Unit Test (Solution): Electricity: Circuits and their Components | Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT PDF Download
Maximum Marks: 30
Attempt all questions
- Question numbers 1 to 7 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 8 to 12 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 13 to 15 carry 3 marks each.
- Question numbers 16 carry 4 marks each.
Q1. What is the source of electrical energy in a torchlight? (1 Mark)
(i) Switch
(ii) Electric cell
(iii) Filament
(iv) Wire
Ans: (ii) Electric cell
An electric cell is a portable source of electrical energy that powers devices like a torchlight.
Q2. The thin wire inside an incandescent lamp that glows is called the __________. (1 Mark)
Ans: filament
The filament is the thin wire in an incandescent lamp that gets hot and glows to produce light when electric current passes through it.
Q3. Which of the following is a characteristic of an LED? (1 Mark)
(i) It has a filament
(ii) It allows current to flow in both directions
(iii) It has a positive and negative terminal
(iv) It requires four cells to glow
Ans: (iii) It has a positive and negative terminal
An LED has two terminals, one positive (longer wire) and one negative (shorter wire), and allows current to flow in one direction only.
Q4. What is the purpose of a switch in an electrical circuit? (1 Mark)
Ans: A switch completes or breaks an electrical circuit to control the flow of current.
For example, in a torchlight, sliding the switch to the “ON” position completes the circuit, making the lamp glow, while moving it to “OFF” breaks the circuit, turning the lamp off.
Q5. Which material is commonly used for making electrical wires? (1 Mark)
(i) Plastic
(ii) Rubber
(iii) Copper
(iv) Glass
Ans: (iii) Copper
Copper is widely used for electrical wires due to its high conductivity and availability.
Q6. Materials that do not allow electric current to pass through are called __________. (1 Mark)
Ans: insulators
Insulators, such as plastic and rubber, prevent the flow of electric current.
Q7. Why does an LED glow only in one specific connection? (1 Mark)
(i) It has a filament
(ii) Current flows through it in one direction only
(iii) It requires a switch
(iv) It uses multiple cells
Ans: (ii) Current flows through it in one direction only
An LED glows only when its positive terminal is connected to the positive terminal of the battery and its negative terminal to the negative terminal, as current flows through it in one direction.
Q8. Explain the difference between a conductor and an insulator. (2 Mark)
Ans: Conductors are materials, like metals (e.g., copper), that allow electric current to flow easily due to their ability to conduct electricity. Insulators, such as plastic, rubber, or glass, do not allow electric current to pass through, preventing the flow of electricity. Conductors are used in wires, while insulators are used to cover wires to ensure safety.
Q9. Why is it important to connect cells in a specific order in a battery? (2 Mark)
Ans: Cells in a battery must be connected with the positive terminal of one cell to the negative terminal of the next to ensure proper current flow. This arrangement forms a complete circuit, providing sufficient energy to power a device. Incorrect connections may prevent the device, like a torch, from functioning.
Q10. How does an incandescent lamp produce light? (2 Mark)
Ans: An incandescent lamp produces light when electric current passes through its filament, a thin wire inside the bulb. The filament gets hot and glows, emitting light. The filament is supported by two thicker wires connected to the lamp’s terminals.
Q11. What is an electrical circuit, and why is it necessary for a lamp to glow? (2 Mark)
Ans: An electrical circuit is a complete path that allows electric current to flow from the positive to the negative terminal of a power source, like a cell. It is necessary for a lamp to glow because the current must pass through the lamp’s filament or LED to produce light, which only happens when the circuit is complete.
Q12. Why are electrical wires covered with plastic or rubber? (2 Mark)
Ans: Electrical wires are covered with plastic or rubber because these materials are insulators, preventing unwanted flow of electric current. This covering protects users from electric shocks and prevents short circuits by ensuring current flows only through the conductive metal inside the wire.
