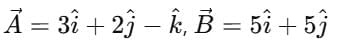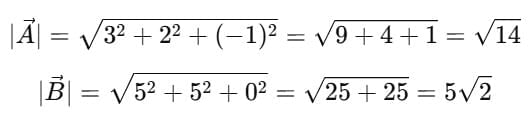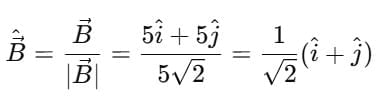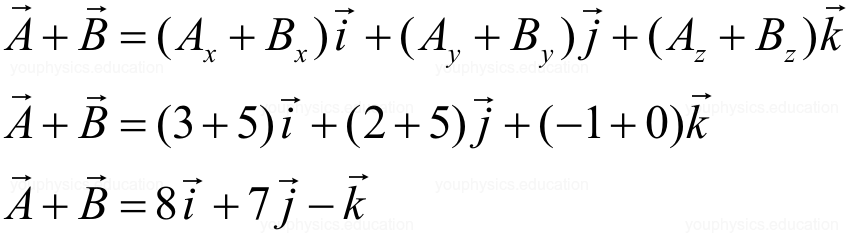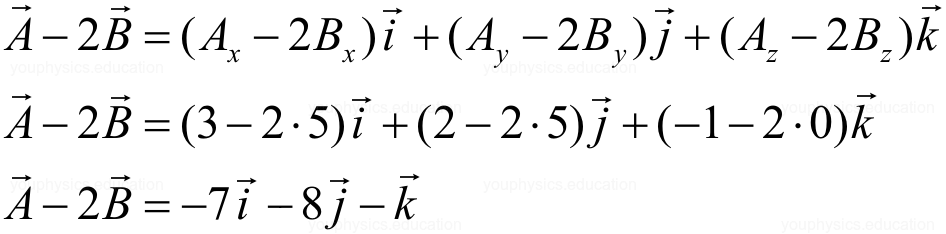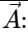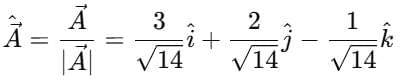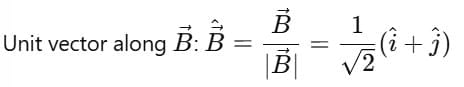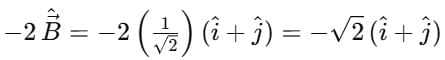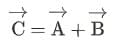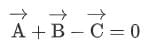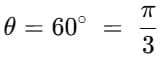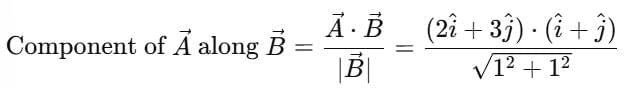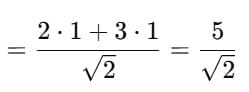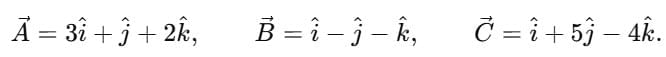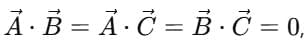Vectors: Definition, Types & Unit Vectors | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Scalar and Vector Quantities |

|
| Representation of a Vector |

|
| Types of Vectors |

|
| Unit Vector: Representation & Notation |

|
| Solved Examples |

|
Scalar and Vector Quantities
Scalar Quantities
- Definition: Scalars have only magnitude (a numerical value with unit) and no direction.
- Examples: Mass (5 kg), Temperature (300 K), Time (10 s), Work (20 J), Electric charge (2 C).
You can add or subtract scalars by simple arithmetic.
E.g., Time taken = 5 s + 10 s = 15
Vector Quantities
- Definition: Vectors have both magnitude and direction.
- Examples: Displacement (10 m east), Velocity (20 m/s north), Force (5 N upward), Acceleration.
