Unit Test (Solutions): From Barter to Money | Social Science Class 7 - New NCERT PDF Download
Attempt all questions. Time: 1 hour, M.M. 30
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question numbers 12 to 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q.1. The ancient Indian coins were called __________. (1 mark)
Ans: karshapana
The term karshapana refers to the ancient Indian coins that were widely used in trade and commerce.
Q.2. Which of the following is a limitation of the barter system? (1 mark)
a) Universal acceptance
b) Double coincidence of wants
c) Standard of deferred payment
d) Store of value
Ans: b) Double coincidence of wants
The barter system requires a double coincidence of wants, meaning both parties must have what the other desires, which limits its efficiency. Other options do not directly pertain to the fundamental limitations of barter.
Q.3. Which authority in India controls the issue of currency today? (1 mark)
a) State Bank of India
b) Reserve Bank of India
c) Ministry of Finance
d) Indian Mint
Ans: b) Reserve Bank of India
The Reserve Bank of India is the sole authority responsible for issuing currency in India, ensuring the stability and integrity of the nation's monetary system.
Q.4. The Junbeel Mela is held in __________ district of Assam. (1 mark)
Ans: Morigaon
The Junbeel Mela is a traditional fair held in the Morigaon district of Assam, showcasing the rich cultural heritage and local traditions of the region.

Q.5. The ₹ symbol was designed by __________. (1 mark)
Ans: Udaya Kumar
The ₹ symbol, representing the Indian Rupee, was designed by Udaya Kumar, a professor at the Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay, in 2010.
Q6. How does money address the issue of portability in trade? (2 marks)
Ans: Money addresses the issue of portability in trade by:
- Being easily carried and transferred, unlike bulky goods.
- Allowing for quick transactions without the need for bartering items.
- Enabling individuals to store value for future use, making it a convenient medium of exchange.
Q7. What symbols were typically engraved on ancient Indian coins? (2 marks)
Ans: Ancient Indian coins featured a variety of symbols and motifs on both sides. These included:
- Nature motifs such as animals, trees, and hills.
- Images of kings or queens.
- Depictions of deities.
For instance, coins from the Chalukyas displayed a Varaha image (an avatar of Vishnu) on one side and a decorated three-tiered parasol on the other.
Q8. Why is money considered a standard of deferred payment? (2 marks)
Ans: Money is considered a standard of deferred payment for several reasons:
- It allows individuals to make purchases now and pay later, facilitating transactions over time.
- Money serves as a common measure of value, enabling easy comparison of prices for goods and services.
- For example, if you want to buy a book worth £100 but only have £50, you might ask the shopkeeper to accept the remaining payment later.
- This acceptance of money for future payments confirms its role as a standard for deferred payments.
Q9. How did the use of coinage enhance India’s maritime trade? (3 marks)
Ans: The use of coinage significantly enhanced India's maritime trade in several ways:
- Standardisation: Coins provided a consistent medium of exchange, making transactions simpler and more efficient.
- Wider Acceptance: Coins issued by powerful rulers were accepted across various kingdoms, facilitating trade beyond local borders.
- Trade Evidence: Archaeological findings of coins in regions like Kerala and Tamil Nadu indicate active trading with other countries.
- Economic Growth: The ability to trade more easily contributed to the economic prosperity of southern India.
Q10. Explain the socio-cultural significance of the Junbeel Mela. (3 marks)
Ans: The Junbeel Mela is a significant socio-cultural event in Assam, India, with deep historical roots. It serves various important functions:
- Junbeel Mela is a traditional fair in Assam that promotes social harmony among tribes like Tiwa, Karbi, Khasi, and Jaintia.
- It revives the ancient barter system, encouraging exchange of local goods without money.
- The mela preserves cultural heritage through rituals like Agni Puja and showcases traditional art, music, and customs.
Q11.Explain how digital payment methods solve the problems of the barter system (3 marks)
Ans: Digital payment methods offer significant advantages over the traditional barter system:
- Efficiency: Transactions are quicker and do not require finding a direct match for goods or services.