Q13. How do electric cells or batteries make the use of electrical devices more convenient, and what are some examples of their different forms and uses? (3 Mark)
Ans:
- Electric cells or batteries are compact portable sources of electrical energy that make the use of some electrical devices more convenient.
- These cells and batteries come in various shapes and sizes for different purposes.
- For Example in cylindrical batteries for torchlights, clocks, remotes, toys; button cells for watches, hearing aids; rechargeable batteries for mobile phones, laptops, and electric vehicles.
Q14. Explain how a battery is formed and its advantage over a single cell. (3 Mark)
Ans:
- A battery is formed by connecting two or more electric cells in a specific order, with the positive terminal of one cell connected to the negative terminal of the next.
- This arrangement ensures a continuous flow of current.
- The advantage of a battery over a single cell is that it provides more electrical energy, allowing devices to operate for a longer time or with greater power.
- For example, a torch with a battery of two cells can produce brighter light or function longer than one with a single cell, as the combined cells deliver more energy to the circuit.
Q15. Write the components of an electrical circuit and draw the symbols with which they can be represented. (3 Mark)
Ans: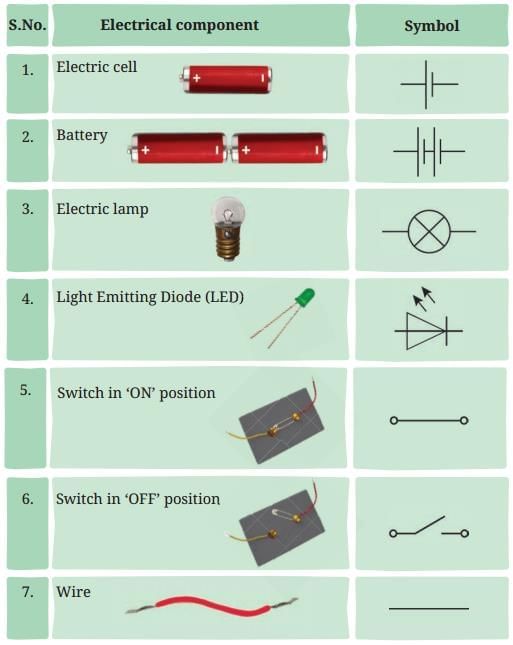 Q16. Read the following passage and answer the questions that follow. (4 Mark)
Q16. Read the following passage and answer the questions that follow. (4 Mark)
Nihal and his friends were excited to explore how torchlights work. During a classroom activity, they dismantled a torch and observed components like the electric cells, a switch, and a lamp. They noticed the lamp glowed only when the cells were placed in a certain order and the switch was turned on. Later, they used the same components—two electric cells, a lamp holder, wires, and a switch—to construct a circuit on a cardboard base. Surprisingly, in some arrangements, the lamp did not glow even when the switch was on. After multiple trials, they learned the importance of making a complete circuit and ensuring the proper connection of terminals.
Answer the following:
(a) Why did the lamp not glow in some arrangements even when the switch was on?
(b) What is meant by a complete circuit, and why is it necessary?
(c) What happens if the wire connections are loose or the filament of the lamp is broken?
(d) State the direction of electric current in a circuit using an electric cell.
Ans:
- (a) The lamp did not glow because the circuit was incomplete or the terminals were not connected properly (e.g., positive to negative).
- (b) A complete circuit is a closed path where electric current flows from the positive to the negative terminal of the cell through the components. It is necessary for current to flow and the lamp to glow.
- (c) If wire connections are loose or the filament is broken (fused), current cannot pass, and the lamp will not glow.
- (d) The direction of electric current is from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of the electric cell.
|
80 videos|319 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solution): Electricity: Circuits and their Components - Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the basic components of an electric circuit? |  |
| 2. How does a series circuit differ from a parallel circuit? |  |
| 3. What is the role of a switch in an electric circuit? |  |
| 4. What safety measures should be taken when working with electrical circuits? |  |
| 5. How can you measure current and voltage in a circuit? |  |





















