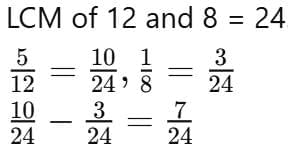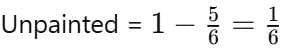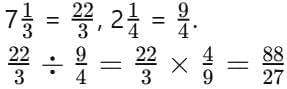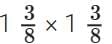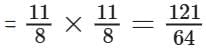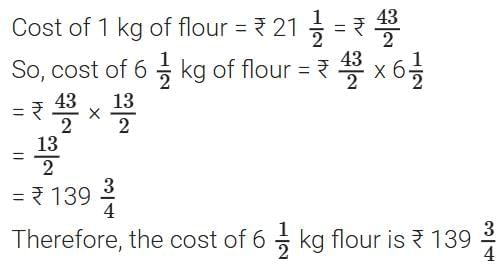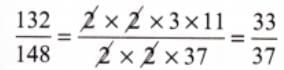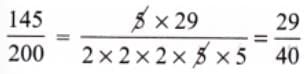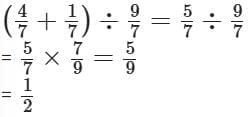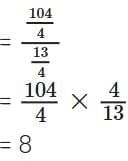Unit Test Solutions: Working with Fractions | Mathematics (Ganita Prakash) Class 7 - New NCERT PDF Download
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
Question number 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1. Sarah has 12 meters of fabric to make curtains, using 3/4 meter for each curtain. How many curtains can she make? (1 mark)
(a) 12
(b) 16
(c) 20
(d) 24
Sol:
Total fabric Sarah has = 12 meters
Fabric used for 1 curtain = 3/4 meterNumber of curtains = Total fabric ÷ Fabric per curtain
= 12 ÷ (3/4)
= 12 × (4/3)
= 12 × 4 / 3
= 48 / 3
= 16Sarah can make 16 curtains.
Answer: (b) 16
Q2. John has 5/6 kg of sugar, and he uses 1/12 kg for each cake. How many cakes can he make? (1 mark)
(a) 5
(b) 8
(c) 10
(d) 12
Sol:
Total sugar John has = 5/6 kg
Sugar used per cake = 1/12 kgNumber of cakes = Total sugar ÷ Sugar per cake
= (5/6) ÷ (1/12)
= (5/6) × (12/1)
= 5 × 12 / 6
= 60 / 6
= 10John can make 10 cakes.
Answer: (c) 10
Q3. A rope of 3/5 meter is cut into 9 equal pieces. What is the length of each piece? (1 mark)
(a) 1/15 meter
(b) 1/10 meter
(c) 1/20 meter
(d) 1/45 meter
Sol:
Total length of rope = 3/5 meter
Number of pieces = 9Length of each piece = Total length ÷ Number of pieces
= (3/5) ÷ 9
= (3/5) × (1/9)
= 3/45
= 1/15 meterThe length of each piece is 1/15 meter.
Answer: (a) 1/15 meter
Q4. When a number is multiplied by a fraction between 1/2 and 1, the product is ___ than the original number. (1 mark)
(a) greater
(b) less
(c) equal
(d) cannot determine
Sol:
When a number is multiplied by a fraction between 1/2 and 1 (e.g., 3/4), the product is smaller than the original number but larger than if it were multiplied by a fraction less than 1/2.Example: 8 × 3/4 = 6 (which is less than 8).
The product is always less than the original number.Answer: (b) less
Q5. A recipe requires 3/8 liter of juice to make 12 servings. How much juice is needed for 1 serving? (1 mark)
(a) 1/16 liter
(b) 1/24 liter
(c) 1/32 liter
(d) 1/48 liter
Sol:
Total juice = 3/8 liter
Number of servings = 12Juice per serving = Total juice ÷ Number of servings
= (3/8) ÷ 12
= (3/8) × (1/12)
= 3/96
= 1/32 literThe amount of juice needed for 1 serving is 1/32 liter.
Answer: (c) 1/32 liter
Q6: Simplify: 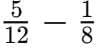 (2 mark)
(2 mark)
Sol:
Q7. If a painting is 5/6 painted, how much is unpainted? (2 mark)
Ans:
Q8. Convert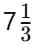 into an improper fraction and divide it by
into an improper fraction and divide it by 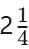 . (2 mark)
. (2 mark)
Ans:
Q9. Each side of a square iron sheet is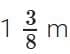 . Find its area (3 mark)
. Find its area (3 mark)
Sol: Area of a square sheet = side x side =
Q10. The cost of 1 kg of flour is 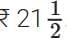 . Find the cost of
. Find the cost of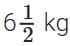 of flour. (3 mark)
of flour. (3 mark)
Sol:
Q11. Reduce the following fractions into their simplest form (3 mark)
(a) 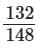
Sol:
(b) 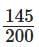
Sol:
Q12. Divide the sum of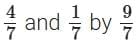 (5 mark)
(5 mark)
Sol:
Q13. A machine can print 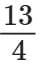 pages in one minute. How many minutes will it take to print
pages in one minute. How many minutes will it take to print 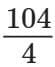 pages? (5 mark)
pages? (5 mark)
Sol: Number of minutes required to print
pages
|
41 videos|251 docs|8 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test Solutions: Working with Fractions - Mathematics (Ganita Prakash) Class 7 - New NCERT
| 1. What are fractions and how are they represented? |  |
| 2. How can you add and subtract fractions with different denominators? |  |
| 3. What is the process for multiplying fractions? |  |
| 4. How do you divide fractions? |  |
| 5. What are mixed numbers and how can they be converted to improper fractions? |  |