UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 2nd November 2024 | Daily GK & Current Affairs Tests - Bank Exams PDF Download
GS3/Defence & Security
Exercise GARUD SHAKTI 24
Source: Mint

Why in News?
The Indian Army contingent has set off for Cijantung, Jakarta, Indonesia, to participate in the 9th edition of the India-Indonesia Joint Special Forces Exercise GARUD SHAKTI 24.
- Note: Garuda represents a bilateral air force exercise involving the Indian Air Force and the French Air and Space Force, while Shakti is a biennial training event alternated between India and France.
About
- What is it? A joint special forces exercise aimed at boosting military collaboration, held alternately in India and Indonesia.
- History Initiated in 2012 as a part of defense cooperation between India and Indonesia.
Objectives
- Enhance mutual understanding and cooperation between special forces.
- Share best practices and experiences in counter-terrorism efforts.
- Conduct joint operations and drills to improve interoperability.
Activities
- Joint planning and execution of special operations.
- Orientation on advanced special forces skills.
- Information sharing on weapons, tactics, and techniques.
- Practice operations in various terrains.
- Cultural exchanges between troops.
Significance
- Strengthens bilateral relations between India and Indonesia.
- Fosters trust and cooperation.
- Contributes to regional security and addresses challenges related to terrorism.
- Enhances the operational capabilities of both armies.
Recent Edition
- Ninth Edition (2024): Scheduled from November 1 to 12, focusing on enhancing understanding, cooperation, and interoperability.
GS2/Polity
Prevention of Money Laundering Act
Source: The Hindu Why in News?
Why in News?
The Supreme Court has highlighted that sickness and infirmity of an accused are grounds for bail even under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA).
About Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002:
The Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), enacted in January 2003, aims to combat money laundering in India. It has three primary objectives:
- To prevent and control money laundering.
- To confiscate and seize properties obtained through laundered money.
- To address other issues related to money laundering in India.
Section 3 of the Act defines money laundering offenses as any direct or indirect attempt to participate in or assist activities connected with the proceeds of crime, falsely portraying them as legitimate property.
The Act has undergone amendments through the Prevention of Money Laundering (Amendment) Act in 2009 and again in 2012.
Major Provisions of the Act:
- The Act mandates banking companies, financial institutions, and intermediaries to verify and maintain records of their clients' identities and all transactions.
- PMLA empowers the Directorate of Enforcement (ED) to investigate money laundering offenses and attach properties involved.
- The ED is responsible for enforcing economic laws and combating economic crimes in India.
- The Act establishes an Adjudicating Authority to confirm property attachments or confiscation orders.
- It also sets up an Appellate Tribunal to handle appeals against the Adjudicating Authority's decisions.
- PMLA designates certain courts as Special Courts to adjudicate offenses under the Act.
- The Central Government may enter into agreements with foreign governments to enforce PMLA provisions.
Section 45 of the PMLA:
Section 45 addresses bail provisions for money laundering offenses and imposes strict conditions for granting bail, making it one of the more contentious aspects of the Act.
- Twin Conditions for Bail:Under Section 45(1), two conditions must be satisfied before granting bail:
- Prima Facie Innocence: The court must have reasonable grounds to believe the accused is not guilty.
- No Risk of Tampering: The court must be convinced the accused will not commit further offenses if released on bail.
- Non-Bailable Offenses: Offenses under PMLA are classified as non-bailable, which means bail is at the court's discretion and not guaranteed.
- Amendments and Court Rulings: The stringent nature of Section 45 has faced legal challenges, with claims that it infringes on personal liberty. The Supreme Court, in the case of Nikesh Tarachand Shah v. Union of India (2017), deemed the twin conditions unconstitutional, but they were reintroduced in the PMLA amendments of 2018.
News Summary:
- The Supreme Court of India recently emphasized that illness and frailty can be legitimate grounds for granting bail under the PMLA.
- A three-judge bench, led by Chief Justice D.Y. Chandrachud, granted interim bail to Amar Sadhuram Mulchandani, the former chairperson of Seva Vikas Co-operative Bank, due to his severe health issues.
- Section 45 of the PMLA typically imposes strict conditions for bail, requiring courts to establish the accused's presumed innocence and their likelihood to refrain from further offenses.
- However, a provision in Section 45(1) allows courts discretionary power to exempt minors, women, and individuals who are sick or infirm from these stringent conditions.
