Unit Test Solutions: The World of Metals and Non-metals | Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT PDF Download
Time: 1 Hour
Maximum Marks: 30
Instructions:
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
Question numbers 12 and 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1. What is the property of a material that allows it to be beaten into thin sheets called? (1 Mark)
a) Ductility
b) Malleability
c) Sonority
d) Conduction
Answer: b) Malleability
Sol: Malleability is the property that allows metals to be hammered into thin sheets without breaking, like aluminium foil.
Q2. Name a metal that is liquid at room temperature. (1 Mark)
a) Iron
b) Copper
c) Mercury
d) Aluminium
Answer: c) Mercury
Sol: Mercury is unique because it is the only metal that remains liquid at room temperature, used in devices like thermometers.
Q3. Which non-metal is used in water purification to make drinking water safe? (1 Mark)
a) Carbon
b) Nitrogen
c) Chlorine
d) Sulfur
Answer: c) Chlorine
Sol: Chlorine is a non-metal used to purify drinking water by killing harmful bacteria, ensuring it is safe to drink.
Q4. What is the term for the ringing sound produced by metals when struck? (1 Mark)
a) Brittleness
b) Malleability
c) Ductility
d) Sonority
Answer: d) Sonority
Sol: Sonority is the property of metals that produces a ringing sound when struck, like in school bells.
Q5. What is the brown deposit formed on iron when it reacts with air and water called? (1 Mark)
a) Oxide
b) Rust
c) Alloy
d) Corrosion
Answer: b) Rust
Sol:Rust is the brown deposit formed on iron due to a chemical reaction with oxygen and moisture, weakening the iron.
Q6. Name two metals that are soft and can be cut with a knife. (2 Mark)
Sol: Unlike most metals, which are hard and strong, sodium and potassium are exceptions because they are soft enough to be cut easily, similar to cutting butter
Q7. Name two methods to prevent rusting of iron. (2 Mark)
Sol: Two methods to prevent rusting are
- Painting the iron surface
- Applying oil or grease to form a protective layer.
Q8. Why are vessel handles often made of wood or plastic? (2 Mark)
Sol: Wood and plastic do not conduct heat well, so they remain cool even when attached to a hot metal vessel. This makes them safe for holding, protecting the user’s hand from burns, unlike metals, which conduct heat quickly.
Q9: Explain why sodium is stored in kerosene and not in water, and describe the nature of its oxide. (3 Mark)
Sol: Sodium is kept in kerosene because it reacts vigorously with water and air. If exposed, it can catch fire easily. Kerosene stops sodium from touching water and air, keeping it safe.
When sodium reacts with oxygen, it forms sodium oxide, which is basic in nature. This can turn red litmus paper blue.
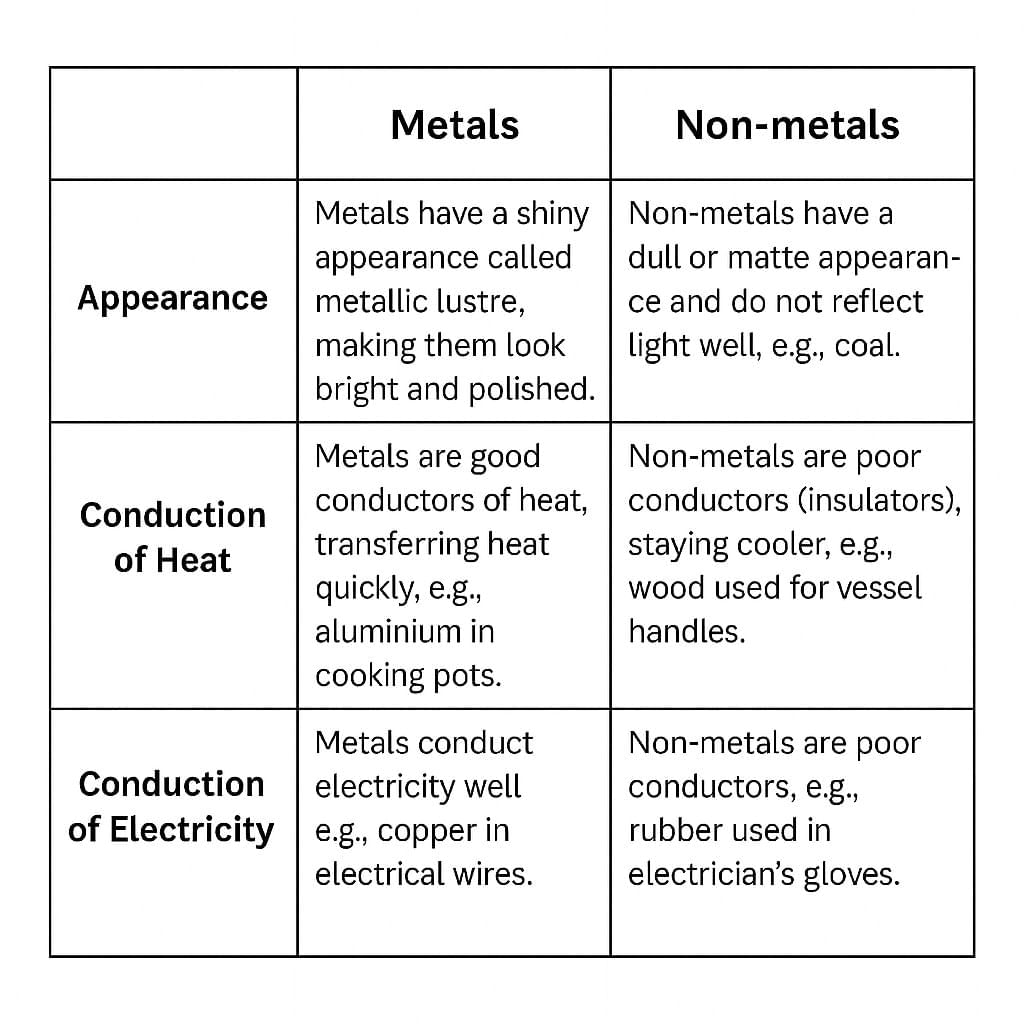
Q10: Compare the properties of metals and non-metals in terms of their appearance and ability to conduct heat and electricity. (3 Mark)
Sol:
Q11: Explain the difference between conductors and insulators using examples of materials and their applications. (3 Mark)
Sol: 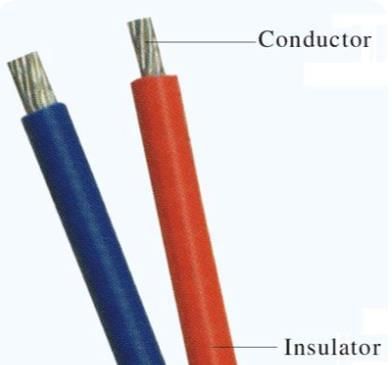
Conductors:
- Materials that allow electricity to pass through them easily.
