CA Foundation Exam > CA Foundation Notes > Business Laws for CA Foundation > Types of Law in the Indian Legal System
Types of Law in the Indian Legal System | Business Laws for CA Foundation PDF Download
Introduction
- In the Indian constitution, numerous rights are granted to every citizen, and with the provision of these rights, there also exists the possibility of their infringement.
- To address this, our legislature has enacted various laws aimed at enforcing and safeguarding these rights, contributing to the cultivation of a civilized society and the preservation of peace and harmony among individuals.

- Law, fundamentally, consists of a set of rules formulated and enforced by a specific country or community through social or governmental institutions to regulate the behaviour of its members.
- India employs a federal judicial system primarily rooted in mixed law, drawing from parliamentary legislature, court laws, customary practices, and religious laws. The Indian Judicial System evolves through the decisions, orders, and judgments made by judges.
- Legal systems can be classified into five types:
1. Civil law
2. Common law
3. Customary law
4. Religious law
5. Mixed law
Question for Types of Law in the Indian Legal SystemTry yourself: Which type of legal system is primarily rooted in court laws and judicial decisions?View Solution
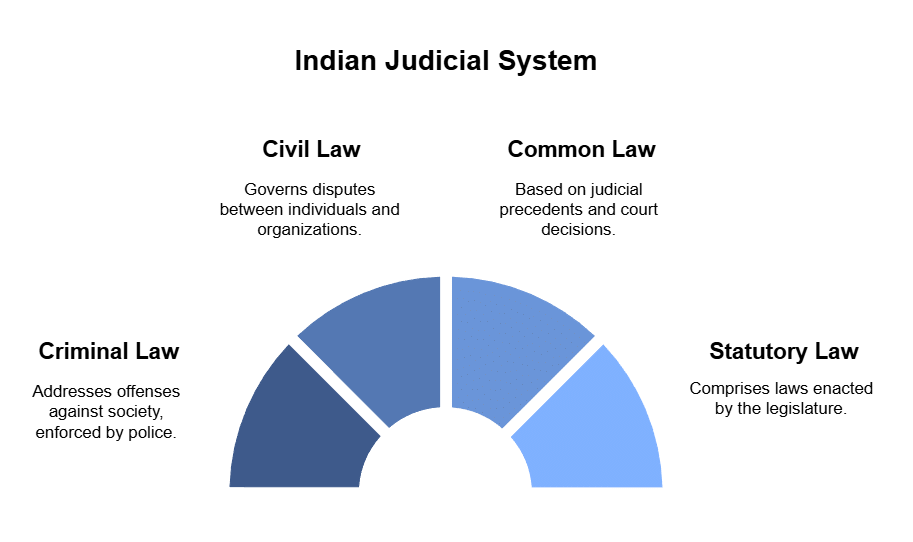
Types of law
In Indian Judicial System there are four types of law.
Criminal law
- The enforcement of criminal law falls within the purview of the police.
- Criminal law addresses cases such as murder, rape, assault, and robbery.
- Offences falling under criminal law are those committed against an individual but are perceived as transgressions against society as a whole, even if the impact is not direct.
- For instance, a house burglary is an individual's loss, but it poses a threat to all homeowners who could potentially experience similar break-ins.
- Due to the perspective that such crimes endanger the public at large, these cases are handled by public services and not private investigators.
Civil law
- Civil law pertains to legal matters that do not involve criminal offences. It constitutes a branch of law addressing conflicts between individuals and organizations, encompassing diverse areas such as:
1. Defamation
2. Child custody
3. Educational rights
4. Divorce
5. Trade union membership
6. Property disputes
7. Ownership issues
8. Copyright
9. Insurance claims - For instance, scenarios involving the forcible occupation of someone else's property without permission, refusal to vacate, or a legal dispute between two companies over a trade matter fall under civil law.
- Similarly, individuals who have suffered losses or injuries in a car accident may file claims against the responsible driver in the realm of civil law.
Common law
- Common Law, alternatively known as case law, judicial precedent, or judge-made law, is a legal category derived from the decisions of courts and similar tribunals.
- As the name implies, it is applicable universally.
- The precedents set by higher courts carry a binding effect on cases heard in lower courts.
- While lower courts have the option to overturn a precedent, this occurrence is infrequent.
- An illustration of common law in practice is seen in common-law marriages, where two individuals cohabit for a period exceeding 10 years.
- This arrangement grants them legal rights to share their assets based on the duration of their cohabitation.
Statutory law
- Statute or Statutory Law refers to legislation established through an act of the legislature and subsequently signed by the executive or legislative body.
- In the case of state law, these acts are passed by the state legislature and signed by the state governor.
- In exceptional situations, the executive (President or governor) may decline to sign the bill, exercising a "veto" power to reject it.
Question for Types of Law in the Indian Legal SystemTry yourself: Which type of law addresses conflicts between individuals and organizations such as property disputes and copyright issues?View Solution
The document Types of Law in the Indian Legal System | Business Laws for CA Foundation is a part of the CA Foundation Course Business Laws for CA Foundation.
All you need of CA Foundation at this link: CA Foundation
|
32 videos|185 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Types of Law in the Indian Legal System - Business Laws for CA Foundation
| 1. What are the main types of law in the Indian legal system? |  |
Ans. The main types of law in the Indian legal system include Constitutional Law, Statutory Law, Administrative Law, Criminal Law, Civil Law, and International Law. Each type serves a specific purpose in governing the rights and duties of individuals and entities within the country.
| 2. How does Constitutional Law function in India? |  |
Ans. Constitutional Law in India serves as the supreme law of the land and provides the framework for the governance of the country. It outlines the structure, powers, and limits of government institutions and guarantees fundamental rights to citizens, ensuring that all laws and actions adhere to these principles.
| 3. What is the difference between Criminal Law and Civil Law in India? |  |
Ans. Criminal Law deals with offenses against the state and prescribes punishments for those found guilty, while Civil Law pertains to disputes between individuals or entities, focusing on the rights and obligations of parties involved. In Civil Law, the remedy usually involves compensation or restitution rather than punishment.
| 4. What role does Statutory Law play in the Indian legal system? |  |
Ans. Statutory Law comprises laws enacted by the Parliament or state legislatures. It provides detailed rules and regulations governing various aspects of society, such as labor, property, and contracts. Statutory laws are essential for implementing the principles laid out in the Constitution and addressing specific societal needs.
| 5. Can you explain Administrative Law in India? |  |
Ans. Administrative Law governs the activities of administrative agencies of government. It includes rules, regulations, and orders created by governmental entities that implement and enforce statutory laws. This type of law ensures that government actions are lawful and that individuals have the right to challenge administrative decisions when necessary.
Related Searches

