- The court underscored this humane provision, citing Mulchandani's deteriorating health, which includes cardiac and kidney problems, diabetes, and hypertension, as adequate grounds for granting bail.
GS3/Science and Technology
What is Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD)?
Source: Times of India
Why in News?
A recent case of Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) has been confirmed in the United States.
About Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD)
- CWD is a severe, transmissible disease impacting the brain and central nervous system of deer, elk, and moose.
- First identified in 1967, CWD is classified as a prion disease, where normal proteins misfold, ultimately leading to fatal symptoms.
Transmission
- The disease spreads through contact between animals or via contaminated feed and water due to infected saliva or waste.
- Environmental contamination can result from soil exposure to bodily fluids or remains of infected animals.
- High-risk areas are typically locations where deer and elk congregate, such as feeding or watering sites.
Species Affected
- CWD does not naturally infect cows, other livestock, or pets.
- While there is no strong evidence of transmission to humans, health officials recommend against consuming meat from infected animals.
Symptoms of CWD
- Infected animals display drastic weight loss, lack of coordination, drooling, lethargy, and excessive thirst.
- Other signs may include drooping ears and a noticeable reduction in fear of humans.
Prevention
- To mitigate the spread of CWD, it is advised to avoid handling or consuming meat from sick animals.
- Using synthetic lures, disposing of carcass remains in landfills, and reporting sick or unusual deer to wildlife authorities are recommended practices.
GS3/Environment
Why the goal to arrest global temperature rise to 1.5°C is unrealistic?
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
Over nine years ago, the world committed to significantly reduce emissions. However, progress has been inadequate, making it increasingly clear that maintaining global warming below 1.5 degrees Celsius is becoming unattainable.
Is the 1.5°C Target Still Achievable?
- Rising Emissions: Global emissions continue to rise, reaching record heights in 2023. Despite advancements in clean energy, the reductions achieved have not been sufficient to meet the necessary pace for the 1.5°C goal.
- Potential for Emission Peaking: The UNEP Emissions Gap Report indicates that emissions could peak by 2023 or 2024 if significant additional measures are implemented. However, global actions remain inconsistent and often inadequate.
- Need for Accelerated Action: To achieve the 1.5°C target, global emissions must decrease by at least 43% by 2030, compared to 2019 levels. Current projections only suggest a reduction of 2.6% by 2030, falling far short of the required cuts.
- Technological and Financial Challenges: Realizing the 1.5°C target depends on rapid deployment of technology, transitioning to renewable energy, and significant financing for climate initiatives. These efforts are hindered by a lack of coordination and available resources.
Implications of Exceeding the 1.5°C Limit
- Increased Frequency of Extreme Events: Surpassing the 1.5°C threshold is likely to result in a rise in the frequency and severity of extreme weather events, including heatwaves, droughts, wildfires, and severe storms.
- Impacts on Ecosystems and Biodiversity: Many species and ecosystems are highly sensitive to even minor temperature increases. For example, coral reefs are at risk of near-total collapse if warming exceeds 1.5°C.
- Threats to Human Health and Livelihoods: Exceeding the 1.5°C mark may lead to increased cases of heat-related illnesses, reduced productivity, water scarcity, and threats to food security, with vulnerable populations bearing the brunt of these impacts.
- Feedback Loops: Warming beyond 1.5°C could trigger feedback loops, such as the melting of Arctic ice and thawing permafrost, leading to irreversible changes and complicating future climate control efforts.
Should We Reconsider the Focus on the 1.5°C Target?
- Adaptation vs. Mitigation: As limiting warming to 1.5°C becomes increasingly challenging, there are calls to refocus on adaptation strategies to address the unavoidable consequences of higher temperatures.
- Realigning Expectations: Although the 1.5°C target has been essential in mobilizing global climate action, shifting towards more realistic and achievable goals may facilitate gradual yet sustained progress, especially if current mitigation efforts fall short.
- Moving Towards a ‘Just Transition’: With an anticipated overshoot of the 1.5°C target, it is crucial to ensure that adaptation and resilience strategies do not disproportionately impact low-income countries and communities.
- Science-Based Overshoot Scenarios: The IPCC and other scientific organizations are evaluating scenarios where temporary overshooting of 1.5°C could occur, followed by a return to lower temperatures. However, achieving this requires significant and sustained negative emissions, which are currently unachievable at scale.
