UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 2nd April 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
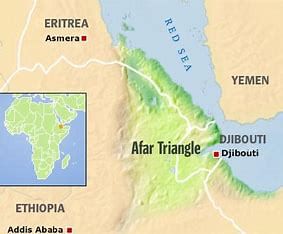
AFAR TRIANGLE
Subject: Geography
Why in News?
Geologists have predicted that the African continent's rift in the Afar Triangle might result in the creation of a new ocean in the next 5 to 10 million years.
Background
- Over an extensive period, this rift has the potential to widen and eventually fill with seawater, leading to the formation of a new ocean. This transformation is expected to occur over millions of years based on current geological knowledge and forecasts.
- It serves as a captivating example of the constant changes and evolution taking place on our planet.
About the Afar Triangle
- The Afar Triangle, also known as the Afar Depression, is a geological depression located in the Horn of Africa.
- Situated in the northeastern part of Africa, the Afar Triangle stands out as one of the most dynamically active regions globally.
- It is the point where the Arabian, Nubian, and Somali tectonic plates are diverging from each other, resulting in a rift system that is causing the African continent to split.
Geological Context
- The Afar Triangle is a consequence of the Afar Triple Junction, which is a part of the Great Rift Valley in East Africa.
- It spans across the borders of Eritrea, Djibouti, and the entire Afar Region of Ethiopia.
- This region is distinguished by its distinctive geological characteristics and has unveiled fossil remains of the earliest hominins, considered the earliest members of the human clade.
- Some scientists regard it as the birthplace of human evolution.
Geographical Highlights
- The Afar Triangle encompasses Lake Assal in Djibouti, which stands as the lowest point in Africa, lying 155 meters (509 feet) below sea level.
- The region is nourished by the Awash River, supporting a narrow green belt that sustains vegetation, wildlife, and the nomadic Afar community residing in the Danakil Desert.
- The northern segment of the Afar Depression is also recognized as the Danakil Depression.
- This area endures extreme heat, aridity, and limited air circulation, making it one of the hottest locations on Earth throughout the year.
Source: Times of India
GS-II
Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016 (RERA)
Subject: Polity and Governance

Why in News?
The Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016 (RERA), which was passed by Parliament eight years ago, is currently under review by the Union Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
Background
As part of this review, senior officials have initiated regular meetings with homebuyers to gather feedback on the Act's effectiveness. These meetings aim to assess key dimensions such as transparency, accountability, information dissemination, and grievance redressal.
About The Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016
The Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016 (RERA) is a significant legislation passed by the Indian Parliament to regulate and promote the real estate sector in the country.
Purpose and Establishment
- RERA aims to protect homebuyers and enhance transparency and efficiency in real estate transactions.
- It establishes a Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA) in each state, serving as an adjudicating body for quick dispute resolution.
Applicability
- RERA applies to under-construction projects with either of the following criteria:
- Plot size exceeding 500 square meters.
- Projects with 8 apartments or more.
Salient Provisions
- Mandatory Registration: All real estate projects falling under the specified criteria must be registered with RERA.
- Fast-Track Dispute Resolution: RERA sets up an appellate tribunal and dedicated adjudicating officers for settling disputes efficiently.
- Consent for Transfer: If a promoter wishes to transfer rights and liabilities to a third party, written consent from two-thirds of allottees and RERA approval are required.
- Complaint Mechanism: Individuals can file complaints with RERA regarding violations by promoters, buyers, or agents.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
- Promoters failing to follow RERA orders may face penalties up to 5% of the evaluated property cost.
- Non-compliance with Appellate Tribunal orders can result in imprisonment or fines.
Jurisdiction
Civil courts have no jurisdiction over matters covered by RERA or the Appellate Tribunal.
Source: Indian Express
Why SC Barred Unregulated Soil Extraction for Linear Projects
Subject: Polity and Governance

