Unit Test (Solutions): The Rise of Empires | Social Science Class 7 - New NCERT PDF Download
Attempt all questions. Time: 1 hour, M.M. 30
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question numbers 12 to 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1: The term 'empire' comes from the Latin word __________, meaning supreme power. (1 mark)
Ans: imperium
The term 'empire' is derived from the Latin word imperium, which signifies supreme power. This term encapsulates the authority held by an emperor over various territories.
Q.2. Which dynasty founded the first major empire in India? (1 mark)
a) Nanda
b) Maurya
c) Gupta
d) Chola
Ans: b) Maurya
The Maurya dynasty founded the first major empire in India, establishing a centralized and expansive rule that marked a significant period in Indian history.
Q.3. What was the capital city of the Maurya Empire? (1 mark)
a) Kausambi
b) Ujjain
c) Pataliputra
d) Taxila
Ans: c) Pataliputra
Pataliputra was the capital city of the Maurya Empire, serving as a political and cultural center during its height.
Q.4. The mentor of Chandragupta Maurya was ________. (1 mark)
Ans: Kautilya
The mentor of Chandragupta Maurya was Kautilya, also known as Chanakya, who played a crucial role in the establishment of the Maurya Empire.
Q.5. Ashoka’s edicts were written in the __________ language. (1 mark)
Ans: Prakrit
Ashoka's edicts were inscribed in Prakrit, which was the common language of the people during his reign, making his messages accessible.
Q.6. Why were trade routes important for empires? (2 marks)
Ans. Trade routes were vital for empires as they enabled the trade of goods like textiles, spices, and gems, which increased wealth and economic prosperity. Controlling these routes also ensured a steady flow of tax revenue, which strengthened the empire’s economy and supported its military and administrative needs.
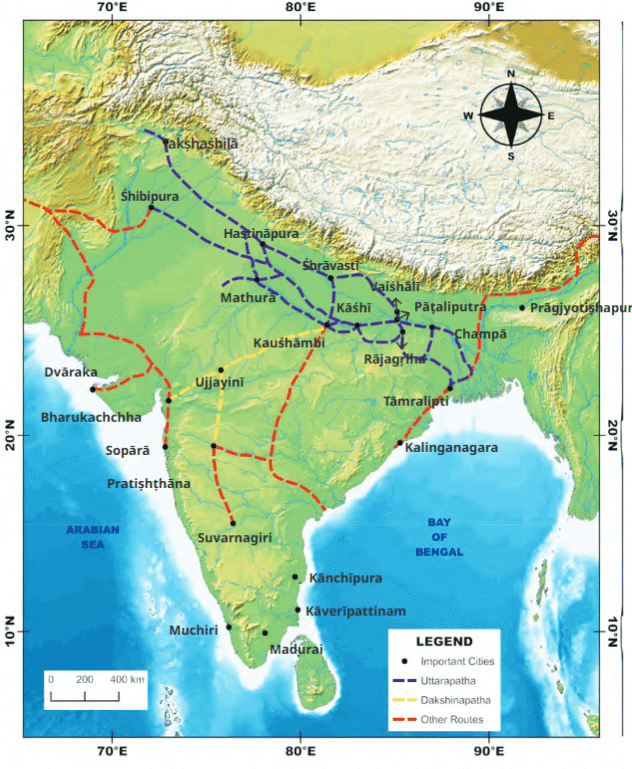 Trade Routes
Trade Routes
Q.7. What was the role of guilds in ancient Indian trade? (2 marks)
Ans. Guilds in ancient India were associations of traders, craftsmen, moneylenders, and agriculturists who collaborated to share resources and market information, enhancing trade efficiency. They had the autonomy to set their own rules, which helped regulate trade practices and contributed to economic growth without royal interference.
Q.8. How did the Ganga plains contribute to the rise of Magadha? (2 marks)
Ans. The Ganga plains were crucial for Magadha’s rise due to their fertile land, which supported surplus agriculture, leading to increased food production and population growth. Access to iron ore in nearby hills and the Ganga and Son rivers facilitated tool-making and trade, boosting Magadha’s economy and power.
Q.9. What is an empire, and how is it different from a kingdom? (3 marks)
Ans.
- An empire is a collection of smaller kingdoms or territories ruled by an emperor, often through conquest.
- Smaller territories in an empire have local rulers but pay tribute to the emperor.
- A kingdom is a single territory ruled by a king, smaller and less complex than an empire.

Q.10. Describe Kautilya’s saptanga concept of a kingdom. ( 3 marks)
Ans.
- Kautilya’s saptanga includes seven parts: king, ministers, fortified cities, army, territory with population, treasury, and allies.
- These elements ensure a well-protected and prosperous kingdom.
- Emphasised strong administration, law enforcement, and alliances for stability.
Q.11. How did Ashoka promote the welfare of his subjects? (3 marks)
Ans.
- Provided medical care for people and animals, even beyond his empire.
- Built rest houses, wells, and planted fruit and shade trees along roads.
- Issued edicts encouraging fairness, impartiality, and respect for all sects.
Q.12. Explain the factors that helped Magadha rise as a powerful empire. (5 marks)
Ans. The rise of Magadha as a powerful empire was influenced by several key factors:
- It was located in the fertile Ganga plains, which provided excellent land for agriculture and access to iron ore for tools and weapons.
- The Ganga and Son rivers enhanced trade and transportation, significantly boosting the economy.
- Surplus food production allowed for population growth and a focus on arts, crafts, and trade.
- Strong rulers, particularly Mahapadma Nanda, unified smaller kingdoms and expanded the empire's territory.
- Large armies equipped with iron weapons and elephants ensured military dominance.

Q.13. Discuss why Ashoka is considered a unique ruler in Indian history, focusing on his actions after the Kalinga war. (5marks)
Ans. Ashoka is considered a unique ruler in Indian history due to his remarkable transformation after the Kalinga war.
- He adopted non-violence and embraced the teachings of Buddhism following the war's devastation.
- Ashoka issued edicts in Prakrit and Brahmi script, promoting dharma and ethical behaviour.
- He supported public welfare by constructing rest houses, wells, and providing medical care for both humans and animals.
- Ashoka encouraged religious tolerance, urging various sects to respect one another's beliefs.
- He sent emissaries to spread Buddhist principles to regions such as Sri Lanka and Central Asia.
|
23 videos|276 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): The Rise of Empires - Social Science Class 7 - New NCERT
| 1. What were the key factors that contributed to the rise of empires in ancient history? |  |
| 2. How did geography influence the development of empires? |  |
| 3. What role did governance play in the stability of empires? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the concept of cultural assimilation in the context of empires? |  |
| 5. What were some notable empires in history, and what distinguished them? |  |

