Way forward:
- Prioritize Scalable Emissions Reductions and Resilient Adaptation: Accelerate the global transition to renewable energy, enhance energy efficiency, and reduce emissions from methane and other non-CO₂ sources. At the same time, invest in adaptation measures to assist vulnerable communities in coping with the effects of warming beyond 1.5°C.
- Strengthen Climate Finance and International Cooperation: Mobilize substantial climate financing for developing countries to bolster both mitigation and adaptation efforts. Enhance cross-border technology sharing and policy alignment to facilitate collective, equitable climate action.
Mains PYQ: ‘Climate change’ is a global problem. How India will be affected by climate change? How Himalayan and coastal states of India will be affected by climate change? (UPSC IAS/2017)
GS3/Science and Technology
How remote sensing system LiDAR helped discover a lost Mayan city?
Source: Indian Express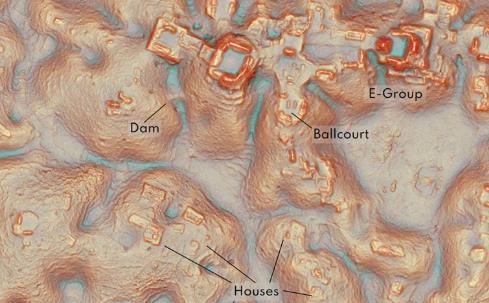 Why in News?
Why in News?
Scientists have successfully utilized LiDAR technology to uncover an ancient Mayan city that lay concealed for centuries beneath a dense jungle in Mexico.
What is LiDAR?
- LiDAR stands for Light Detection and Ranging.
- It is a remote sensing method that employs laser light pulses to gauge distances between a sensor, typically airborne, and the Earth's surface.
- This technology generates high-resolution, three-dimensional models of land elevation, achieving vertical precision within 10 centimeters, as reported by the US Geological Survey.
How Does LiDAR Work?
- LiDAR Setup: It consists of a laser, a scanner, and a GPS receiver. The laser emits rapid light pulses which bounce back from various surfaces on the ground, including both natural and artificial features.
- Data Collection: The light that is reflected returns to the sensor, allowing the LiDAR system to compute the two-way travel time to ascertain the distance from the sensor to each point on the Earth's surface.
- Data Processing: Information from the GPS and Inertial Measurement Systems (IMS) is utilized to develop accurate maps. The initial data compilation forms a "point cloud" that represents surfaces like vegetation, buildings, and terrain.
- "Bare Earth" Model: By eliminating structures and vegetation, LiDAR can produce a Digital Elevation Model that highlights only the ground terrain.
Applications of LiDAR
- Geography and Mapping: LiDAR creates precise three-dimensional data for topographic mapping.
- Urban Planning and Infrastructure: It assists in planning transport routes, assessing flood risks, and managing natural resources.
- Conservation: Useful for monitoring forest health, managing habitats, and detecting environmental changes.
- Engineering and Policy: Provides data essential for infrastructure design, environmental policymaking, and land-use planning.
Why is LiDAR Useful for Archaeologists?
- Large-Area Surveying: LiDAR allows archaeologists to examine extensive regions swiftly, eliminating the need for labor-intensive ground exploration.
- Vegetation Penetration: The technology can "see through" thick tree canopies by capturing reflections that penetrate gaps, enabling the mapping of concealed structures and terrains.
- Detailed Site Mapping: With "bare earth" models, archaeologists can remove layers of vegetation to reveal hidden archaeological sites.
- Case Study – Maya Civilization: The lost Mayan city of Valeriana in Mexico was discovered by analyzing publicly available LiDAR data, revealing plazas, temple pyramids, a ball court, and other features characteristic of a Classic Maya capital.
Where is the Indian Government using LiDAR?
- High-Speed Rail Projects: The National High-Speed Rail Corporation Limited (NHSRCL) employs aerial LiDAR surveys for the Delhi-Varanasi High-Speed Rail Corridor, significantly cutting survey durations from 10-12 months to just 3-4 months while capturing detailed topographical data within a 300-meter corridor.
- National Highways: The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) mandates the use of Mobile LiDAR for feasibility studies and project reports, enhancing the accuracy and effectiveness of highway surveys across large networks.
