Important Viscosity & Poiseuille’s Formula Formulas for JEE and NEET
| Table of contents |

|
| Viscosity |

|
| Variation of Viscosity |

|
| Poiseuille’s Formula |

|
| The Rate of Flow of Liquid |

|
| Stoke's Law |

|
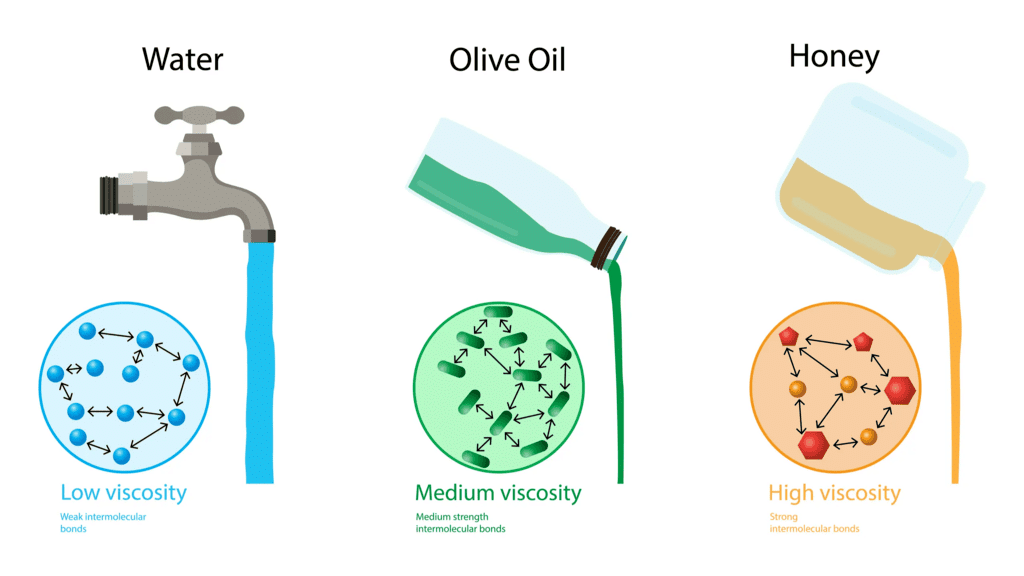
Viscosity
- The property of a fluid by virtue of which an internal frictional force acts between its different layers which opposes their relative motion is called viscosity.
- These internal frictional force is called viscous force.
 Viscosity
Viscosity
- Viscous forces are inter-molecular forces acting between the molecules of different layers of liquid moving with different velocities.
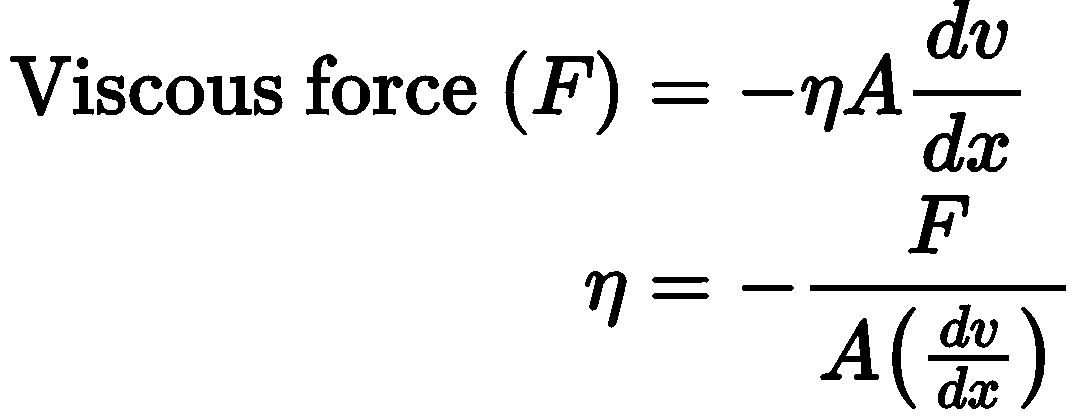
- where, (dv/dx) = rate of change of velocity with distance called velocity gradient, A = area of cross-section and = coefficient of viscosity.
- SI unit of η is Nsm-2 or pascal-second or decapoise. Its dimensional formula is [ML-1T-1].
- The knowledge of the coefficient of viscosity of different oils and its variation with temperature helps us to select a suitable lubricant for a given machine.
- Viscosity is due to transport of momentum. The value of viscosity (and compressibility) for ideal liquid is zero.
