Unit Test Solutions: Heat Transfer in Nature | Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT PDF Download
Time: 1 Hour
Maximum Marks: 30
Instructions:
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each .
Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
Question numbers 12 and 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1. Which process transfers heat through direct contact in solids? (1 Mark)
a) Convection
b) Radiation
c) Conduction
d) Evaporation
Answer: c) Conduction
Sol:Conduction is the process of heat transfer through direct contact in solids, where particles vibrate and pass heat to neighboring particles.
Q2. What is a material that does not allow heat to pass through easily called? (1 Mark)
a) Conductor
b) Insulator
c) Aquifer
d) Radiator
Answer: b) Insulator
Sol: An insulator, like wood or glass, does not allow heat to pass through easily,.
Q3. Which process in the water cycle involves water turning into vapor due to heat? (1 Mark)
a) Condensation
b) Precipitation
c) Evaporation
d) Seepage
Answer: c) Evaporation
Sol:Evaporation is the process where water turns into vapor due to the Sun’s heat, a key part of the water cycle.
Q4. What is the traditional Himalayan heater called that uses wood or charcoal? (1 Mark)
a) Ice Stupa
b) Bukhari
c) Aquifer
d) Convector
Answer: b) Bukhari
Sol:The bukhari is a traditional Himalayan heater that uses wood or charcoal to warm rooms and cook food.
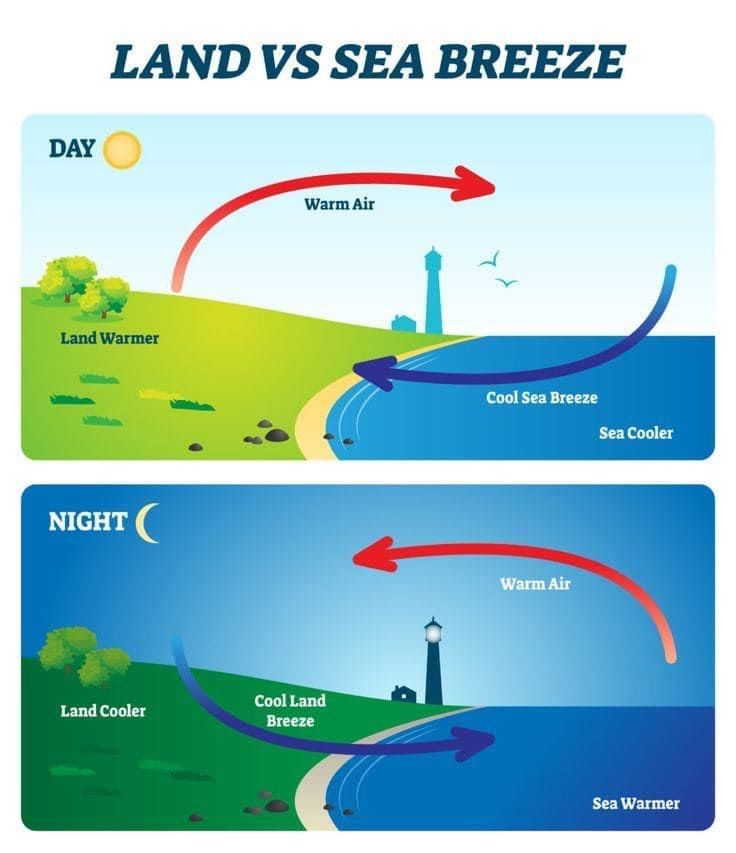
Q5. What causes a sea breeze during the day in coastal areas? (1 Mark)
a) Cooler land air moving to the sea
b) Warmer sea air rising
c) Cooler sea air moving to the land
d) Warmer land air sinking
Answer: c) Cooler sea air moving to the land
Sol: During the day, land heats up faster, causing warm air to rise, and cooler sea air moves in to create a sea breeze.
Q6. Why are woollen clothes effective in keeping us warm? (2 Mark)
Sol: Woollen clothes trap air in their pores, and air is a poor conductor of heat, reducing heat loss from the body to the surroundings, keeping us warm.