- Forest Mapping: The Ministry of Environment is piloting LiDAR-based forest mapping initiatives across various states to improve forest management and accurately monitor changes in forest cover.
- Water Resource Management: WAPCOS is utilizing LiDAR technology to identify groundwater recharge zones, which aids in water resource management and helps mitigate human-animal conflicts in forested areas.
- Regions like Chandigarh and Gujarat are employing LiDAR for GIS mapping and drone-based surveys to enhance city models, urban planning, and infrastructure mapping.
Conclusion:
LiDAR technology has transformed various fields, ranging from archaeology to urban planning, by offering precise three-dimensional mapping capabilities. In India, it is enhancing infrastructure projects, environmental monitoring, and urban planning, proving to be invaluable for efficient and large-scale data collection and analysis.
GS2/International Relations
US cracks down on Indian companies for supplies to Russian firms
Source: Hindustan Times Why in news?
Why in news?
The U.S. has recently imposed sanctions on approximately 400 entities and individuals, which includes 19 Indian companies and two Indian nationals, due to their connections with Russia's military efforts in Ukraine. These sanctions are designed to limit trade, investment, and financial dealings with the targeted entities, thereby aiming to disrupt their economic and operational capabilities by restricting access to U.S.-based resources and systems.
- For affected companies, this could lead to exclusion from the U.S. market, loss of American business partners, and substantial financial and operational challenges, potentially disrupting global trade and their business functions.
Understanding Sanctions
Sanctions are intended to restrict or terminate economic relationships between the imposing entity and the target. They can manifest in various forms, including import/export bans, trade limitations, asset freezes, and exclusion from banking facilities.
- Types of Sanctions:
- Comprehensive: These apply to entire countries, such as the U.S. embargo on Cuba.
- Targeted: These focus on specific entities, groups, or individuals, as seen with U.S. sanctions on Russian companies.
Global Mechanisms for Sanctions
Sanctions are typically enacted by individual nations, including the U.S. against countries like Iran, North Korea, and Russia, which is now recognized as the most sanctioned nation following the Ukraine conflict. Additionally, international organizations like the UN (via its Security Council) and the EU also possess frameworks for imposing sanctions.
Efficacy and Criticisms of Sanctions
While sanctions are intended to exert economic pressure, their effectiveness remains a topic of debate. Targets often develop strategies to circumvent these restrictions, and the enforcement of sanctions can adversely affect both the sanctioning country and its industries that depend on the sanctioned imports. For example, despite extensive sanctions from Western nations, Russia's economy has shown resilience, maintaining trade relations with countries such as India and China. Furthermore, the UN lacks direct enforcement authority and relies on member states for implementation.
The United States has targeted Indian firms for supplying essential components to Russian companies linked to the defense sector, thereby limiting trade and financial interactions with these firms and individuals.
Companies sanctioned – few examples
| Company Name | Details |
|---|---|
| Ascend Aviation India Private Limited | Shipped over 700 items worth more than $200,000, including U.S.-origin aircraft parts from the Common High Priority List (CHPL) to Russian firms between March 2023 and March 2024. |
| Mask Trans | Provided over $300,000 in CHPL-listed aviation components to Russia's S7 ENGINEERING LLC from June 2023 to April 2024. |
| TSMD Global Private Limited | Exported CHPL items valued at least $430,000, including integrated circuits and CPUs, to Russian companies from July 2023 to March 2024. |
| Futrevo | Supplied over $1.4 million worth of CHPL-listed electronic components to SMT-ILOGIC, a manufacturer of Orlan drones, between January 2023 and February 2024. |
Individuals sanctioned
The directors of Ascend Aviation India, Vivek Kumar Mishra and Sudhir Kumar, have also been sanctioned.
Impact on Indian Defence Sector
The U.S. sanctions, which are aimed at curtailing the supply of dual-use items to Russia, are anticipated to have a limited impact on India's defense ecosystem. Most of the sanctioned companies do not have substantial links to major defense projects, with only RRG Engineering engaged in minor collaborations with the DRDO and the Indian armed forces.
Trading Activities and Foreign Connections
Several sanctioned entities appear to be involved in trading and importing Western electronics, which are then resold to sanctioned Russian firms. For instance:
- Denvas Services: Supplies digital kiosks and has Russian nationals on its board and among its shareholders. It has been accused of sourcing U.S.-origin microelectronics for Russia's conventional arms.