- Representation: Usually shown by an arrow, where:
Arrow length → magnitude
Arrow head → direction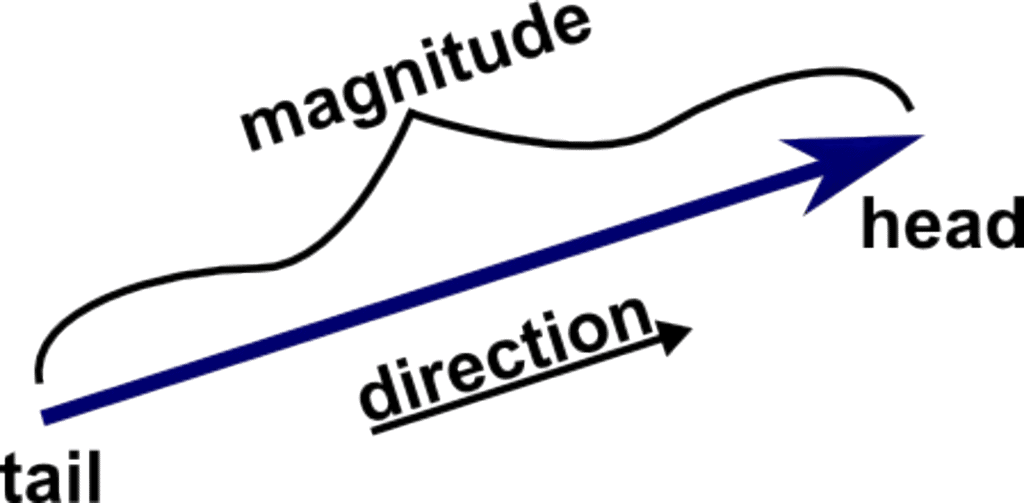
Representation of a Vector
- Vectors are like arrows. Arrows have two important things: how long they are (that's their size), and the direction they point.
- Think of a vector like an arrow, where one end is where it starts (that's the tail), and the other end is where it's pointing to (that's the head).
- So, a vector has a length and shows you a specific direction, just like an arrow.
 Examples of Vectors
Examples of Vectors Parts of a Vector
Parts of a Vector
Types of Vectors
There are 10 types of vectors in mathematics which are: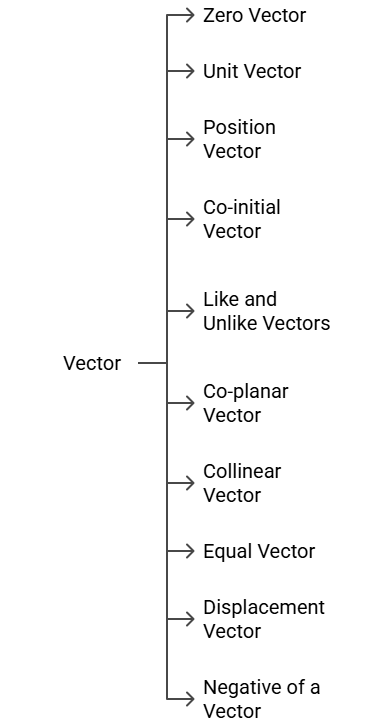
All these vectors are extremely important and the concepts are frequently required in mathematics and other higher-level science topics. The detailed explanations on each of these 10 vector types are given below.
1. Zero Vector
A zero vector is a vector when the magnitude of the vector is zero and the starting point of the vector coincides with the terminal point.
"In other words, for a vector 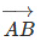 , the coordinates of the point A are the same as those of the point B, then the vector is said to be a zero vector and is denoted by 0.
, the coordinates of the point A are the same as those of the point B, then the vector is said to be a zero vector and is denoted by 0.
This follows that the magnitude of the zero vector is zero, and the direction of such a vector is indeterminate.
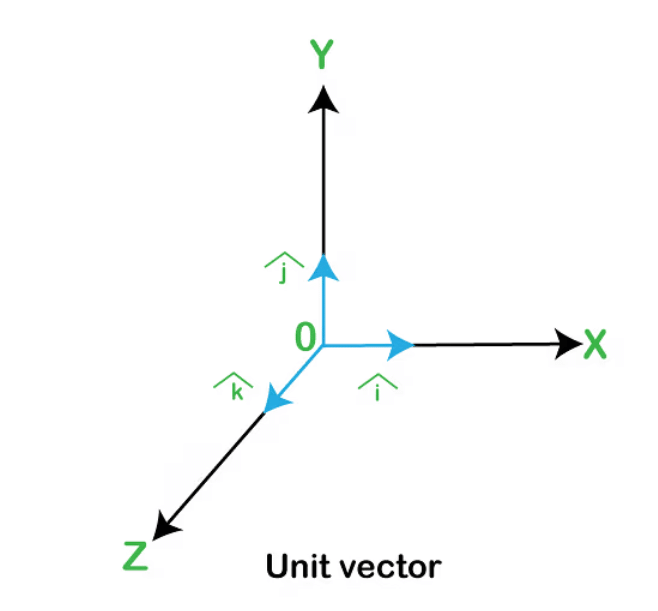
2. Unit Vector
A vector which has a magnitude of unit length is called a unit vector.
Suppose if 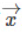 is a vector having a magnitude x, then the unit vector is denoted by x̂ in the direction of the vector
is a vector having a magnitude x, then the unit vector is denoted by x̂ in the direction of the vector 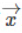 and has the magnitude equal to 1. Therefore,
and has the magnitude equal to 1. Therefore, 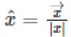
It must be carefully noted that any two unit vectors must not be considered equal because they might have the same magnitude, but the direction in which the vectors are taken might be different.