- The viscosity of air and of some liquids are utilised for damping the given parts of some instruments.
- The knowledge of viscosity of some organic liquids is used in determining the molecular weight and shape of large organic moleculars like proteins and cellulose.
Variation of Viscosity
The viscosity of liquids decreases with increase in temperature
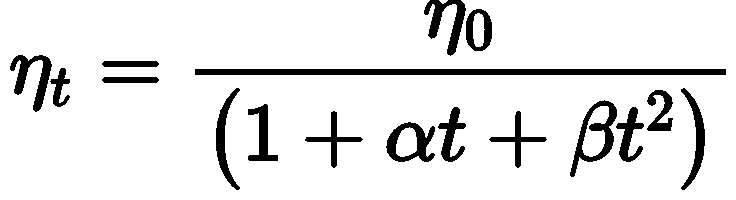
where, η0 and ηt is are coefficient of viscosities at 0°C and t°C, α and β are constants.
The viscosity of gases increases with increase in temperatures as
η ∝ √T
The viscosity of liquids increases with increase in pressure but the viscosity of water decreases with increase in pressure.
The viscosity of gases do not changes with pressure.
Poiseuille’s Formula
The rate of flow (v) of liquid through a horizontal pipe for steady flow is given by
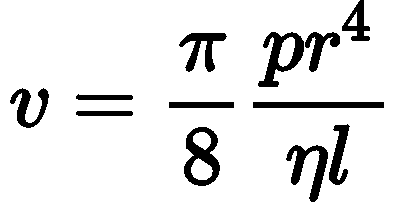
where, p = pressure difference across the two ends of the tube. r = radius of the tube, n = coefficient of viscosity and 1 = length of the tube.
The Rate of Flow of Liquid
Rate of flow of liquid through a tube is given by
v = (P/R)
where, R = (8 ηl/πr4), called liquid resistance and p = liquid pressure.
Stoke's Law
When a sphere moves through a thick liquid, like honey, the resistance it faces depends on how fast it's moving, how big the sphere is, and how thick the liquid is. This resistance is called Stokes' drag.