- Another Company: Has limited defense ties and is accused of sending microelectronics to Russia-based Arteks Limited Company. It has provided manpower for DRDO projects and delivered non-critical supplies, including NBC warfare detectors and satcom stations.
Availability of Equipment in India
Industry experts suggest that the sanctioned equipment, such as microelectronics and NBC detectors, is readily available within India, allowing for sourcing when needed and potentially alleviating disruptions arising from these sanctions.
GS3/Environment
Why post-Diwali Delhi air was cleaner this year
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
Delhi’s 24-hour average air quality prior to and during Diwali this year was poorer compared to the last two years. However, the subsequent day showed a notable improvement, recording the best post-Diwali Air Quality Index (AQI) since 2015, with the exception of 2022. The AQI on Friday registered at 339, a decrease from 358 the previous year. The lowest recorded post-Diwali AQI in recent years was in 2021, which reached 462.
Introduction to AQI
The Air Quality Index (AQI) was introduced by the Indian government in 2014 as part of the Swachh Bharat initiative to simplify the understanding of air pollution levels. A collaborative effort involving medical professionals and air quality experts, alongside IIT Kanpur, led to the development of the AQI framework.
How AQI is Calculated
The AQI consolidates complex data on various pollutants into a single numerical value and corresponding color code. The pollutants monitored include:
- PM10
- PM2.5
- Nitrogen Dioxide
- Ozone
- Carbon Monoxide
Each pollutant is weighted based on its health effects, with the most severely weighted pollutant determining the overall air quality, resulting in a singular AQI value, rather than multiple readings.
Impact of Harmful Pollutants
Particulate matter, particularly PM2.5 (particles smaller than 2.5 micrometers), presents significant health hazards. Due to their tiny size, PM2.5 particles can infiltrate the respiratory system and bloodstream, causing serious health concerns such as asthma, heart attacks, and chronic respiratory diseases.
Influence of AQI on Government Policy
Governments utilize AQI data to enact measures designed to enhance air quality. In areas such as Delhi, the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) is implemented in response to declining air quality. This plan may result in:
- Bans on the use of coal and firewood
- Restrictions on diesel generators
- Increased parking fees to discourage private vehicle use
Warmer Temperatures
This year, Delhi experienced its warmest October in 73 years, with average temperatures reaching:
- 35.1°C (maximum)
- 21.2°C (minimum)
In contrast, last year’s Diwali occurred in November, when the average temperatures were significantly cooler:
- 27.8°C
- 13°C
Colder weather typically exacerbates pollution problems due to a lower inversion height, which traps pollutants nearer to the ground. A temperature inversion occurs when the air close to the ground cools more quickly than the air above it. This year’s warmer October temperatures facilitated better pollution dispersion, resulting in improved air quality after Diwali, even though pollution levels were higher on the festival day. As temperatures decrease, the inversion height lowers, leading to increased concentrations of air pollutants.
Strong Winds
High wind speeds greatly enhanced the dispersion of pollution in Delhi after Diwali. The India Meteorological Department (IMD) reported westerly winds that began at speeds of 3-7 kmph, escalating to 10 kmph by 9 AM and reaching 15 kmph by noon. These wind conditions helped lower the levels of PM2.5 and PM10, which had surged due to firecracker use and stubble burning in surrounding states. Even though air quality remained classified as 'poor' to 'very poor' throughout Diwali, these wind patterns ultimately contributed to a reduction in pollution levels the following day.
GS2/International Relations
Exercise VAJRA PRAHAR
Source: Business Standard

Why in news?
The Indian Army has sent a contingent for the 15th edition of Exercise VAJRA PRAHAR, which is a collaborative Special Forces training exercise with the US Army. This event highlights the ongoing military cooperation between the two nations.
About Exercise VAJRA PRAHAR:
- What is it? A joint Special Forces exercise designed to strengthen military collaboration between India and the US.
- Inception: Launched in 2010, this exercise forms part of the bilateral defense partnership between India and the US.
- Frequency: This exercise occurs annually, alternating between locations in India and the United States.
- Past Exercises: No exercises were conducted from 2012 to 2015, and again in 2020.
- 15th Edition Dates: The current exercise is scheduled to take place from November 2 to November 22, 2024, at the Orchard Combat Training Centre in Idaho, USA.
