Once the leaves make glucose, it travels through the plant to other parts, like the potato, through special tubes called phloem. The potato acts like a storage place where the glucose is turned into starch and stored for later use, which is why when you test a potato with iodine, you see a blue-black color, showing the presence of starch.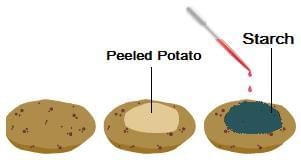
Unit Test Solutions: Life Processes in Plants | Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT PDF Download
Time: 1 Hour
Maximum Marks: 30
Instructions:
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each .
Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
Question numbers 12 and 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1. What process do plants use to make their own food? (1 Mark)
a) Respiration
b) Photosynthesis
c) Transport
d) Absorption
Answer: b) Photosynthesis
Sol: Photosynthesis is the process where plants make food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water
Q2. Which pigment in leaves captures sunlight for photosynthesis? (1 Mark)
a) Starch
b) Glucose
c) Chlorophyll
d) Xylem
Answer: c) Chlorophyll
Sol: Chlorophyll is the green pigment in leaves that captures sunlight for photosynthesis
Q3. What tissue transports water and minerals in plants? (1 Mark)
a) Phloem
b) Stomata
c) Xylem
d) Chlorophyll
Answer: c) Xylem
Sol:Xylem is the tissue that carries water and minerals from roots to other parts of the plant,
Q4. What gas is released by plants during photosynthesis? (1 Mark)
a) Carbon dioxide
b) Oxygen
c) Nitrogen
d) Water vapor
Answer: b) Oxygen
Sol: Plants release oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis
Q5. What do plants produce during respiration? (1 Mark)
a) Glucose and oxygen
b) Carbon dioxide and water
c) Starch and chlorophyll
d) Water and minerals
Answer: b) Carbon dioxide and water
Sol: During respiration, plants break down glucose to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy
Q6. What does the phloem do in plants? (2 Mark)
Sol:
Phloem is a tissue that carries food (glucose or starch) made in the leaves to non-green parts like roots, stems, and fruits for growth and storage.
Q7. What happens during plant respiration? (2 Mark)
Sol: During respiration, plants break down glucose using oxygen to release energy, carbon dioxide, and water. This energy helps plants grow and do other functions.
Q8. Why do leaves need chlorophyll for photosynthesis? (2 Mark)
Sol: Chlorophyll is a green pigment in leaves that captures sunlight. It uses this sunlight energy to combine carbon dioxide and water to make food (glucose), which is why it’s essential for photosynthesis.
Q9. How does the iodine test show that leaves produce starch during photosynthesis? (3 Mark)
Sol:
The iodine test shows starch in leaves by turning them blue-black.
You take a leaf exposed to sunlight, decolourise it to remove green colour, and add iodine solution.
If the leaf turns blue-black, it means starch (made during photosynthesis) is present.
A leaf kept in darkness won’t turn blue-black because it didn’t make starch without sunlight. This proves photosynthesis needs sunlight to produce food.
Q10. What happens to a plant without water, and why is water important for growth? (3 Mark)
Sol: Without water, a plant may wilt or die because water is essential for transporting nutrients and keeping the plant’s structure firm. Water is also needed for photosynthesis to make food (glucose). For example, the notes say a plant without water has fewer leaves and poor growth, while one with water grows tall with vibrant green leaves.
Q11. Why are leaves called the “food factories” of plants? Give an example. (3 Mark)
Sol: Leaves are called “food factories” because they make food (glucose) through photosynthesis using sunlight, chlorophyll, carbon dioxide, and water. Their broad, flat shape and chlorophyll help capture sunlight to produce starch. For example, the notes say an iodine test on a leaf exposed to sunlight turns blue-black, showing starch production, proving leaves make food for the plant.
Q12. Where does the starch in potatoes come from? Where is the food synthesised in the plant, and how does it reach the potato? (5 Mark)
Sol: The starch in potatoes comes from the food made in the leaves of the plant. The plant makes food in the form of glucose through a process called photosynthesis, which happens in the leaves when the plant takes in sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water.
Transport of Water (Xylem):
Xylem is a tissue with tube-like structures that carries water and minerals from roots to stems, leaves, and flowers.
Roots absorb water and minerals from soil, and xylem moves them upward to support photosynthesis and keep plants firm.
Example: In the colored water experiment, a twig in red water shows color moving up the stem to leaves, proving xylem transports water.
Transport of Food (Phloem):
Phloem is a tissue that carries food (glucose or starch) made in leaves to non-green parts like roots, stems, and fruits for growth and storage.
Example: Glucose made in leaves reaches developing fruits, helping them grow, like apples getting sweeter.
Respiration vs. Photosynthesis:
Respiration: Plants break down glucose using oxygen in all parts (green or non-green) to release energy, carbon dioxide, and water. This energy helps growth and nutrient transport.
Photosynthesis: Leaves use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to make glucose and oxygen, only in green parts with chlorophyll.
Difference: Photosynthesis makes food in sunlight, while respiration uses that food for energy anytime, producing opposite gases (oxygen out in photosynthesis, carbon dioxide out in respiration).
|
80 videos|319 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test Solutions: Life Processes in Plants - Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the main life processes in plants? |  |
| 2. How do plants perform photosynthesis? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of transpiration in plants? |  |
| 4. What types of reproduction do plants undergo? |  |
| 5. What role does respiration play in a plant's life processes? |  |
