Q7. What is an ice stupa, and what is its purpose? (2 Mark)
Sol:
An ice stupa is a cone-shaped ice structure in Ladakh, formed by freezing water in winter. It melts slowly in spring to provide water for farming and daily use.
Q8. What is groundwater, and how is it accessed? (2 Mark)
Sol: Groundwater is water stored in pores of sediments or cracks in rocks below the Earth’s surface, called aquifers. It can be used by digging wells or drilling bore wells
Q9. Why do hollow bricks help maintain comfortable indoor temperatures in houses? (3 Mark)
Sol:
- Hollow bricks contain air trapped in their hollow parts, which acts as a poor conductor of heat.
- In winter, this trapped air reduces heat loss from the house to the cold outside, keeping it warm.
- In summer, it slows heat gain from the hot outside, keeping the house cool.
This insulation property helps maintain a comfortable indoor temperature year-round.
Q10. What is seepage, and how does it depend on the type of soil? (3 Mark)
Sol: Seepage is when water soaks into the ground through soil or rocks, becoming groundwater. The speed of seepage depends on soil type.
- Gravel has big spaces between particles, so water flows fast.
- Sand has smaller spaces, so water moves slower.
- Clay has tiny spaces, so water seeps very slowly.
For example, in the activity with bottles, water flows fastest through gravel, slower through sand, and slowest through clay(as shown below)
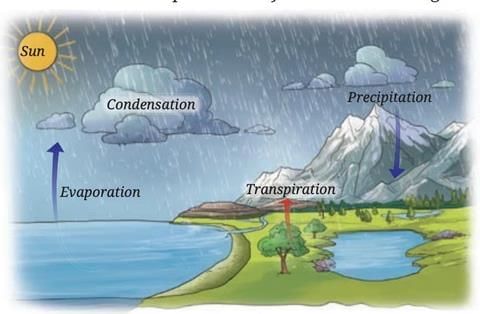
Q11. How does the Sun’s heat cause precipitation in the water cycle? Give an example. (3 Mark)
Sol: The Sun’s heat cause precipitation in the water cycle as
- The Sun’s heat evaporates water from oceans and rivers into vapor, which rises into the sky.
- The vapor cools and condenses into clouds made of tiny water droplets.
- When clouds get heavy, they release water as precipitation, like rain or snow.
For example, after a sunny day, you might see rain because the Sun’s heat made water vapor form clouds that then rained.
Q12. Describe how convection creates land and sea breezes. Suggest one way people in coastal areas can use this knowledge. (5 Mark)
Sol:
Land and Sea Breezes:
- During the day, the land near the beach heats up faster than the water in the sea. This is because different materials absorb heat at different rates.
- However, at night, the situation changes: the land cools down faster than the water.
- This difference in how quickly land and water heat up and cool down is what causes the land and sea breeze.
Using This Knowledge:
People in coastal areas can plan outdoor activities, like picnics, in the afternoon when the sea breeze makes it cooler and more comfortable, instead of the hot morning when the land is warmest.
Q13. Explain the water cycle’s role in providing fresh water, including all main processes. Describe how ice stupas in Ladakh help with water scarcity. (5 Mark)
Sol:
Water Cycle: The water cycle is the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. It has the following main four processes
1. Evaporation: The Sun’s heat turns water from oceans, rivers, and lakes into vapor. Plants add vapor through transpiration.
2. Condensation: Vapor rises, cools, and forms clouds of tiny water droplets.
3. Precipitation: Clouds release water as rain, snow, or hail, which fills rivers, lakes, and groundwater.
4. Seepage and Runoff: Some water soaks into the ground as groundwater, and some flows into rivers and oceans. This cycle brings fresh water to places where people and plants need it, like rivers for drinking or rain for crops.
In Ladakh, they make ice stupas—artificial ice cones built in winter. These ice stupas melt slowly in warmer months, providing water for farming and daily use.
|
80 videos|224 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test Solutions: Heat Transfer in Nature - Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the three main types of heat transfer found in nature? |  |
| 2. How does conduction work in everyday life? |  |
| 3. Can you explain how convection is important in weather patterns? |  |
| 4. What is the role of radiation in heating the Earth? |  |
| 5. How do animals adapt to different methods of heat transfer in their environments? |  |