Imagine stirring honey with a spoon—the harder and faster you stir (velocity), the bigger the spoon (radius), and the thicker the honey (viscosity), the more resistance you feel.
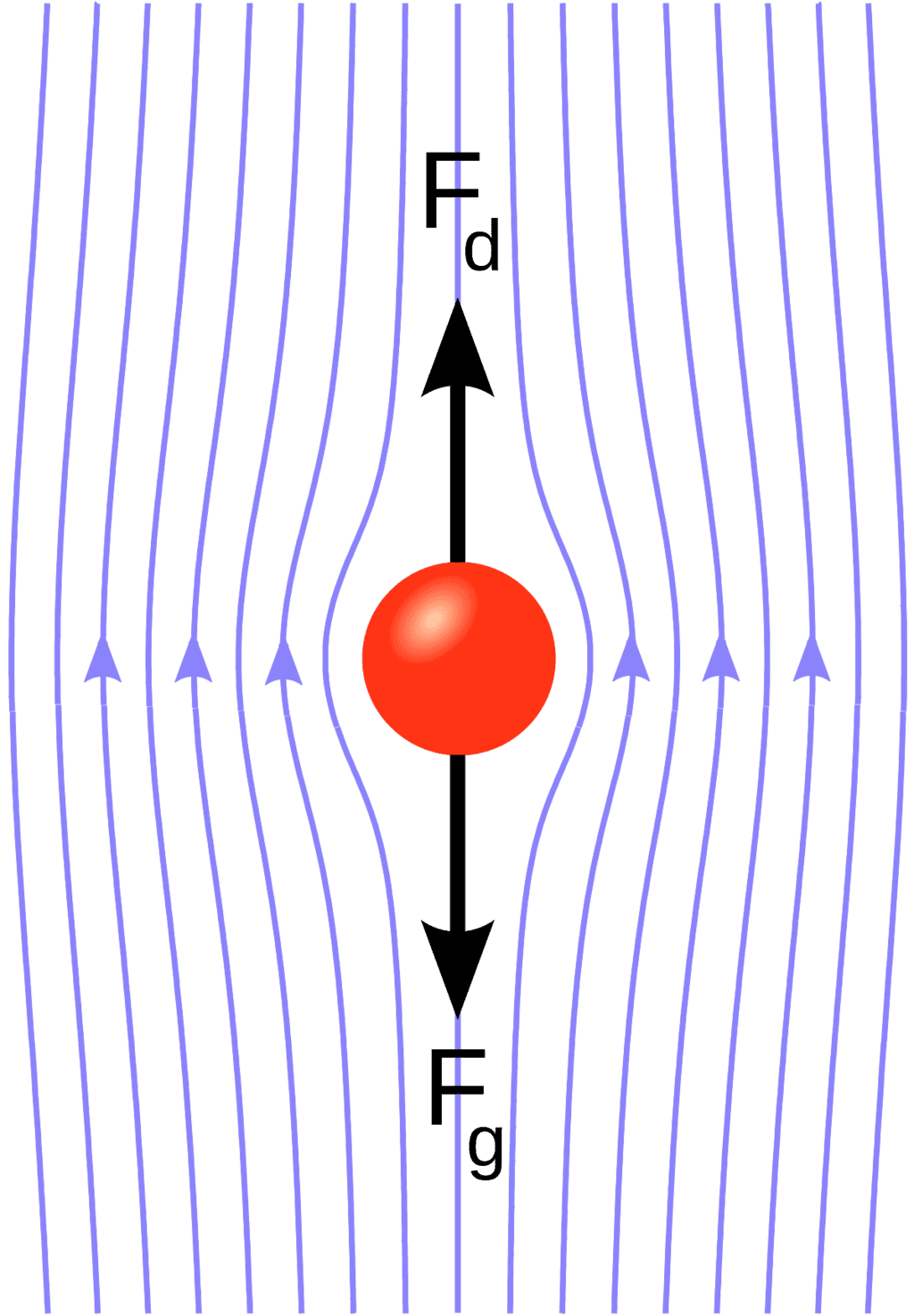 Illustration of Stoke's Law
Illustration of Stoke's Law
This resistance force is calculated using a formula that takes into account the viscosity of the liquid, the size of the sphere, and how fast it's moving.
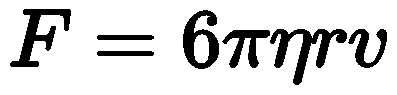
- where F is the frictional force — known as Stokes' drag — acting on the interface between the fluid and the particle
- η is the viscosity
- R is the radius of the spherical object
- V is the flow velocity
|
320 videos|946 docs|172 tests
|
FAQs on Important Viscosity & Poiseuille’s Formula Formulas for JEE and NEET
| 1. What is viscosity and how is it related to the rate of flow of liquid? |  |
| 2. How does viscosity vary with temperature? |  |
| 3. What is Poiseuille's formula and how is it used to calculate the rate of flow of liquid in a pipe? |  |
| 4. How does Stokes's Law relate to viscosity? |  |
| 5. How can viscosity be measured experimentally? |  |





