- Convenience: Payments can be made anytime and anywhere using devices like smartphones or computers.
- Security: Digital payments reduce the risk of theft and loss associated with carrying physical goods or cash.
- Record Keeping: Electronic transactions provide automatic records, making it easier to track spending and manage finances.
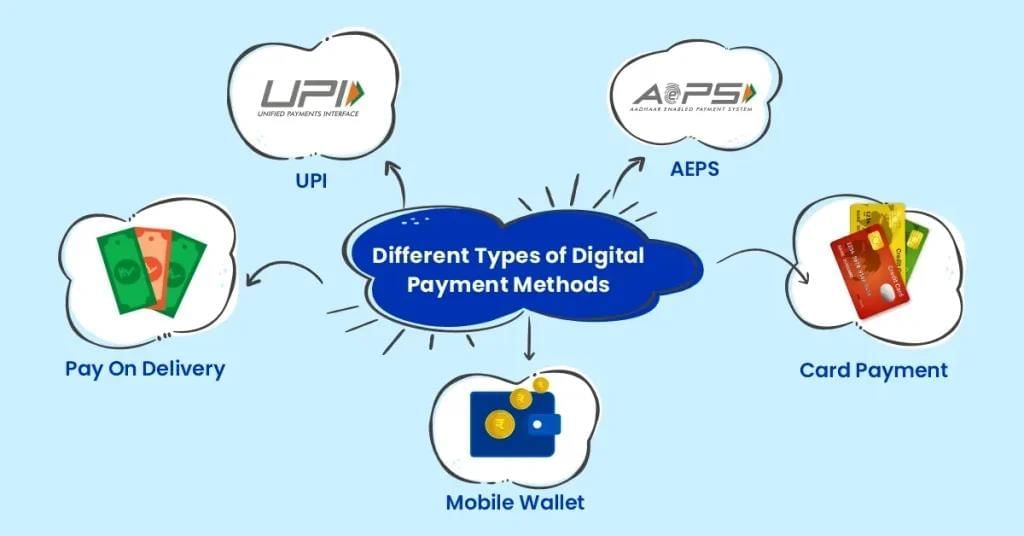
Q12. Analyze the problems of the barter system that necessitated the invention of money. (5 marks)
Ans: The barter system had several significant problems that led to the need for money:
- Double coincidence of wants: Both parties needed to have what the other wanted, making exchanges difficult.
- Lack of common measure: There was no standard way to value goods, complicating trade.
- Indivisibility: Some goods could not be easily divided into smaller parts for trade.
- Storage issues: Perishable items could not be stored for long periods, leading to waste.
- Transport difficulties: Carrying large quantities of goods was cumbersome and impractical.
These limitations highlighted the need for a more efficient medium of exchange, ultimately leading to the invention of money.
Q13. Evaluate the role of money’s evolution in shaping India’s trade and economy. (5 marks)
Ans: The evolution of money has significantly influenced India's trade and economy over the centuries. Here are the key points regarding its role:
- Barter Limitations: Before money, the barter system was used, which had limitations such as the need for a double coincidence of wants. This made trade cumbersome.
- Introduction of Coins: Ancient Indian coins, made from precious metals like gold and silver, were introduced to facilitate easier transactions. They were widely accepted across different kingdoms.
- Trade Expansion: The acceptance of coins from powerful rulers allowed for increased trade across regions, enhancing economic interactions.
- Medium of Exchange: Over time, money evolved from coins to paper currency and now includes digital forms, making transactions more efficient.
- Global Trade: The evolution of money has enabled India to engage in international trade, boosting its economy and connecting it with global markets.
In summary, the evolution of money has transformed India's trade practices and economic structure, facilitating smoother exchanges and expanding trade opportunities.
|
23 videos|204 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): From Barter to Money - Social Science Class 7 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the concept of barter and how does it differ from money? |  |
| 2. How did money evolve from the barter system? |  |
| 3. What are the types of money that have been used historically? |  |
| 4. What are the advantages of using money over bartering? |  |
| 5. What role does money play in modern economies? |  |
