- Metals like copper conduct electricity well and are used in electrical wires to power homes and appliances.
- Aluminium conducts heat well and is used in cooking pots to heat food evenly.
Insulators:
- Materials that do not allow electricity to pass through; they stop or slow down the flow, keeping us safe.
- Non-metals like rubber are poor conductors of electricity, used in electrician’s gloves to prevent shocks.
- Wood is a poor conductor of heat, used in vessel handles to avoid burns.
Q12: Describe the process of rusting in iron, including the conditions required and its impact on iron objects. Suggest two methods to prevent rusting and explain how they work. (5 Mark)
Sol:
Rusting Process:
Rusting is a chemical reaction where iron reacts with oxygen (from air) and moisture (water) to form reddish-brown substance called rust. This reaction occurs on the iron’s surface, causing it to weaken over time.
Conditions Required:
Rusting requires both oxygen and moisture.
Iron does not rust in dry air alone or in water without air exposure, as both components are necessary for the chemical reaction to proceed.
Impact:
Rusting weakens iron objects, making them brittle and unsafe.
It damages structures like bridges, vehicles, and tools, leading to costly repairs or replacements.
Prevention Methods:
Painting: Painting iron surfaces creates a barrier that prevents oxygen and moisture from reaching the iron, stopping the rusting reaction. For example, painted railings remain rust-free.
Galvanisation: Coating iron with a layer of zinc protects it because zinc is more resistant to rust and forms a protective layer.
Q13. Explain why metals are used in cooking vessels and electrical wires, while non-metals are used for handles and insulation. Provide one example for each use and describe the properties involved. (5 Mark)
Sol:
Metals in Cooking Vessels:
- Metals like aluminium are used in cooking vessels because they are good conductors of heat, transferring heat quickly and evenly to cook food.
Metals in Electrical Wires:
- Metals like copper are used in electrical wires because they are ductile (can be drawn into wires) and good conductors of electricity.
Properties of Metals Involved:
- Metals are malleable and ductile
- Metals have high electrical and thermal conductivity.
Non-Metals for Handles:
- Non-metals like wood are used for vessel handles because they are poor conductors of heat .
- Since wood is a poor conductor of heat, the handle stays cool and you won’t burn your hand when you lift the pot.
Non-Metals for Insulation:
- Rubber is used to cover electric wires because it does not let electricity pass through it which makes it a good insulator.
Properties of Non-Metals Involved:
- Non-metals are insulators, which stops heat and electricity flow
|
80 videos|224 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test Solutions: The World of Metals and Non-metals - Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the main differences between metals and non-metals? |  |
| 2. Can you explain the properties of metals and how they are useful in daily life? |  |
| 3. What are some common examples of non-metals and their uses? |  |
| 4. How do metals and non-metals react chemically? |  |
| 5. What role do metals and non-metals play in the periodic table? |  |