Why in News?
The Supreme Court invalidated a 2020 Environment Ministry notification exempting the extraction of ordinary earth for linear projects like roads and pipelines from Environmental Clearance (EC).
Background of the Notification Exempting Earth Extraction for Linear Projects
- In 2006, the Environment Ministry specified activities needing prior EC under the Environment (Protection) Act 1986 (EPA).
- A subsequent 2016 notification exempted certain projects from this requirement.
- The 2020 notification added earth extraction for linear projects to the exempted activities list.
Reasons for Issuing the Notification
- The Centre argued that the exemption aimed to benefit various non-mining activities and align with amendments to the Mines and Minerals Act 1957.
- It contended that judicial intervention was unnecessary as it was a policy decision.
Challenges to the 2020 Exemption
- The exemption faced legal challenges for being arbitrary and violating constitutional provisions like Article 14.
- It was criticized for bypassing public objections procedures during the COVID-19 lockdown, favoring private miners.
- The National Green Tribunal urged the Centre to revise the notification within three months with appropriate safeguards.
Government's Response
- The Centre delayed action until the Supreme Court intervened, prompting the issuance of an Office Memorandum outlining enforcement mechanisms.
- The Ministry emphasized compliance with environmental safeguards and procedures for the exemption.
Supreme Court's Decision
- The court deemed the blanket exemption as arbitrary and violative of Article 14 due to lack of clarity on terms like 'linear projects' and extraction parameters.
- It criticized the rushed issuance of the notification during a nationwide lockdown when construction activities were halted.
Previous Judicial Scrutiny of Similar Exemptions
- In past cases, exemptions like the 2016 notification for building projects and 2014 notification for educational institutions faced legal challenges and were overturned for lack of environmental justifications.
- Judicial bodies emphasized the importance of prior approval under the EPA for environmental protection.
Source: Indian Express
Two States: a comparison on access to life-saving C-sections
Subject: Polity and Governance
Why in News?
The study released by IIT Madras highlights the concerns related to high rates of C-section deliveries among women in Tamil Nadu, especially in private hospitals.
- This indicates the necessity for corrective measures to address the situation.
What is a Caesarean section?
- Also known as C-section or cesarean delivery, it is the surgical procedure by which one or more babies are delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen.
- It is often performed when vaginal delivery would pose risks to the mother or child.
Changes in C-section Rates:
- Public Hospitals: In public sector hospitals in Tamil Nadu, nearly 40% of women underwent C-sections during 2019-21.
- Private Hospitals: Close to 64% of women underwent C-sections in private sector hospitals in Tamil Nadu during 2019-21, significantly higher than both the national average and Chhattisgarh's rate.
- Regional Disparities: In Chhattisgarh, the likelihood of a woman undergoing a C-section in a private hospital is ten times higher than in a public hospital.
Factors Influencing C-section Rates:
- Socioeconomic Factors: The study suggests that poorer households opt for public hospitals while richer households prefer private ones for deliveries, contributing to inequitable access to healthcare services.
- Maternal Age and Weight Status: Factors like maternal age (35-49) and overweight status increase the likelihood of C-section delivery.
- Disparity: In India, the gap in C-section prevalence between the poor and non-poor narrowed in private facilities, but Tamil Nadu exhibited a concerning trend where a higher percentage of the poor underwent C-sections compared to the non-poor.
Recommendations by WHO:
- Cesarean delivery rates ideally should not exceed 10-15% to achieve the lowest maternal and neonatal mortality rates.
- Global C-section rates surpassed 20% in 2021 and are projected to reach 30% by 2030.
Conclusion:
- Access to C-sections in Tamil Nadu shows disparities, with high rates in both public and private hospitals.
- Addressing regional and socioeconomic factors and adhering to WHO recommendations are crucial for equitable maternal healthcare.
Source: Indian Express
GS-III
WHITE RABBIT TECHNOLOGY
Subject: Science and Technology

Why in News?
Recently, CERN introduced the White Rabbit Collaboration.
Background:
- CERN, officially referred to as the European Organization for Nuclear Research, is a globally renowned center for scientific exploration. It is primarily dedicated to fundamental physics, with a key objective of uncovering the mysteries of the Universe and understanding its structure and mechanisms.
About WHITE RABBIT TECHNOLOGY
- White Rabbit (WR) is an innovative technology created at CERN, offering remarkable sub-nanosecond accuracy and picoseconds precision for synchronization in diverse applications.
- This technology is open source, follows recognized standards, and has been integrated into the Precision Time Protocol (PTP), a global industry standard overseen by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
- Beyond particle physics, White Rabbit serves as a notable example of open-source collaboration and innovation.
Applications Beyond Particle Physics:
- Finance Sector: White Rabbit is currently utilized within financial systems.
- Research Infrastructures: It finds practical applications in various research facilities.
- Future Quantum Internet: Under evaluation for potential use in the upcoming quantum internet.
- Global Time Dissemination: It may play a crucial role in global time dissemination technologies, potentially reducing reliance on satellites.
Source: CERN
 |
Download the notes
UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 2nd April 2024
|
Download as PDF |
Status of Leopards in India 2022
Subject: Environment and Ecology