3. Position Vector
If O is taken as reference origin and P is an arbitrary point in space then the vector
is called as the position vector of the point.
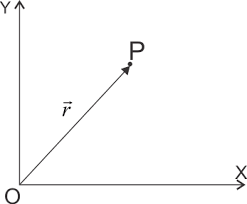
Position vector simply denotes the position or location of a point in the three-dimensional Cartesian system with respect to a reference origin.
4. Co-initial Vectors
The vectors which have the same starting point are called co-initial vectors.
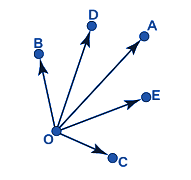 Co- initial Vectors
Co- initial Vectors
5. Like and Unlike Vectors
The vectors having the same direction are known as like vectors. On the contrary, the vectors having the opposite direction with respect to each other are termed to be unlike vectors.
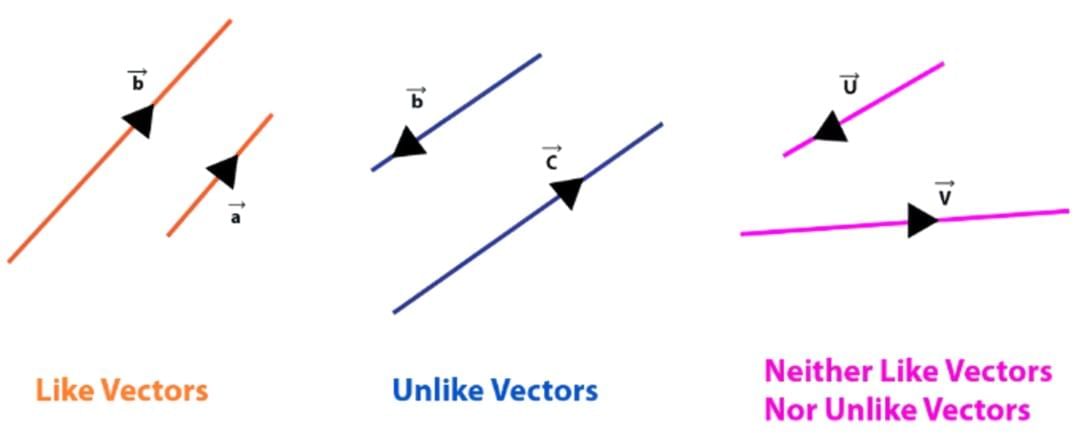
6. Co-planar Vectors
Three or more vectors lying in the same plane or parallel to the same plane are known as co-planar vectors.
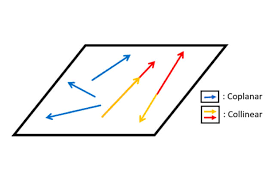
7. Collinear Vectors
Vectors that lie along the same line or parallel lines are known to be collinear vectors. They are also known as parallel vectors.
Two vectors are collinear if they are parallel to the same line, irrespective of their magnitudes and direction. For any two vectors to be parallel to one another, the condition is that one of the vectors should be a scalar multiple of the other vector.
The figure below shows the collinear vectors in the opposite direction.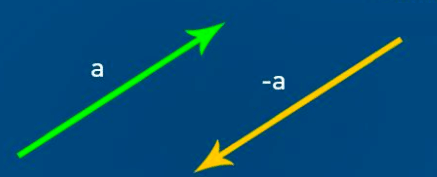
8. Equal Vectors
Two or more vectors are said to be equal when their magnitude is equal and also their direction is the same.
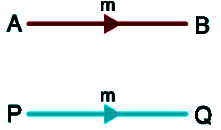
9. Displacement Vector
If a point is displaced from position A to B then the displacement AB represents a vector
which is known as the displacement vector.
10. Negative of a Vector
If two vectors are the same in magnitude but exactly opposite in direction then both the vectors are negative of each other.
For instance, if vector a has the same magnitude as vector b but points in the opposite direction, it can be represented as a = -b.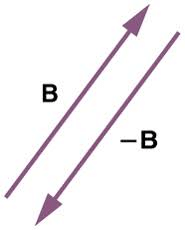
Magnitude of a Vector
The magnitude of a vector is a crucial measure that provides the numeric value for a given vector. It is denoted as 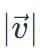 and can be calculated using the formula:
and can be calculated using the formula:
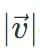 = √(a² + b² + c²)
= √(a² + b² + c²)
This formula summarizes the individual measures of the vector along the x, y, and z axes.
Unit Vector: Representation & Notation
As we have studied the definition of unit vectors above, Let's study in detail more.
