Unit Test Solutions: Earth, Moon and the Sun | Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT PDF Download
Time: 1 Hour
Maximum Marks: 30
Instructions:
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each .
Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
Question numbers 12 and 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1. What causes the day-night cycle on Earth? (1 Mark)
a) Earth’s revolution
b) Earth’s rotation
c) Moon’s orbit
d) Sun’s movement
Answer: b) Earth’s rotation
Sol:The Earth’s rotation on its axis every 24 hours causes the day-night cycle,
Q2. Which direction does the Earth rotate when viewed from above the North Pole? (1 Mark)
a) East to west
b) West to east
c) North to south
d) South to north
Answer: b) West to east
Sol: The Earth rotates counterclockwise from west to east
Q3. What is the longest day in the Northern Hemisphere called? (1 Mark)
a) Winter solstice
b) Spring equinox
c) Summer solstice
d) Autumn equinox
Answer: c) Summer solstice
Sol: The summer solstice, around June 21, is the longest day in the Northern Hemisphere
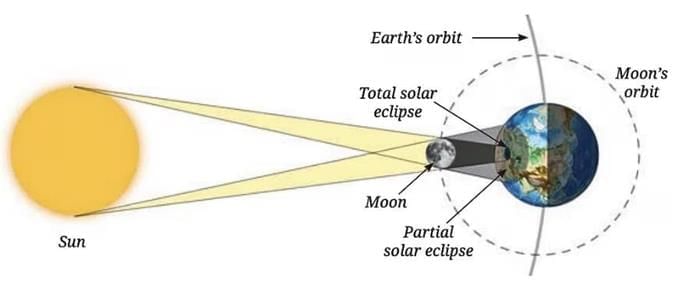
Q4. What happens during a total solar eclipse? (1 Mark)
a) Earth blocks sunlight from the Moon
b) Moon blocks sunlight from Earth
c) Sun blocks the Moon’s light
d) Venus crosses the Sun
Answer: b) Moon blocks sunlight from Earth
Sol:A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon blocks sunlight from Earth,
Q5. Why does the Pole Star appear almost stationary in the sky? (1 Mark)
a) It moves with the Earth
b) Earth’s axis points close to it
c) It is closer to Earth
d) It revolves around the Sun
Answer: b) Earth’s axis points close to it
Solution: The Pole Star appears stationary because the Earth’s axis points near it
Q6. Why does the Sun appear to rise in the east? (2 Mark)
Answer: The Sun appears to rise in the east because Earth rotates from west to east, making the eastern side face the Sun first
Q7. What is an equinox, and when does it occur? (2 Mark)
Sol: An equinox is when day and night are equal (12 hours each), occurring around March 21 (spring equinox) and September 23 (autumn equinox).
Q8. Why do we see different constellations in the night sky during different months? (2 Mark)
Sol: As the Earth revolves around the Sun, we face different directions in space. This causes different constellations to be visible at different times of the year.
Q9. How does Earth’s tilt cause seasonal temperature changes? Explain with an example of a season in the Northern Hemisphere. (3 Mark)
Sol: Earth’s tilted axis causes seasons by changing how directly sunlight hits the Northern or Southern Hemisphere, as per the notes. In June, the Northern Hemisphere tilts toward the Sun, receiving more intense sunlight, causing warmer summer temperatures. For example, in India, June is hot because the Sun’s rays are more direct, increasing heat and daylight hours.
Q10. Why is direct viewing of a solar eclipse dangerous, and how can it be done safely? (3 Mark)
Sol:
Direct viewing of a solar eclipse is dangerous because the Sun’s intense light can cause permanent blindness, even when partially covered, as per the notes. Safe methods include using specialized solar goggles or projecting the Sun’s image with a mirror. For example, at organized viewing events, solar goggles protect eyes while allowing safe observation of the eclipse.
Q11. Describe the difference between Earth’s rotation and revolution. (3 Mark)
Sol:
Earth's Rotation
1. Earth’s rotation refers to its spinning on its axis, taking about 24 hours to complete one rotation.
2. This causes day and night.
Earth's Revoloution
1. Earth's revolution is the motion of the Earth around the Sun, taking approximately 365 days and 6 hours to complete one full orbit.
2. The revolution is responsible for the changing seasons on Earth.
Q12.Explain in detail how the Earth's revolution and tilt cause the seasons. Use examples from both hemispheres. (5 Mark)
Sol: The Earth revolves around the Sun in about 365 days. Its axis is tilted at about 23.5°. Due to this tilt:
In June, the Northern Hemisphere tilts towards the Sun, receiving more direct sunlight and longer days. Hence, it is summer in the Northern Hemisphere and winter in the Southern Hemisphere.
In December, the situation reverses: the Northern Hemisphere tilts away, getting less sunlight and shorter days, leading to winter, while the Southern Hemisphere gets summer.
This variation in sunlight intensity and duration causes seasonal changes in temperature and weather. For example, in June, India experiences summer, while Australia experiences winter.
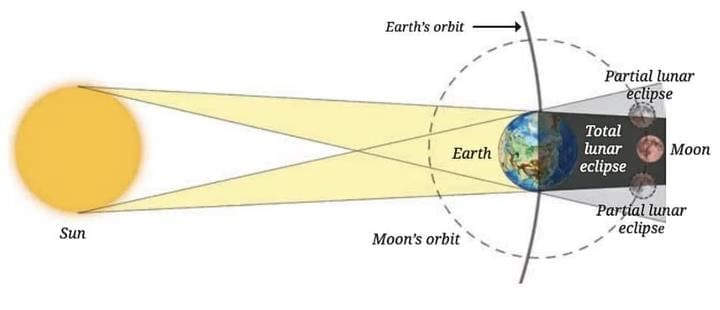
Q13. Compare and contrast solar and lunar eclipses in terms of cause, types, appearance, and viewing safety. (5 Mark)
Sol:
Solar Eclipse
1. Cause:
Moon comes between Earth and Sun, blocking sunlight.
2. Types:
Solar Eclipse are basically of two types : Total and Partial3. Appearence :
Sun appears fully or partially blocked. In total eclipse, a ‘diamond ring’ may be seen.4. Visibility:
Solar eclipses are visible from a small area for a few minutes.5. Viewing Safety:
Requires solar filters or indirect methods. Never view directly with naked eyes.Lunar Eclipse
1. Cause:
Lunar eclipse: Earth comes between Sun and Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon.2. Types:
Lunar eclipse are basically of two types: Total and Partial3. Appearance:
Lunar: Moon appears red in total eclipse (blood moon); partially dark in partial eclipse.4. Visibility:
Lunar eclipses are visible from half the Earth and last longer.5. Viewing Safety:
Lunar: Completely safe to view with naked eyes.
|
80 videos|224 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test Solutions: Earth, Moon and the Sun - Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the main characteristics of the Earth, Moon, and Sun? |  |
| 2. How do the Earth, Moon, and Sun interact with each other? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the Moon phases in relation to Earth and the Sun? |  |
| 4. How does the distance between the Earth and the Sun affect life on Earth? |  |
| 5. What are the historical milestones in the study of the Earth, Moon, and Sun? |  |