- Participants: The exercise will involve 45 personnel from each country, consisting of the Indian Army's Special Forces and the US Army's Green Berets.
Objectives:
- To enhance military cooperation between India and the US.
- To promote interoperability and facilitate tactical exchanges.
- To improve combined operational capabilities in joint missions.
Key Focus Areas:
- Maintaining high physical fitness standards among participants.
- Engaging in joint planning and conducting tactical drills.
Significance:
- Joint Team Mission Planning allows for synchronized operations.
- Conducting reconnaissance missions to gather intelligence.
- Utilization of Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) for advanced operations.
- Execution of special operations to enhance tactical effectiveness.
- Defining the roles of Joint Terminal Attack Controllers during missions.
- Incorporating psychological warfare techniques to gain strategic advantages.
GS3/Environment
India’s National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP)
Source: Times of India

Why in News?
In alignment with the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KM-GBF), India has introduced its National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP), which includes 23 specific national biodiversity targets. This strategy is aimed at tackling urgent issues related to biodiversity conservation and sustainable development.
Overview of the KM-GBF:
The KM-GBF was endorsed by 196 nations during the 2022 UN Biodiversity Conference of the Parties (COP 15) held in Montreal, Canada. It is also referred to as the "Post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework" or the "Paris Agreement for Nature." The framework's primary goal is to halt and reverse the decline of biodiversity by 2030. It contains four long-term goals for 2050 and 23 targets for the year 2030, supporting the attainment of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
By adopting the KM-GBF, all participating countries committed to setting their own national targets for implementation, while other stakeholders have been encouraged to establish and communicate their commitments as well.
India’s National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP):
Background:
India is home to approximately 8% of the world's known plant and animal species, encompassing 3,532 species of fish, 450 amphibian species, 738 reptilian species, 1,346 bird species, and 436 species of mammals. At the ongoing 16th Convention on Biological Diversity (COP-16) in Colombia, India has unveiled its ambitious financial plan for biodiversity and conservation.
India's commitment to reducing threats to biodiversity:
- India's plan aims to restore at least 30% of degraded ecosystems, which includes terrestrial, inland water, marine, and coastal regions.
- This restoration initiative is designed to improve biodiversity, enhance ecosystem functions, ensure ecological integrity, and promote connectivity.
Objectives of NBSAP:
The NBSAP of India is in line with the three main goals of the KM-GBF:
- Reducing threats to biodiversity.
- Satisfying human needs through sustainable use and equitable benefit-sharing.
- Offering tools and solutions for effective implementation and mainstreaming of biodiversity efforts.
Key features of NBSAP:
The NBSAP establishes a detailed framework that emphasizes conservation, sustainable use, and benefit-sharing. It tackles critical national issues, such as:
- The water crisis
- Food insecurity
- Human-wildlife conflicts
- Pollution and emerging diseases
- Disaster risk management
Core targets of NBSAP:
Among the 23 targets outlined, eight specifically focus on mitigating threats to biodiversity, addressing areas such as:
- Alterations to land and sea use.
- Pollution and climate change impacts.
- Management of invasive alien species.
Invasive species management:
To address the challenges posed by invasive alien species, India's action plan incorporates the following strategies:
- Management of pathways to prevent the introduction of new species.
- Eradication and control initiatives in priority regions, including islands.
- Establishment of quarantine measures and databases to monitor and manage invasive species effectively.
Financial requirements:
Realizing these biodiversity targets necessitates considerable financial resources. India has conducted assessments to monitor biodiversity-related expenditures:
| Period | Average Annual Expenditure (Rs) |
|---|---|
| 2017-18 to 2021-22 | 32,207.13 crore |
| Projected for 2024-25 to 2029-30 | 81,664.88 crore |
With significant spending expected from 2025 to 2030, India highlights the necessity for international financial assistance to meet its biodiversity targets under the KM-GBF.
Conclusion:
India's NBSAP presented at COP-16 illustrates a robust commitment to biodiversity conservation, aligning with global objectives set forth by the KM-GBF. Through strategic actions, financial investments, and an emphasis on sustainable practices, India aspires to contribute significantly to a nature-positive world by 2030. Achieving these targets will require a combination of national initiatives and international support in the forms of finance, technology, and capacity-building resources.
|
57 docs|864 tests
|
