Why in News?
The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has published a report on the Status of Leopards in India 2022, covering 20 States of India and focusing on approximately 70% of the expected leopard habitat.
Background
- The fifth cycle leopard population estimation was conducted by the National Tiger Conservation Authority and Wildlife Institute of India in partnership with State Forest Departments.
Key Highlights of the Report on the Status of Leopards in India 2022
- India's leopard population increased by 8% from 12,852 in 2018 to 13,874 in 2022.
- Around 65% of the leopard population resides outside protected areas in the Shivalik landscape, with only about a third within protected areas.
- Central India exhibited a stable or slightly growing leopard population (2018: 8071, 2022: 8820), while the Shivalik hills and Gangetic plains saw a decline (2018: 1253, 2022: 1109) at a rate of 3.4% per annum.
- The highest number of leopards are found in Madhya Pradesh (3,907), followed by Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
- In Odisha, the leopard count decreased from 760 in 2018 to 562 in 2022, and in Uttarakhand, the population dropped from 839 in 2018 to 652 in 2022.
- Leopard densities are higher in Tiger Reserves compared to areas outside Protected Areas, despite the regulatory pressure from tigers on leopards.
- Common threats include poaching of prey for bush meat, targeted poaching for tiger and leopard products, and habitat loss due to human activities like mining.
- In Odisha, wildlife smugglers were caught with 59 leopard skins between 2018 and 2023, while road accidents are a significant cause of leopard deaths.
Central India and Eastern Ghats Landscape
- The region houses the largest leopard population, which is growing due to conservation efforts under the tiger conservation framework.
Threats to Leopards
- Various threats faced by leopards include poaching, habitat loss, and road accidents, impacting their populations negatively.
Comparison of Leopard Populations
- An analysis of leopard populations across different regions of India reveals varying trends, with some areas showing growth and others facing decline.
Impact of Protected Areas
- Leopard densities in Tiger Reserves highlight the importance of protected areas in supporting leopard populations despite challenges.
Source: Times of India
The ART of India's HIV/AIDS Response
Subject: Science and Technology
Why in News?
On April 1, 2004, India initiated Free Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) for Persons living with HIV (PLHIV) to address access and affordability challenges.
The Emergence of HIV/AIDS and Early Challenges
- The onset of HIV/AIDS in the 1980s sparked a global health crisis, initially affecting marginalized groups.
- Initially called GRID, the disease later became known as HIV and AIDS, leading to widespread fear and uncertainty.
- HIV/AIDS was accompanied by social stigma, discrimination, and a lack of effective treatment options.
A Death Sentence Due to Non-Availability of Treatment
- Early on, HIV/AIDS was often considered fatal due to the absence of effective treatments.
- The disease predominantly impacted marginalized communities but later affected individuals from diverse backgrounds.
- People living with HIV/AIDS faced societal ostracization, job loss, and familial rejection.
Limited Access to Treatment and High Cost of Available ART
- Despite global recognition, access to HIV/AIDS treatment was restricted, with high costs of antiretroviral drugs like AZT and HAART.
- HAART was a breakthrough but unaffordable for many, especially in resource-limited settings.
The Launch of Free ART in India
- In 2004, India introduced Free ART to overcome barriers to treatment access and affordability.
- The initiative aimed to provide life-saving medication to all PLHIV, irrespective of their financial status.
The Impact of Free ART and Its Role in Halting the Epidemic
- The Free ART program significantly expanded over two decades, enhancing treatment access for 1.8 million PLHIV across India.
- Improved health outcomes, reduced mortality rates, and lowered HIV transmission were key outcomes of the initiative.
- Free ART not only prolonged lives but also improved quality of life, contributing to a decline in HIV prevalence.
Complementary Initiatives and Patient-Centric Approach
- Free ART's success was complemented by additional services like diagnostics, prevention of transmission, and opportunistic infection management.
- A patient-centric approach, providing extended medication supplies, enhanced treatment adherence.
Challenges and Future Directions
- Challenges include delayed treatment initiation, patient loss to follow-up, and infrastructure limitations in remote areas.
- Enhancing the supply chain, engaging the private sector, and integrating health programs are vital for future success.
- NACP Phase 5 aims to reduce new infections and AIDS-related deaths by 80% by 2025, requiring increased testing and treatment coverage.
Conclusion
- India's Free ART initiative has been pivotal in combating HIV/AIDS, emphasizing accessible healthcare, sustained funding, and community involvement.
- The program's success highlights the importance of political commitment and patient-focused care in managing infectious diseases.
Source: The Hindu
Atal Tunnel
Subject: Geography

Why in News?
The Manali-Leh highway faced recent blockage due to fresh snowfall near the Atal Tunnel in Lahaul and Spiti districts.
About Atal Tunnel:
- Formerly known as Rohtang Tunnel, Atal Tunnel is recognized as the world's longest high-altitude tunnel.
- Situated at a height of around 3,100 meters (10,171 feet) above sea level in the Pir Panjal Range of the Himalayas, it is positioned in Himachal Pradesh and traverses through Rohtang pass.
- Extending over a length of 9.02 km, the tunnel establishes a vital link between Manali and Lahaul and Spiti Valley throughout the year, eliminating the previous seasonal isolation lasting about six months due to heavy snowfall.
- Designed as a horseshoe-shaped, single tube with two lanes, the tunnel boasts a semi-transverse ventilation system, emergency exits every 500 meters, evacuation lighting, broadcasting systems, and fire hydrants to ensure safety.
Source: Hindustan Times
|
39 videos|4862 docs|1056 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 2nd April 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. Why did the Supreme Court bar unregulated soil extraction for linear projects? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016 (RERA)? |  |
| 3. How do two states compare in terms of access to life-saving C-sections? |  |
| 4. What is the current status of leopards in India in 2022? |  |
| 5. How has White Rabbit Technology contributed to the technological landscape? |  |





