Unit Vectors î, ĵ, k̂
In a three-dimensional coordinate system, the unit vectors î, ĵ, and k̂ are particularly significant. They represent unit vectors along the x, y, and z axes, respectively, each having a magnitude of 1. These unit vectors form the basis for expressing any vector in three-dimensional space.Unit Vector Notation and Formula
Unit vectors are denoted by the symbol (^) and can be calculated using the formula:
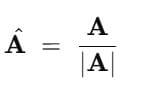
Here, A represents the given vector, and |A| is the magnitude of vector A. The resulting unit vector 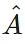 has the same direction as A but a magnitude of 1.
has the same direction as A but a magnitude of 1.
How to Find a Unit Vector
A unit vector is a vector that has the same direction as the given vector but its magnitude is 1.
To get it, simply divide the vector by its own magnitude.
Example
Suppose the given vector is: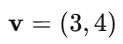
Step 1: Find the magnitude of v.
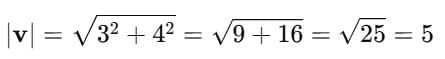
Step 2: Divide the vector by its magnitude.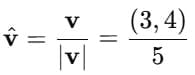
Step 3: Simplify each component.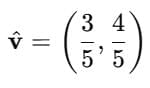
Representation of Unit Vectors
Suppose a vector is given as: A = (x , y , z)
Step 1: Find the magnitude of the vector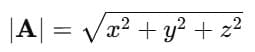
Step 2: Divide each component by the magnitude
(a) Bracket Format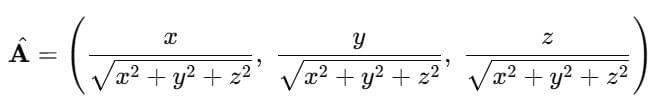
(b) Component (Unit Vector) Format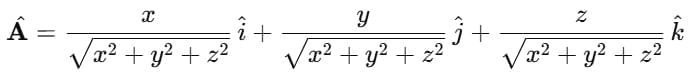
Solved Examples
Example 1: Given the vectors: A = 3i + 2j – k and B = 5i +5j.
Determine:
1. Their magnitude.
2. The direction of B.
3. 
4. 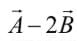
5. A unit vector parallel to A.
6. A vector of magnitude 2 and opposite to B
Ans. Given:1) Magnitudes
2) Direction of
Unit vector along
3.
4.
5. Unit vector parallel to
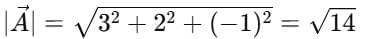
6.
Vector of magnitude opposite to
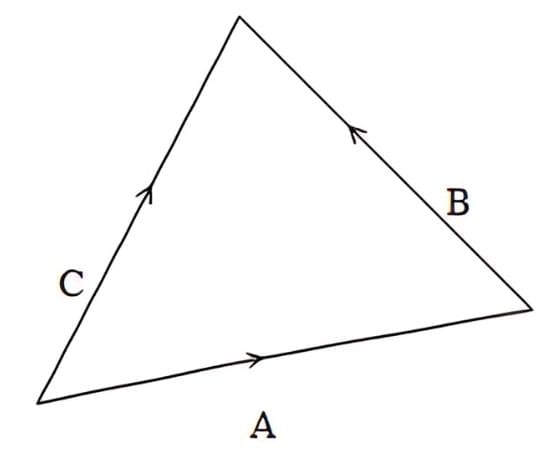
Example 2: How many minimum number of coplanar vectors having different magnitudes can be added to give zero resultant?
Sol: Since the magnitudes are different, two vectors cannot give zero resultant. By the Triangle Law of Vector Addition, at least three coplanar vectors are required to form a closed triangle and hence give a zero resultant.
From the figure we can say that,
Therefore, we can say that,
So we can say that a minimum of 3 coplanar vectors is required to represent the same physical quantity having different magnitudes that can be added to give zero resultant.
Example 3: The square of the resultant of two equal forces is three times their product. What is the angle between the forces?
Sol: Let A and B be the two forces and θ be the angle between them.
Given: A = B = F, and R2 = 3AB = 3F2Formula (parallelogram law):
Substitute A = B = F:
Equate with given:
∴ Angle:
Example 4: 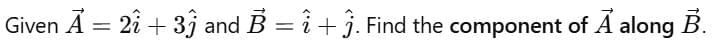
Sol:
Example 5: Prove that the three vectors 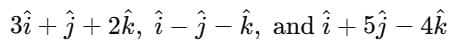
Sol. Let
Vectors are mutually perpendicular if every pair has zero dot product.Since
Therefore, all three vectors are at right angles to one another.
|
268 videos|780 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on Vectors: Definition, Types & Unit Vectors - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What are scalar and vector quantities? |  |
| 2. How is a vector represented graphically? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of vectors? |  |
| 4. What is a unit vector and how is it denoted? |  |
| 5. Can you provide an example of how to add vectors? |  |