Unit Test Solutions: Life Processes in Animals | Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT PDF Download
Time: 1 Hour
Maximum Marks: 30
Instructions:
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each .
Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
Question numbers 12 and 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1. Where does digestion begin in the human body? (1 Mark)
a) Stomach
b) Mouth
c) Small intestine
d) Large intestine
Answer: b) Mouth
Sol:Digestion starts in the mouth, where teeth chew food and saliva breaks down starch,
Q2. What is the wave-like motion that moves food through the food pipe called? (1 Mark)
a) Egestion
b) Peristalsis
c) Respiration
d) Absorption
Answer: b) Peristalsis
Sol:Peristalsis is the wave-like muscle contractions that push food through the food pipe,
Q3. What tiny sacs in the lungs help with gas exchange? (1 Mark)
a) Villi
b) Alveoli
c) Diaphragm
d) Gizzard
Answer: b) Alveoli
Sol: Alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged
Q4. Which animals use gills to breathe? (1 Mark)
a) Birds
b) Fish
c) Earthworms
d) Cows
Answer: b) Fish
Sol:Fish use gills to extract oxygen from water, as mentioned in the notes about respiration in other animals.
Q5. What does the large intestine mainly do in digestion? (1 Mark)
a) Breaks down proteins
b) Absorbs nutrients
c) Absorbs water
d) Produces bile
Answer: c) Absorbs water
Sol:The large intestine absorbs water from undigested food to form stool.
Q6. What is mechanical digestion, and where does it happen in humans? (2 Mark)
Sol: Mechanical digestion is breaking food into smaller pieces by chewing. It happens in the mouth, where teeth crush and chew food to make it easier to swallow and digest.
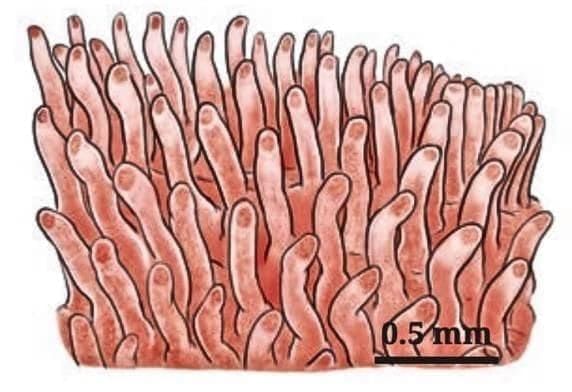
Q7. What are villi, and why are they important in the small intestine? (2 Mark)
Sol:
Villi are tiny finger-like projections on the inner lining of the small intestine. They increase the surface area to absorb nutrients into the blood, helping the body use food for energy and growth.
Q8. How do birds digest food without teeth? (2 Mark)
Sol:
Birds use a gizzard, a special stomach chamber, to grind food. They swallow small stones (grit) that help the gizzard crush food, breaking it down for digestion.
Q9. How does peristalsis help move food through the digestive system? Give an example from the human body. (3 Mark)
Sol: Peristalsis is the wave-like muscle contractions that push food through the digestive system. The walls of the food pipe (oesophagus) and other parts of the alimentary canal contract and relax to move food forward. For example, when you swallow chewed food, peristalsis in the oesophagus gently pushes it down to the stomach, even if you’re lying down, so food doesn’t get stuck.
Q10. What is the role of bile in the small intestine, and why is it important for digestion? (3 Mark)
Sol: Bile, produced by the liver, is a mildly basic liquid that flows into the small intestine. It neutralizes the acid from the stomach, making the food less acidic, and breaks fats into tiny droplets, which makes them easier to digest. This is important because it helps the small intestine’s digestive juices break down fats completely, so nutrients can be absorbed into the blood for energy and growth.
Q11. How does the large intestine work, and why are fiber-rich foods important for it? (3 Mark)
Sol: The large intestine absorbs water and some salts from undigested food, turning it into a semi-solid stool that’s stored in the rectum until it’s expelled through the anus (egestion). Fiber-rich foods, like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, add bulk to the stool, making it easier to pass and keeping the large intestine healthy. For example, eating apples helps prevent hard stools and digestive problems.
Q12. Explain how amphibians like frogs breathe differently from humans. (5 Mark)
Sol: Frog Breathing (Amphibians):
Frogs are amphibians that live in water and on land, so their breathing changes with their life stages.
As tadpoles (baby frogs), they live in water and breathe using gills, which take oxygen dissolved in water and release carbon dioxide, like fish.
As adult frogs, they live on land and use lungs to breathe air, similar to humans.
Adult frogs also breathe through their moist skin in water or damp places, where oxygen passes into the blood and carbon dioxide comes out.
Example: A frog near a pond uses both lungs and skin to breathe, helping it survive in wet environments.
Human Breathing:
Humans breathe only through lungs, using the respiratory system to take in oxygen and remove carbon dioxide.
Air enters through the nostrils, where nasal passages with hairs and mucus trap dust and dirt for cleaner air.
Air travels through the windpipe (trachea) to the lungs, which are protected by the rib cage.
In the lungs, tiny sacs called alveoli allow oxygen to enter the blood and carbon dioxide to be exhaled.
The diaphragm, a muscle below the lungs, moves down to pull air in (inhalation) and up to push air out (exhalation).
Example: When you breathe deeply before running, your diaphragm helps your lungs fill with oxygen for energy.
13. Explain the process of digestion in humans, covering the roles of the mouth, stomach, and small intestine. Describe one way to maintain healthy digestion. (5 Mark)
Sol:
Mouth: Digestion starts in the mouth, where teeth chew food into smaller pieces (mechanical digestion). Saliva moistens the food and contains juices that break down starch into sugar. For example, chewing rice makes it taste sweet because of saliva.
Stomach: The chewed food moves to the stomach through the food pipe by peristalsis. The stomach churns food with its walls and releases digestive juice, acid, and mucus. The juice breaks down proteins, the acid helps digestion and kills bacteria, and mucus protects the stomach lining, turning food into a semi-liquid mass.
Small Intestine: The semi-liquid food enters the small intestine, which is 6 meters long. It receives bile from the liver to break fats into droplets and pancreatic juice to digest carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Villi in the small intestine absorb nutrients into the blood for energy and growth.
Maintaining Healthy Digestion: Eat fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, as suggested in the notes. For example, eating bananas helps the large intestine form soft stool, preventing digestive problems and keeping the digestive system healthy.
|
80 videos|224 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test Solutions: Life Processes in Animals - Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the main life processes in animals? |  |
| 2. How do animals obtain nutrition? |  |
| 3. What is the role of respiration in animals? |  |
| 4. Why is circulation important in animals? |  |
| 5. How do animals reproduce? |  |