of its crossing edges is known as non-planar graph.
Example:
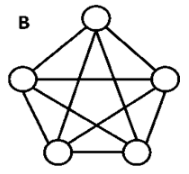
The above graph is a non - planar graph.
|
65 videos|122 docs|94 tests
|

















